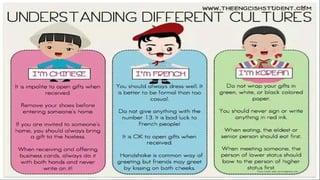
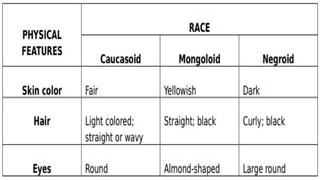
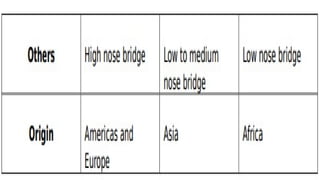
The document discusses the evolution of gender roles, social classes, and cultural identity in the Philippines from pre-colonial times to the present. It outlines the social stratification during different periods, including pre-colonial, Spanish colonial, and modern times, emphasizing the impact of colonialism and socioeconomic status. Additionally, it addresses issues of ethnicity and religion, highlighting challenges related to race, nationality, and exceptionality in society.