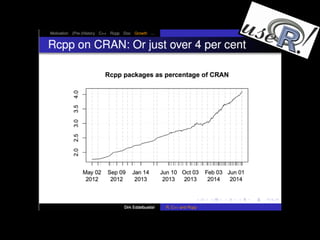
The document discusses the integration of R and C++ using Rcpp and Rcpp11, highlighting their functionalities and differences. It provides various coding examples to illustrate the use of Rcpp and Rcpp11 for data manipulation and function creation while emphasizing the ease of use and performance benefits. Additionally, it mentions the availability of Rcpp11 on CRAN and GitHub, along with system requirements for implementing it in R packages.


















![#include <Rcpp.h>
!
// [[Rcpp::export]]
int add( int a, int b){
return a + b ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-22-320.jpg)
![sourceCpp
#include <Rcpp.h>
!
// [[Rcpp::export]]
int add( int a, int b){
return a + b ;
}
> sourceCpp( "add.cpp" )
> add( 2L, 3L)
[1] 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-23-320.jpg)


![Example: NumericVector
// [[Rcpp::export]]
double sum( NumericVector x){
int n = x.size() ;
!
double res = 0.0 ;
for( int i=0; i<n; i++){
res += x[i] ;
}
!
return res ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-26-320.jpg)
![Example : lists
List res = List::create(
_["a"] = 1,
_["b"] = "foo"
);
res.attr( "class" ) = "myclass" ; !
int a = res["a"] ;
res["b"] = 42 ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-27-320.jpg)
![Example: R function
Function rnorm( "rnorm" ) ;
!
NumericVector x = rnorm(
10,
_["mean"] = 30,
_["sd"] = 100
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-28-320.jpg)


![#include <Rcpp.h>
!
// [[Rcpp::export]]
int foo(){
return 2 ;
}
Rcpp
Rcpp11
0 1 2 3
Less code -> faster compiles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-32-320.jpg)







![create
// old school NumericVector::create (Rcpp style).
NumericVector x = NumericVector::create(1.0, 2.0, 3.0) ;
NumericVector x = NumericVector::create(
_["a"] = 1.0, _["b"] = 2.0, _["c"] = 3.0
) ;
!
!
// create as a free function. Rcpp11 style
NumericVector x = create(1.0, 2.0, 3.0) ;
NumericVector x = create(
_["a"] = 1.0, _["b"] = 2.0, _["c"] = 3.0
) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-40-320.jpg)

![sapply + lambda
#include <Rcpp11>
!
// [[export]]
NumericVector foo( NumericVector x ){
return sapply(x, [](double d){
return exp(d * 2) ;
});
}
x <- 1:3
sapply( x, function(d){
exp(d*2) ;
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-42-320.jpg)
![sapply + lambda + …
#include <Rcpp11>
!
// [[export]]
NumericVector foo( NumericVector x ){
auto fun = [](double d, double y, double z){
return exp(d * y) + z ;
} ;
return sapply(x, fun, 3.0, 4.6);
}
x <- 1:3
sapply( x, function(d, y, z){
exp(d*y) + z ;
}, 3.0, 4.6 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-43-320.jpg)

![attributes companion package
• Standalone impl of Rcpp attributes
[[Rcpp::export]], sourceCpp, compileAttributes
!
• Only available from github:
> install_github( "Rcpp11/attributes" )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-45-320.jpg)
![Use Rcpp11 in your package
• Write your .cpp files
#include <Rcpp11>
!
// [[export]]
void foo( … ) { … } // your code
SystemRequirements: C++11
LinkingTo: Rcpp11
library(attributes)
compileAttributes( "mypkg" )
• Express dep on C++11 and Rcpp11 headers
• Generate the boiler plate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcpp11genentech-140718104134-phpapp02/85/Rcpp11-genentech-46-320.jpg)

