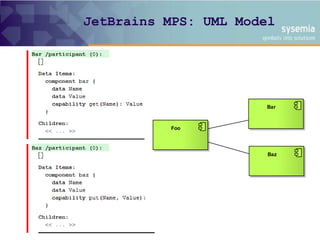
The document discusses a model-driven architecture evaluation focusing on the structure of software systems and the relationships among components. It emphasizes the importance of using scenarios to validate design usability and consistency through architecture evaluation, akin to software testing. The evaluation process aims to ensure that the scenarios cover all relationships and interactions within the model.