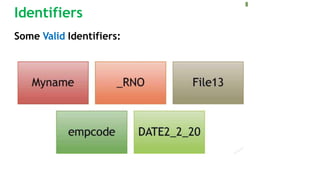
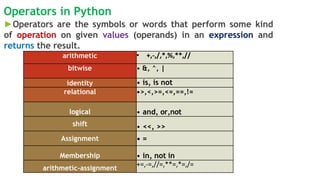
Tokens are the basic elements of a Python program and include keywords, identifiers, literals, operators, and punctuators. Keywords are reserved words with special meaning, identifiers name variables and other elements, and literals provide constant values like strings and numbers. Operators perform operations on operands, while punctuators organize program structure. Together, these tokens form valid Python code.













![Punctuators in Python
►Punctuators are the symbols that are used in
programming language to organize sentence structure,
indicate the rhythm and emphasis of expressions,
statements and Program Structure.
► Common Punctuators are:
( ) { } [ ] @ ,
#
‘ ‘’ “”
, : . ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonyawarrasul-230513030748-8342dd30/85/python_Yawar_Rasul-pptx-16-320.jpg)
