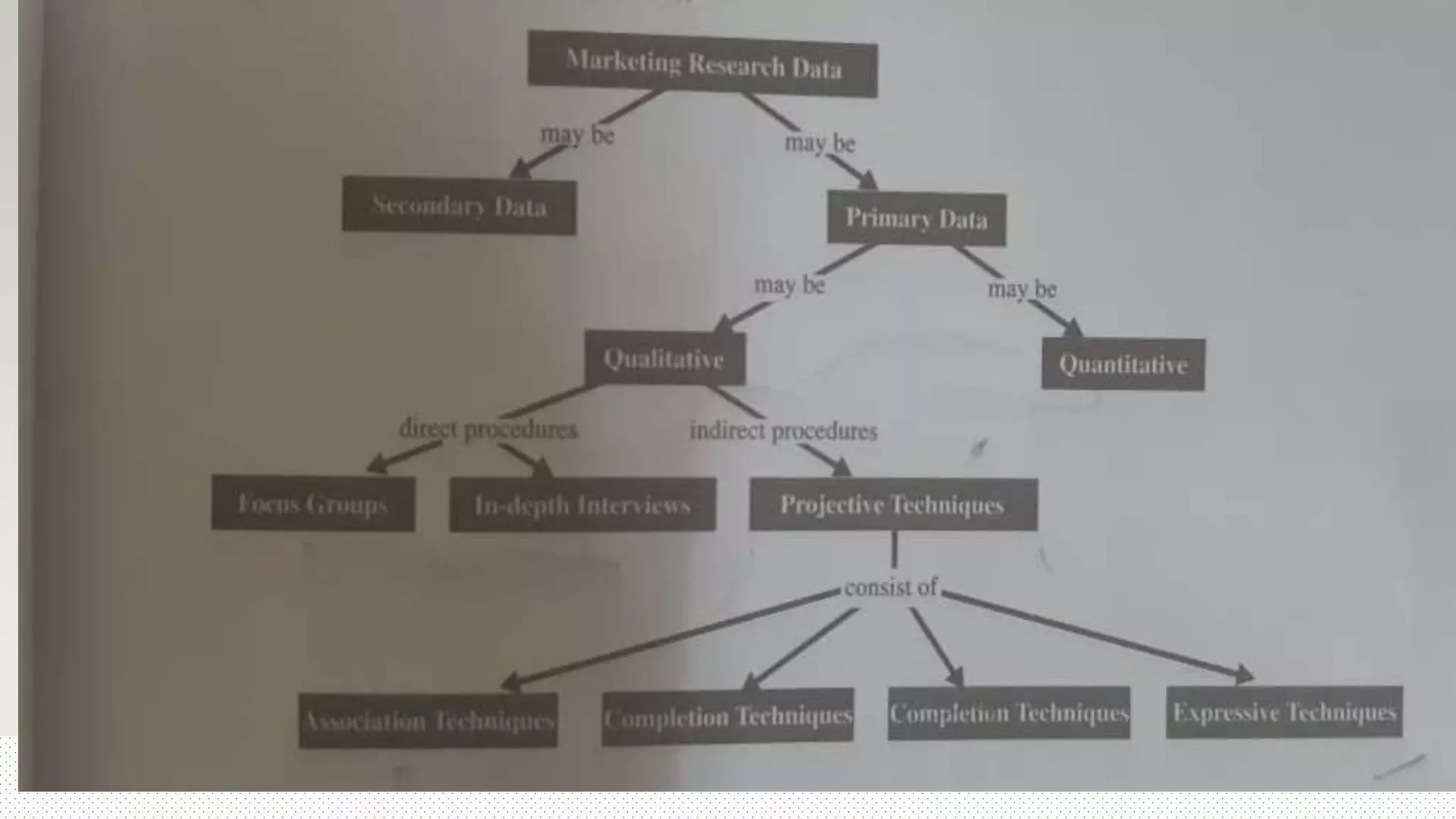
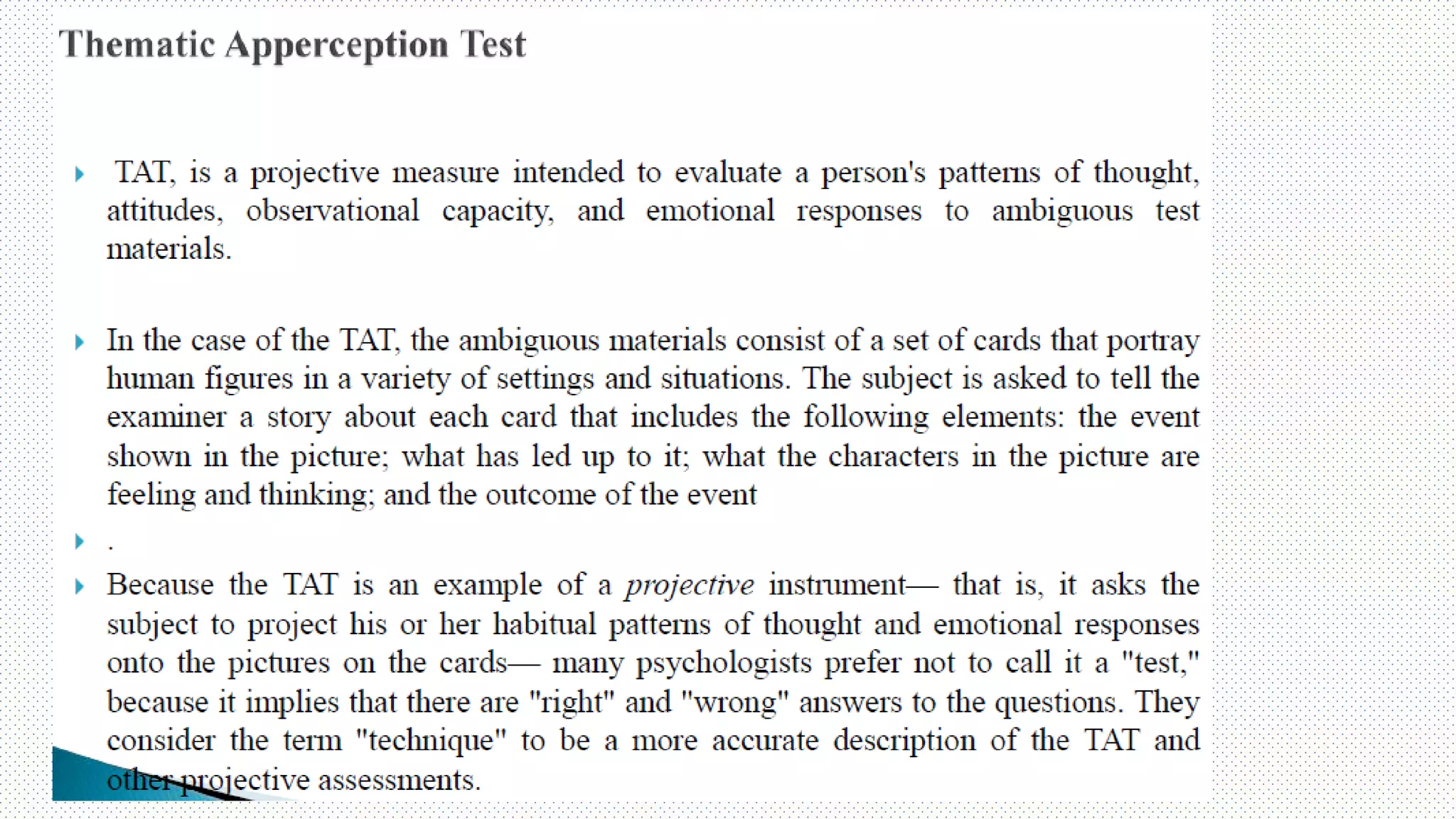
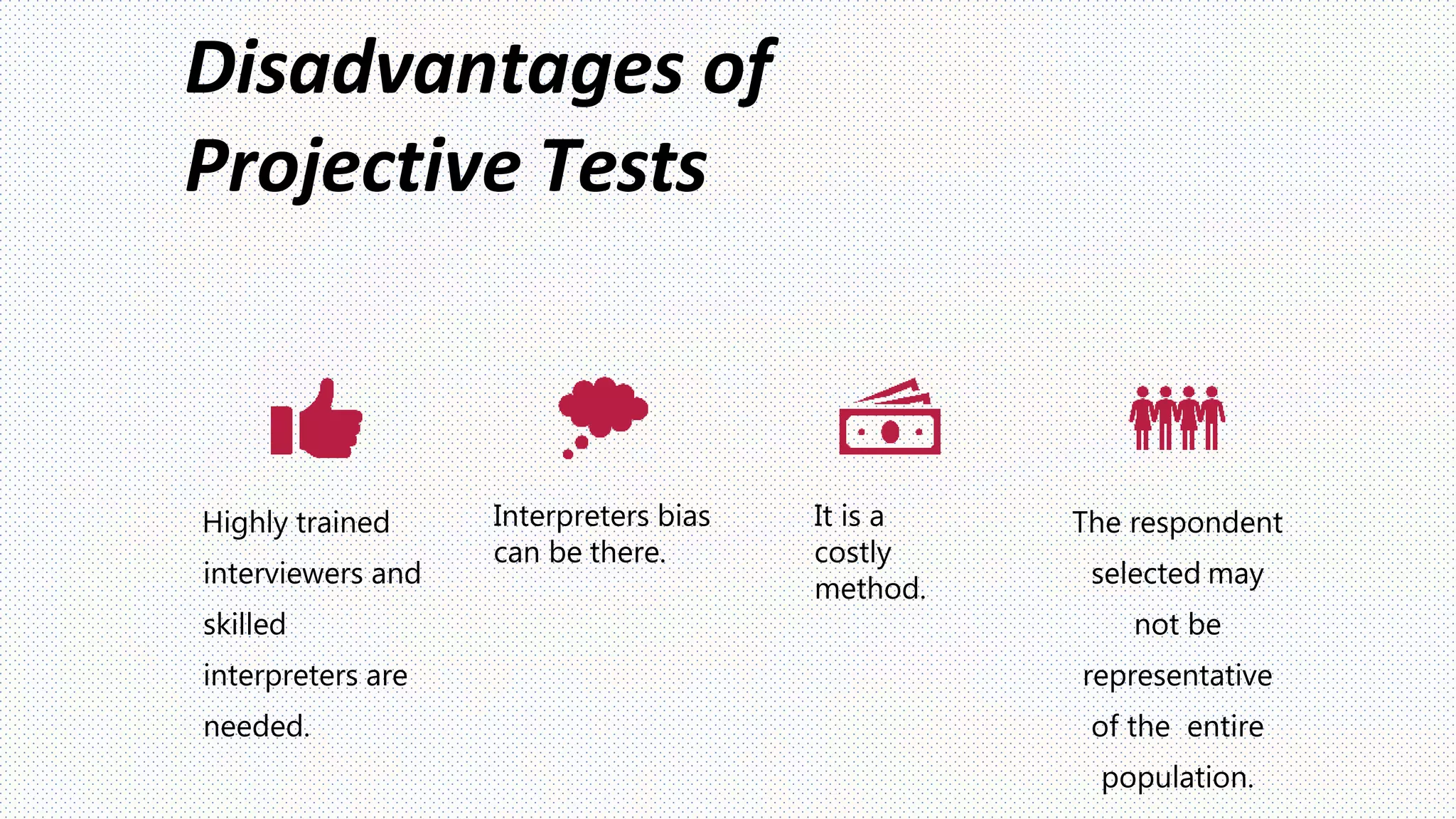
This document discusses projective techniques, which are indirect methods used in qualitative research to understand respondents' underlying motivations, attitudes, and feelings. It describes several types of projective techniques including word associations, sentence or story completions, role playing expressive exercises, and using ambiguous images like Rorschach inkblots. A specific technique called the Zaltman Metaphor Elicitation Technique (ZMET) is also explained, which uses photos to understand unconscious metaphors and how they influence behaviors. The document outlines the steps of a ZMET study and notes that projective techniques can provide insights not obtainable through direct questioning but require skilled interpreters.