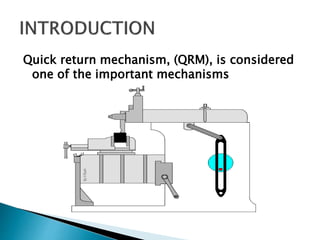
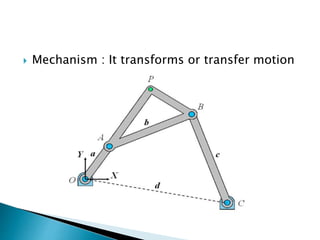
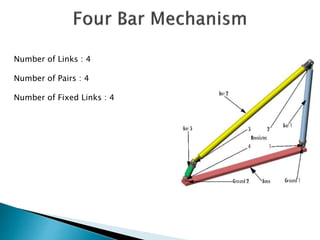
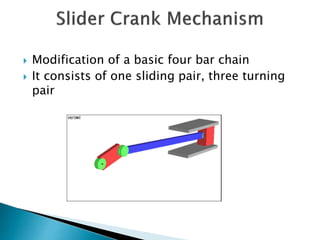
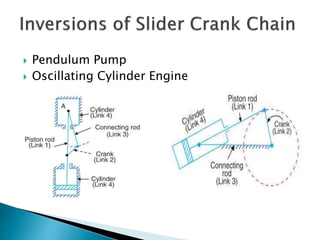
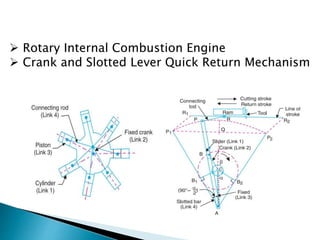
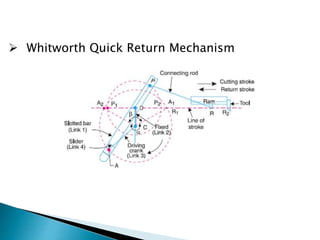
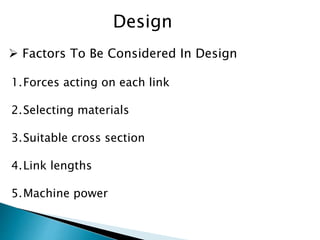
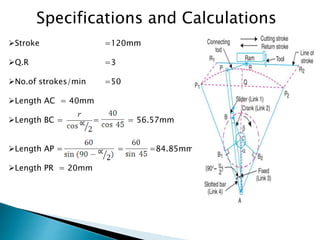
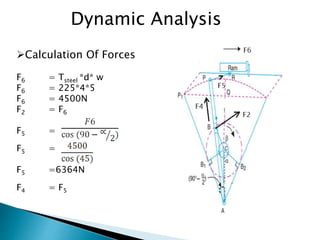
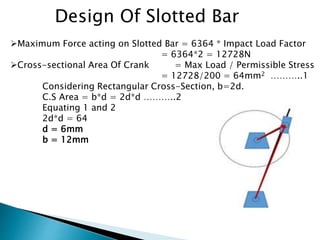
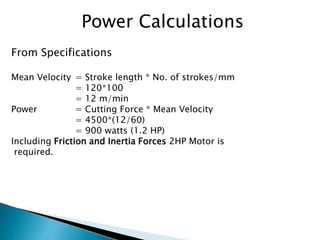
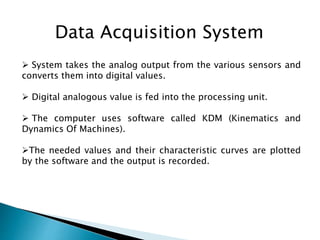
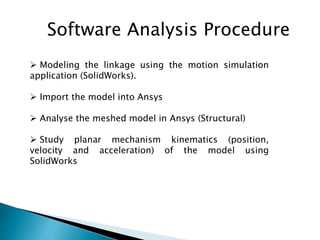
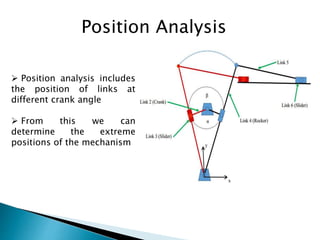
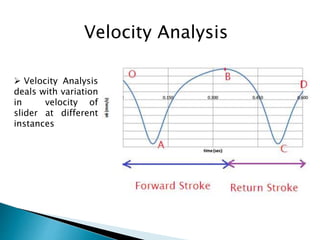
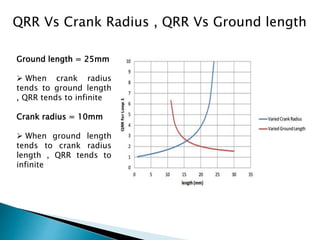
This document outlines a student project to design and build a quick return mechanism. It will involve researching quick return devices, developing a mathematical model, and implementing the design. The project plan includes background research, proposing a design, performing analysis in software, fabrication, and testing. The timeline stretches from July to March. The methodology incorporates designing links, analyzing positions, modifying if needed, implementing, fabricating, and testing performance. References are provided to guide the design process.