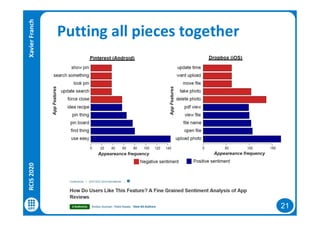
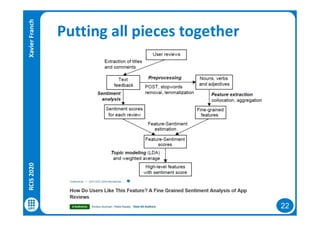
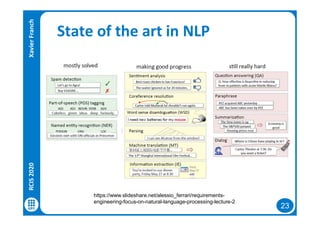
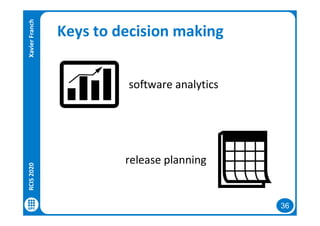
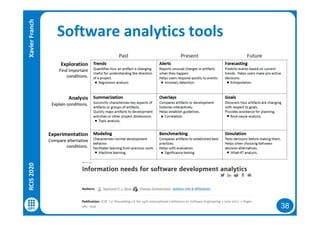
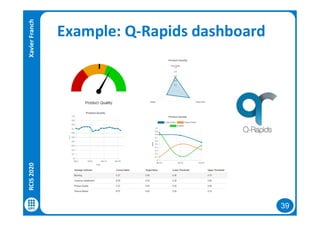
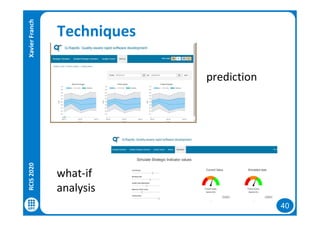
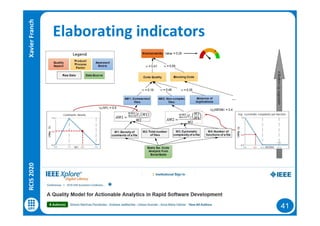
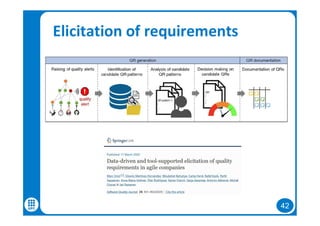
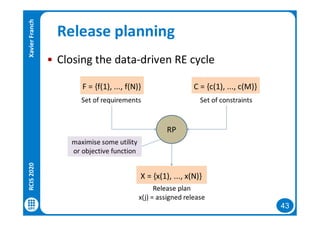
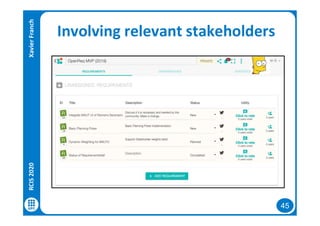
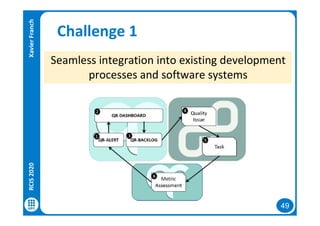
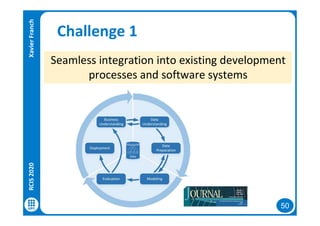
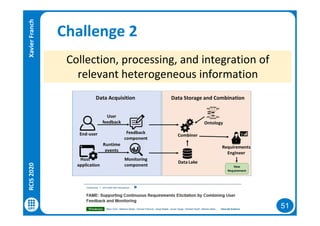
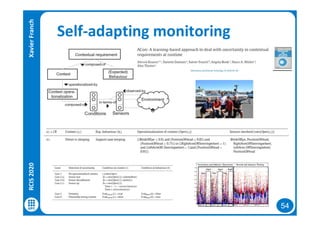
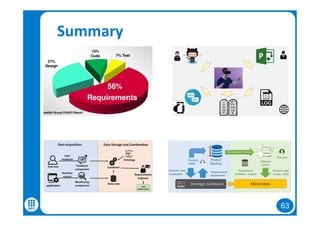
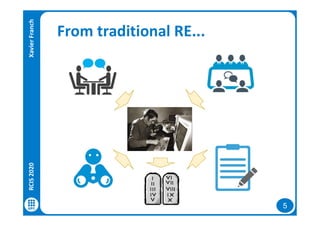
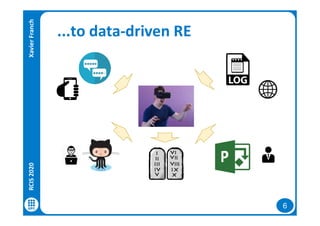
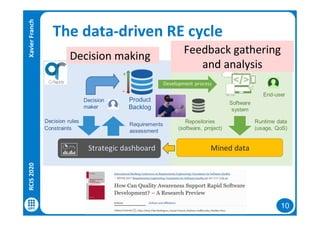
The document discusses data-driven requirements engineering (RE), which uses data collected from system usage to inform the RE process. It describes traditional RE and how data-driven RE aims to supplement it using explicit feedback from users and implicit feedback from usage data. The data is analyzed using natural language processing, machine learning, and topic modeling to categorize issues and identify topics. Challenges of data-driven RE include integrating it into development processes, collecting and processing heterogeneous data, and gaining user trust. Overall, it presents an opportunity to deliver more business value but requires the right approach and consideration of traditional RE methods.










![19
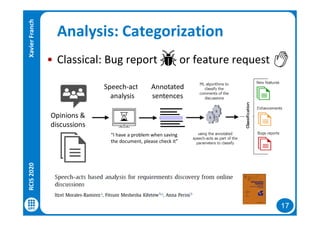
Analysis: Sentiment analysis
Deciding if a piece of text expresses a particular affect or mood
But of course, not easy...:
“Great, I like this feature that gives me this lovely headache”
had fun using it before but now it is really horrible :( help!!
+2 -2-1 -1 -1[+2,-5]
uploading pictures with the app is so annoying!
pleeeeeeease add an unlike button and I will love you forever!!
[+1,-3]
[+5,-1]
Approaches: use of dictionaries and ML/DL techniques
RCIS2020XavierFranch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcis2020tutorialddre-200922115341/85/RCIS-2020-tutorial-DDRE-19-320.jpg)