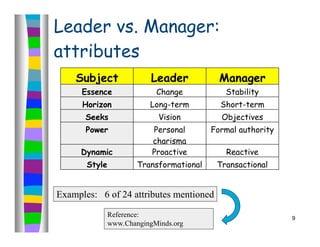
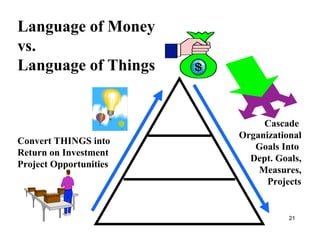
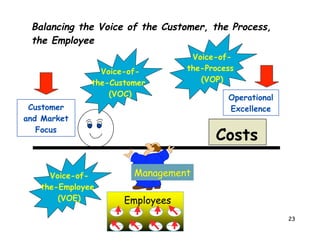
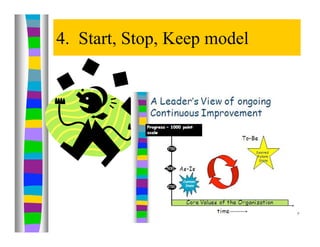
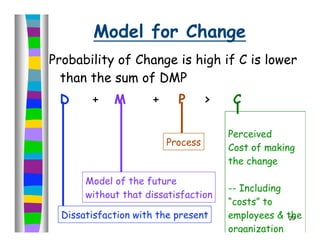
The document discusses leadership and provides information on several leadership topics in 4 sections. Section 1 compares leadership to management, noting leaders seek vision and long-term goals while managers focus on stability and short-term objectives. Section 2 discusses values-driven leadership and the importance of organizational culture. Section 3 explains the importance of asking the "right questions" as a systems thinker. Section 4 presents the "Start, Stop, Keep" model for assessment and planning improvement actions.