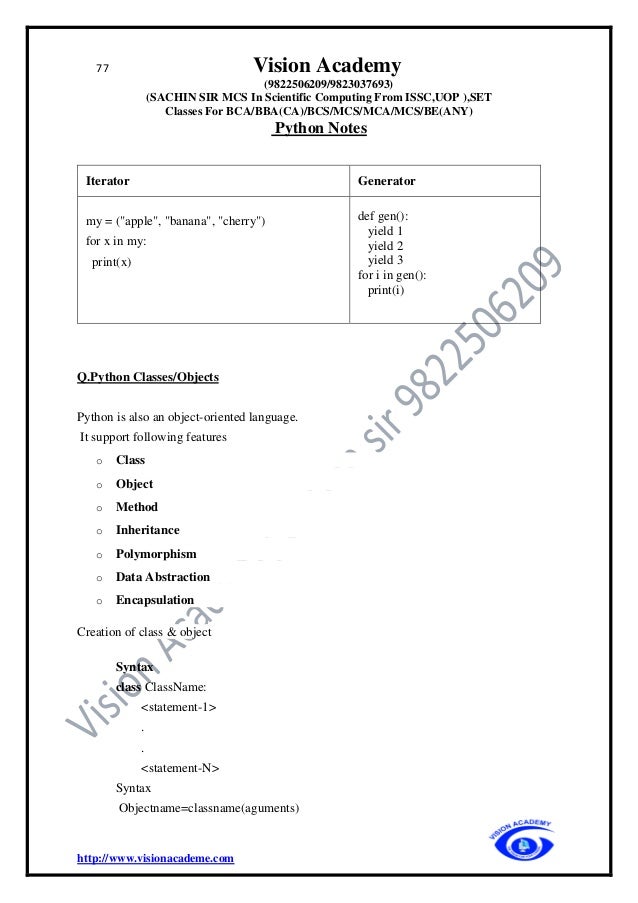
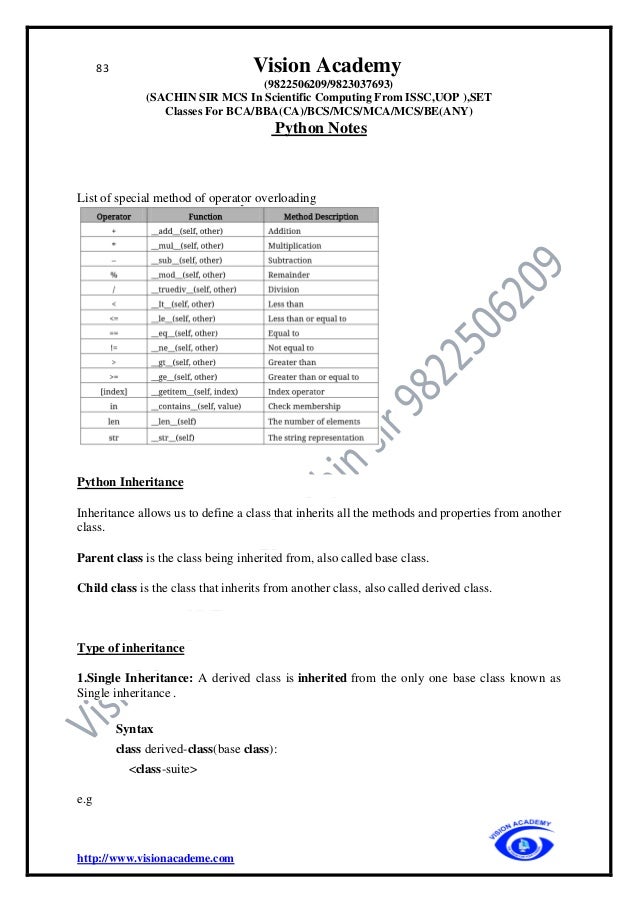
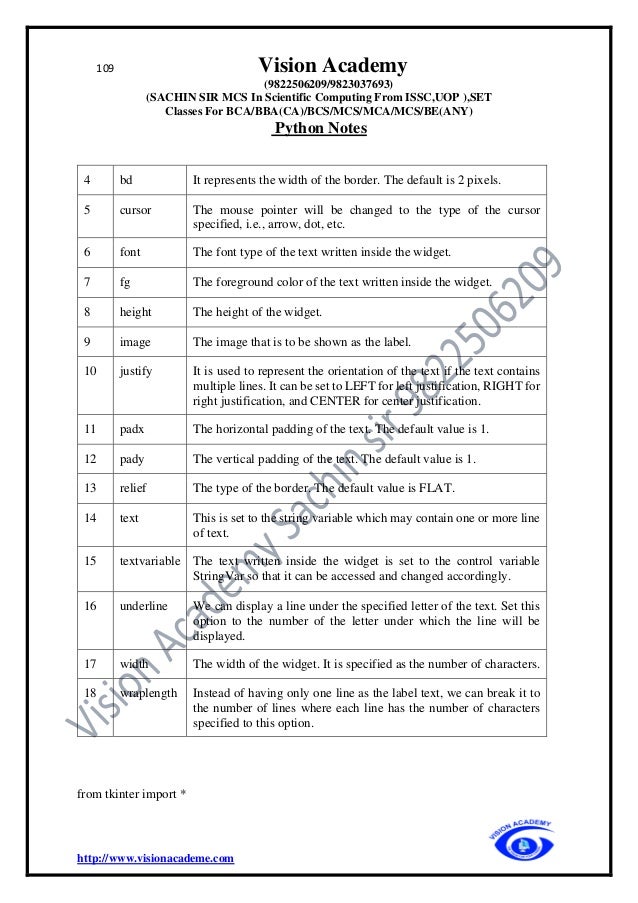
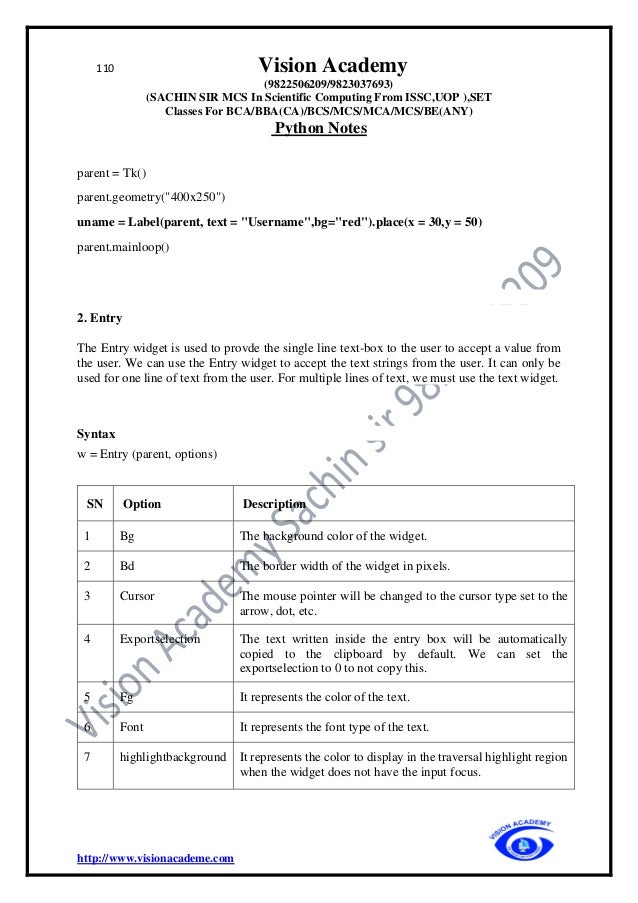
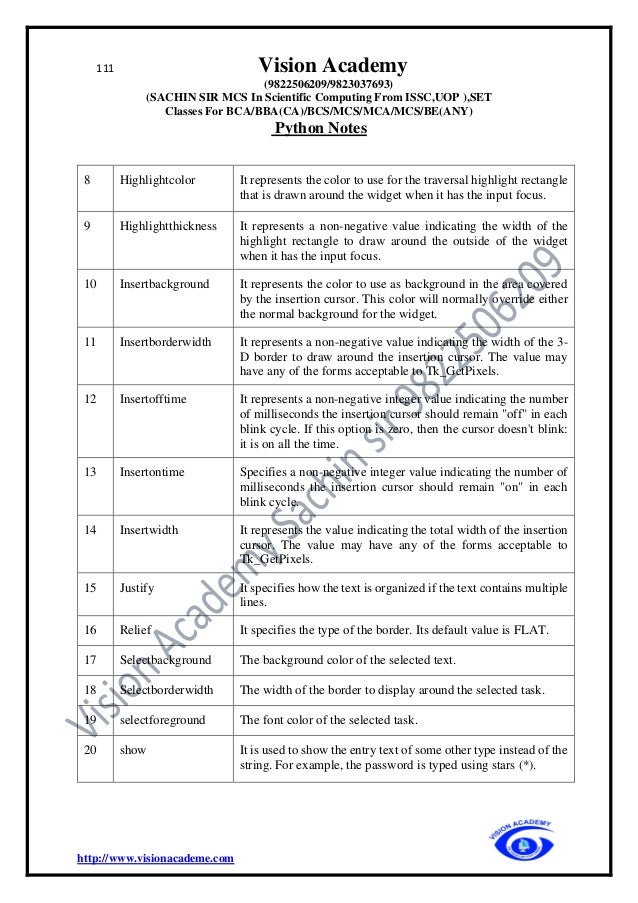
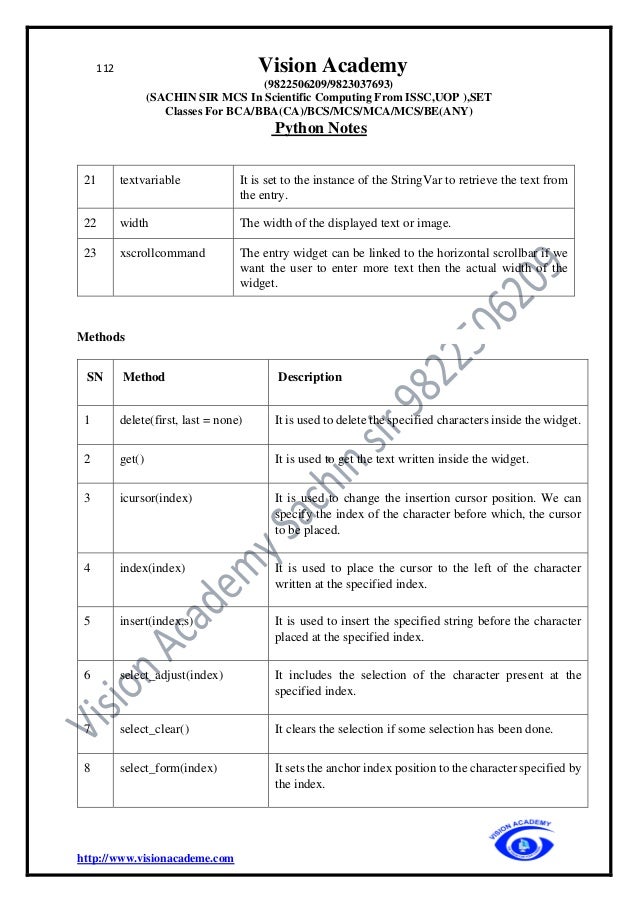
The document provides an extensive overview of Python programming, including its history, features, applications, and comparisons with other programming languages like C and C++. It details Python's advantages such as ease of learning, cross-platform compatibility, and dynamic memory allocation, while also addressing disadvantages such as slow speed and memory inefficiency. Additionally, it covers basic concepts such as identifiers, keywords, comments, variables, and data types in Python.








![12 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
For e.g 1:valid
if condtion:
statement
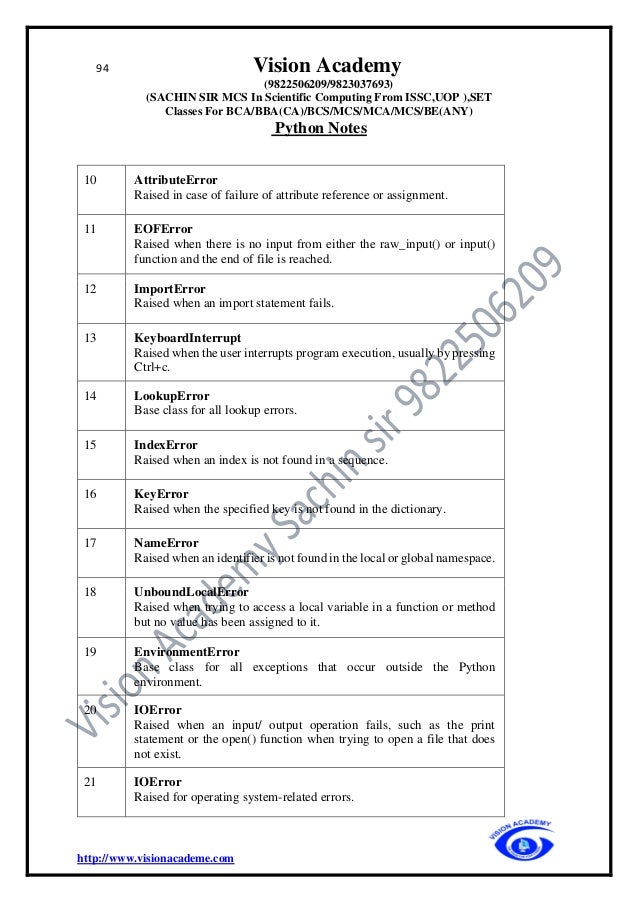
statement
For e.g 2 : invalid
if condtion:
statement
statement
else:
statement
statement
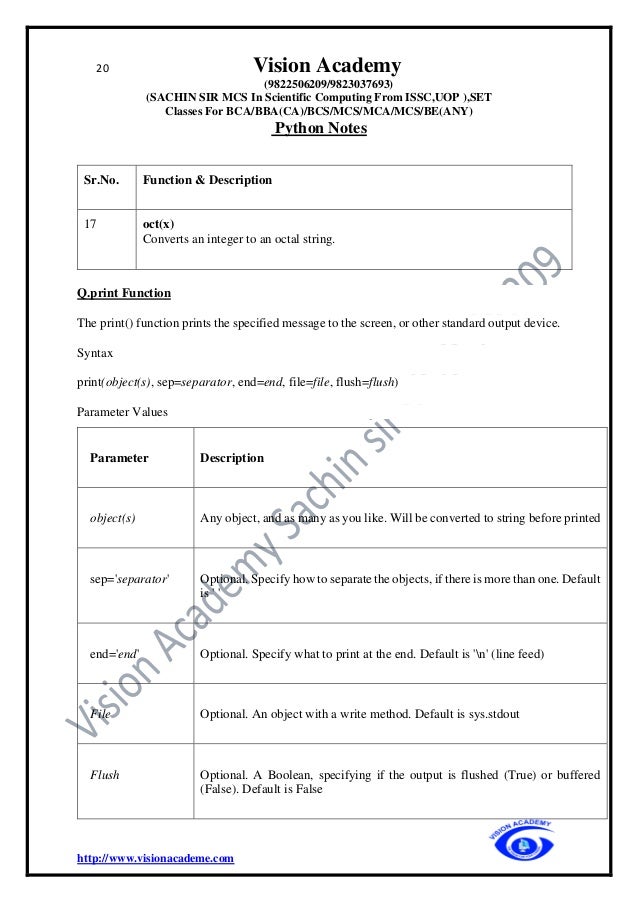
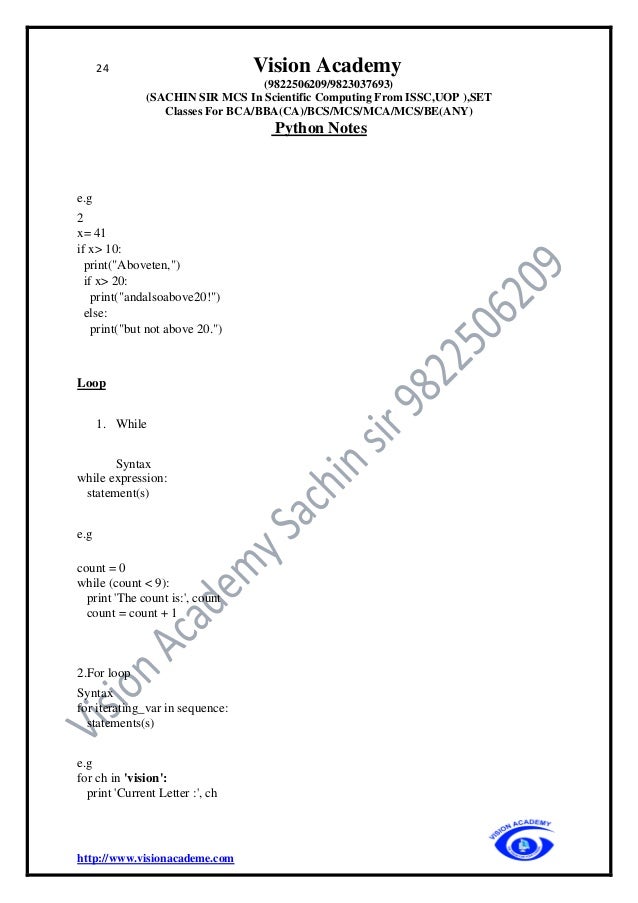
Multi-Line Statements
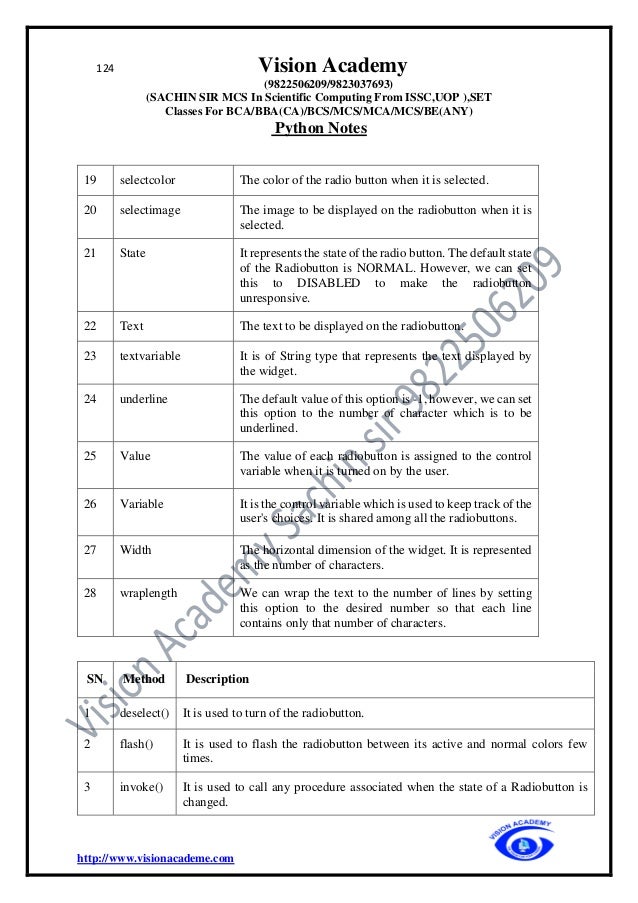
Explicit Line Continuation
• Statements in Python typically end with a new line. Python does, however, allow the
use of the line continuation character () to denote that the line should continue. For
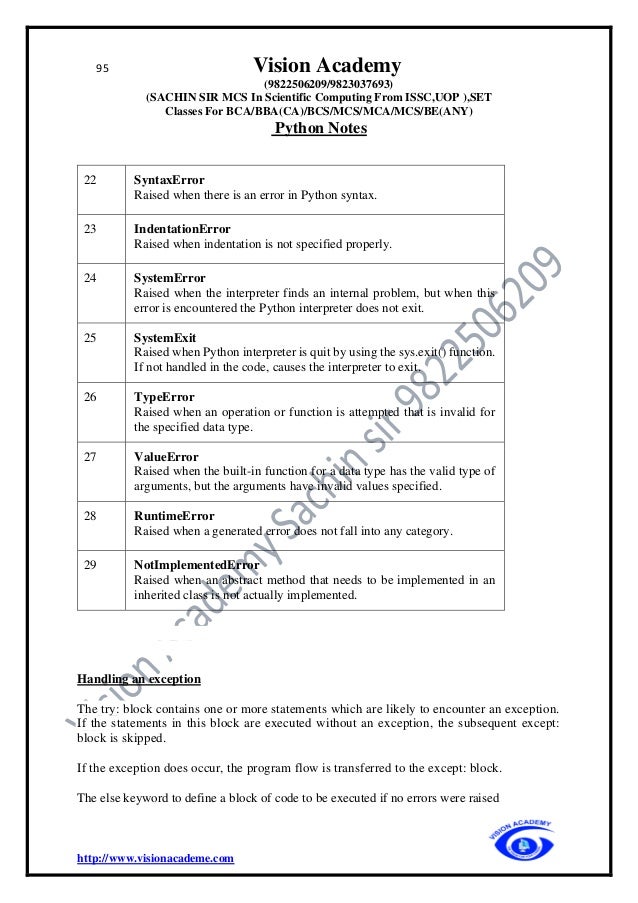
example −
total = item_one +
item_two +
item_three
Implicit Line continuation
• Statements contained within the [], {}, or () brackets do not need to use the line
continuation character. For example −
days = ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday',
'Thursday', 'Friday']
Q.Variables
Python has no command for declaring a variable.
A variable is created the moment you first assign a value to it.
x=5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-12-638.jpg)

![18 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
~ NOT
<< Zero fill left shift
>> Signed right shift
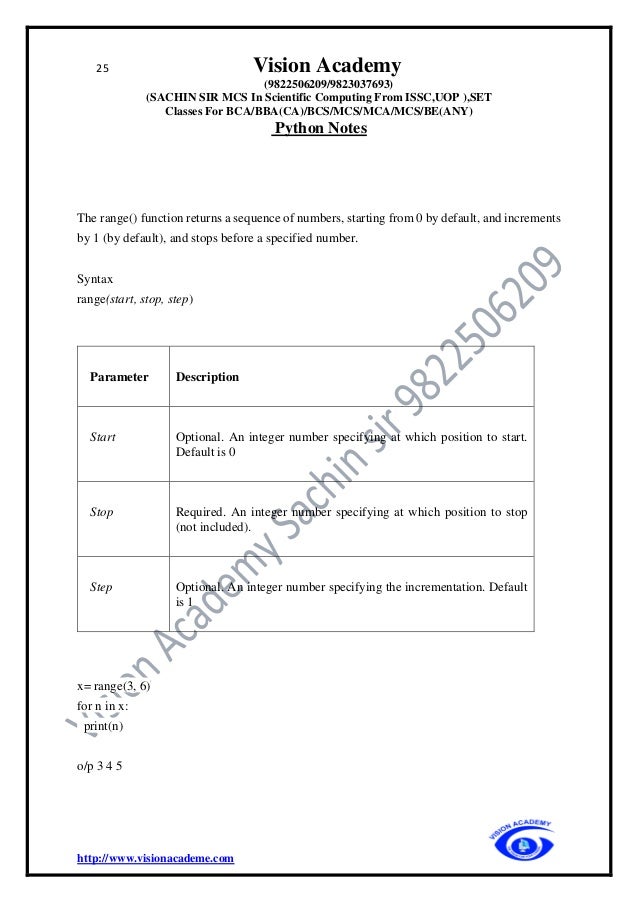
Data Type Conversion
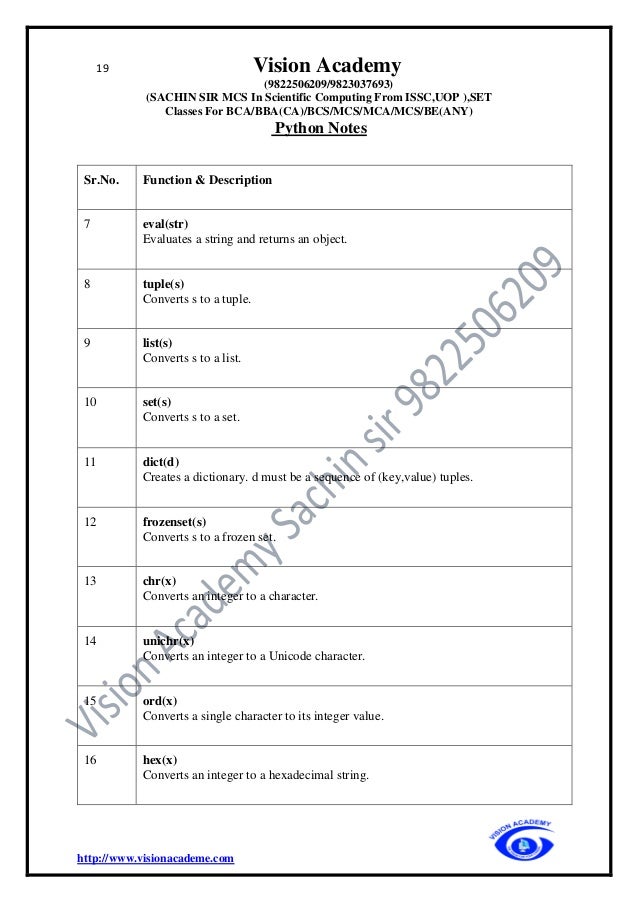
Sr.No. Function & Description
1 int(x[,base])
Converts x to an integer. base specifies the base if x is a string.
2 long(x[,base])
Converts x to a long integer. base specifies the base if x is a string.
3 float(x)
Converts x to a floating-point number.
4 complex(real[,imag])
Creates a complex number.
5 str(x)
Converts object x to a string representation.
6 repr(x)
Converts object x to an expression string.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-18-638.jpg)



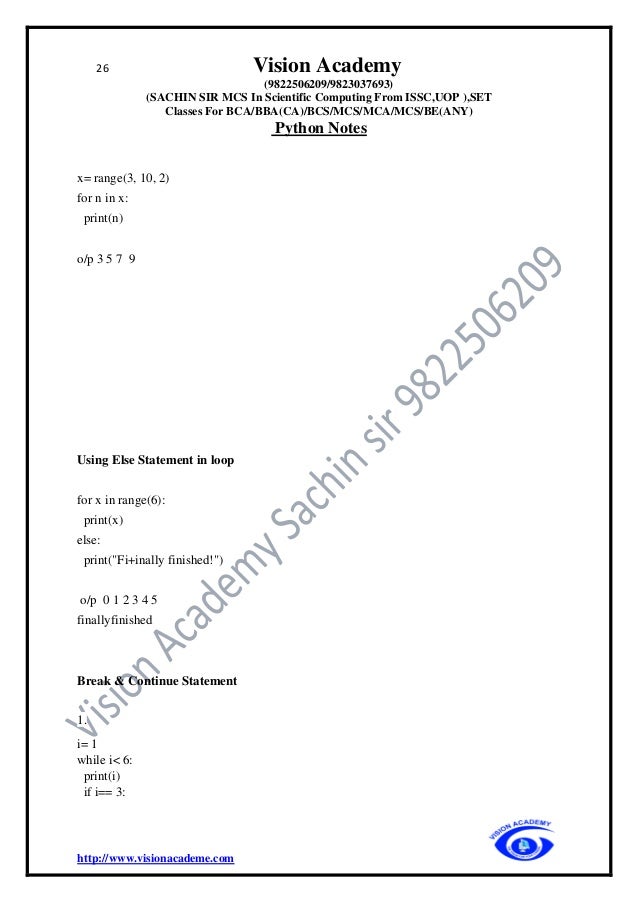

![29 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
isnan(x) Returns True if x is a NaN
ldexp(x, i) Returns x * (2**i)
modf(x) Returns the fractional and integer parts of x
trunc(x) Returns the truncated integer value of x
exp(x) Returns e**x
expm1(x) Returns e**x - 1
log(x[, b]) Returns the logarithm of x to the base b (defaults to e)
log1p(x) Returns the natural logarithm of 1+x
log2(x) Returns the base-2 logarithm of x
log10(x) Returns the base-10 logarithm of x
pow(x, y) Returns x raised to the power y
sqrt(x) Returns the square root of x
acos(x) Returns the arc cosine of x
asin(x) Returns the arc sine of x
atan(x) Returns the arc tangent of x
atan2(y, x) Returns atan(y / x)
cos(x) Returns the cosine of x
hypot(x, y) Returns the Euclidean norm, sqrt(x*x + y*y)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-29-638.jpg)


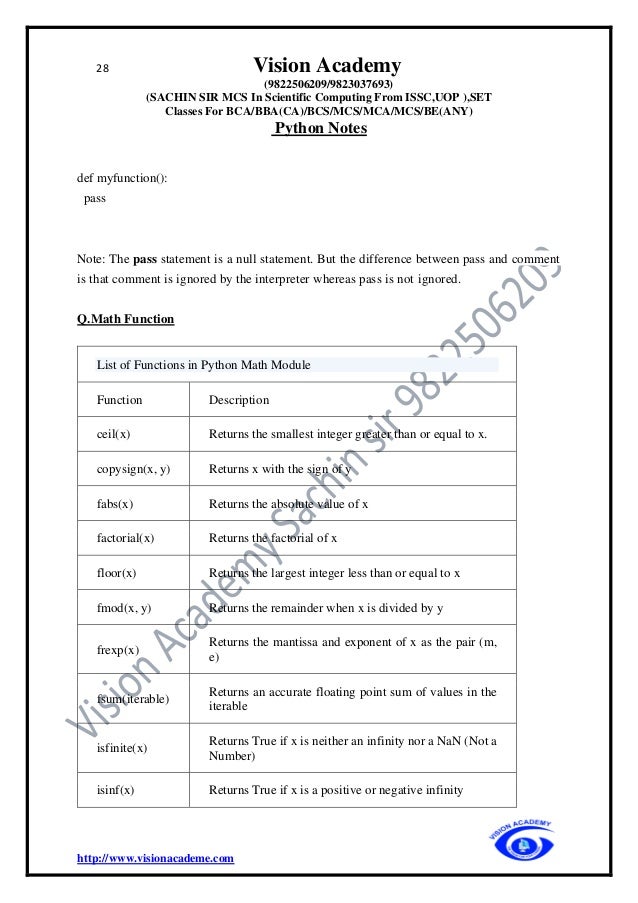
![33 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
e.g
txt = "HellonWorld!"
print(txt)
Slicing a String
If S is a string, the expression S [ start : stop : step ] returns the portion of the string from
index start to index stop, at a step size step.
Syntax
Basic Example
Here is a basic example of string slicing.
S = ' A B C D E F G H I '
print(S[2:7]) # C D E F G](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-33-638.jpg)
![34 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Note that the item at index 7 'H' is not included.
Slice with Negative Indices
You can also specify negative indices while slicing a string.
S = ' A B C D E F G H I '
print(S[-7:-2]) # C D E F G
Slice with Positive & Negative Indices
You can specify both positive and negative indices at the same time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-34-638.jpg)
![35 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
S = ' A B C D E F G H I '
print(S[2:-5]) # C D
Specify Step of the Slicing
You can specify the step of the slicing using step parameter. The step parameter is optional
and by default 1.
# Return every 2nd item between position 2 to 7
S = ' A B C D E F G H I '
print(S[2:7:2]) # C E G
Negative Step Size
You can even specify a negative step size.
# Returns every 2nd item between position 6 to 1 in reverse order
S = ' A B C D E F G H I '
print(S[6:1:-2]) # G E C
Slice at Beginning & End
Omitting the start index starts the slice from the index 0. Meaning, S[:stop] is equivalent
to S[0:stop]
# Slice first three characters from the string
S = ' A B C D E F G H I '
print(S[:3]) # A B C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-35-638.jpg)
![36 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Whereas, omitting the stop index extends the slice to the end of the string.
Meaning, S[start:] is equivalent to S[start:len(S)]
# Slice last three characters from the string
S = ' A B C D E F G H I '
print(S[6:]) # G H I
String operator
String Special Operators
Assume string variable a holds 'Hello' and variable b holds 'Python', then −
Operator Description Example
+ Concatenation - Adds values on either side of the operator a + b will give
HelloPython
* Repetition - Creates new strings, concatenating multiple
copies of the same string
a*2 will give -
HelloHello
[] Slice - Gives the character from the given index a[1] will give e
[ : ] Range Slice - Gives the characters from the given range a[1:4] will give ell
b[2:]=>thon
b[:3]=>Pyt
b[-4:-2]=>th](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-36-638.jpg)
![40 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
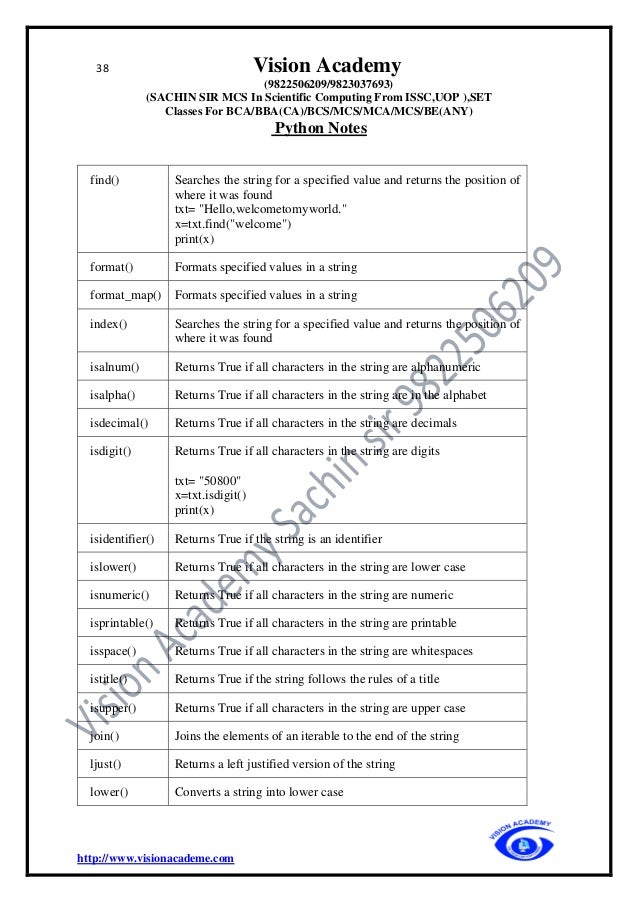
translate() Returns a translated string
upper() Converts a string into upper case
txt= "Hellomyfriends"
x=txt.upper()
print(x)
zfill() Fills the string with a specified number of 0 values at the beginning
Q List
• A list in Python is used to store the sequence of various types of data.
• Python lists are mutable(Its mean it can modify its element after it created).
• A list can be defined as a collection of values or items of different types. The items in
the list are separated with the comma (,) and enclosed with the square brackets [].
• It allowed duplicate value
Syntax
Listname=[value1, value2,…..valuen]
e.g
list1 = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "apple", "cherry"]
list2 = ["abc", 34, True, 40, "male"]
print(list1)
print(list2)
o/p
["apple", "banana", "cherry", "apple", "cherry"]
[‘abc’, 34, True, 40, ‘male’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-40-638.jpg)
![41 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Display List using loop
list=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for i in range(len(list)):
print(list[i])
OR
list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in list:
print(x)
Accessing Element in List
List index
e.g
list1=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
print(list1[1] o/p=>bannan
print(list1[-1]) o/p=>cherry
Slicing List
e.g
list1=["apple", "banana", "cherry", "orange", "kiwi", "melon", "mango"]
print(list1[2:5]) o/p=>[‘cherry’,’orange’,’kiwi’]
print(thislist[:4]) o/p=>[‘apple’,’banana’,’cherry’,’orange’]
print(thislist[2:]) o/p=>[‘cherry’,’kiwi’,’melon’,’msngo’]
print(thislist[-4:-1]) o/p=>[‘orange’,’kiwi’,’melon’]
Inserting Item](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-41-638.jpg)
![42 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
thislist=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist.insert(2, "watermelon")
print(thislist) o/p=➔[‘apple’, ‘banana’,’watermelon’, "cherry"]
Updating List
list = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000];
print "Value available at index 2 : "
print list[2] o/p=➔1997
list[2] = 2001;
print "New value available at index 2 : "
print list[2] o/p➔2001
Change a Range of Item Values
thislist=["apple", "banana", "cherry", "orange", "kiwi", "mango"]
thislist[1:3]=["blackcurrant", "watermelon"]
print(thislist)
o/p[‘apple’,’blackcurrant’,watermelon’,’orange’,’kiwi’,’mango’]
thislist=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist[1:2]=["blackcurrant", "watermelon"]
print(thislist)
o/p[‘apple’,’balckcurrent’,’watermelon’]
thislist=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist[1:3]=["watermelon"]
print(thislist)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-42-638.jpg)
![43 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
o/p [‘apple’,’watermelon’]
Remove Item
1.remove():The remove() method removes the specified item.
list=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
list.remove("banana")
print(list)
o/p [‘apple’,’cherry’]
2.pop():The pop() method removes the specified index.
list=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
list.pop(1)
print(list)
o/p [‘apple’,’cherry’]
If you do not specify the index, the pop() method removes the last item.
list=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
list.pop()
print(list)
o/p [‘apple’,’banana’]
3.Del():The del keyword also removes the specified index
list=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
del list[0]
print(list)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-43-638.jpg)
![44 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
o/p [‘banana’,’cherry’]
The del keyword can also delete the list completely.
list=["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
del list
4.clear():The clear() method empties the list
list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
list.clear()
print(thislist)
Method Description
append() Adds an element at the end of the list fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
fruits.append("orange")
print(x)
copy() Returns a copy of the list fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
x = fruits.copy()
print(x)
count() Returns the number of elements with
the specified value
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
x = fruits.count("cherry")
print(x)
extend() Add the elements of a list (or any
iterable), to the end of the current list
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
cars = ['Ford', 'BMW', 'Volvo']
fruits.extend(cars)
print(fruits)
index() Returns the index of the first element
with the specified value
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
x = fruits.index("cherry")
print(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-44-638.jpg)
![45 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
o/p 2
reverse() Reverses the order of the list fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
fruits.reverse()
print(fruits)
sort() Sorts the list cars = ['Ford', 'BMW', 'Volvo']
cars.sort()
print(cars)
List Comprehension
It is a one line for loop that produce python list data structure. It is complete substitute for
labda function as well as function map(),filter() & reduce function.
Syntax
newlist = [expression for item in iterable if condition == True]
e.g 1
Where
The expression is the current item in the iteration
fruits=["apple", "banana", "cherry", "kiwi", "mango"]
newlist=[x for x in fruits if "a" in x]
print(newlist)
o/p["apple", "banana", "mango"]
e.g 2
newlist = [x for x in range(10)]
print(newlist)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-45-638.jpg)
![46 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
o/p
[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Q Python Tuple
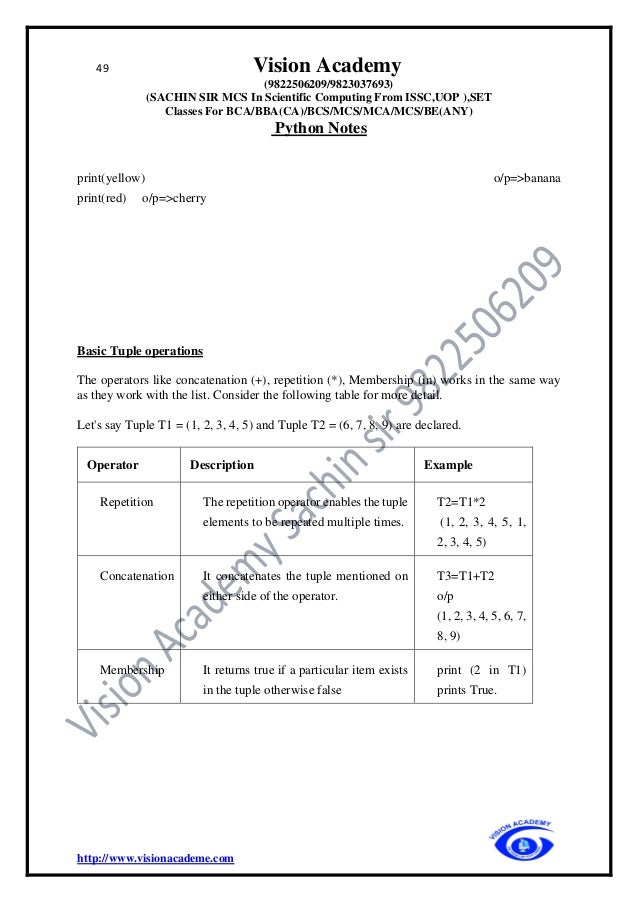
1. Tuples are used to store multiple items in a single variable.
2. Tuples are written with round brackets.
3. A tuple is a is ordered collection & immutable(The value of the items stored in
the tuple cannot be changed after tuple has been created)
4. It allowed duplicate
Syntax
tupleame=(value1, value2,…..valuen)
e.g
tuple=("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(tuple)
o/p
(‘apple’, ‘banana’, ‘cherry’)
Display tuple using loop
t=("apple", "banana", "cherry")
for i in range(len(t)):
print(t[i])
Or
t = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
for x in t:
print(x)
Accessing Element in Tuple](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-46-638.jpg)
![47 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Tuple index
e.g
tuple=("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(tuple[1]) o/p=>bannan
print(tuple[-1]) o/p=>cherry
Slicing
e.g
t = ("apple", "banana", "cherry", "orange", "kiwi", "melon", "mango")
print(t[2:5]) ➔ o/p (‘cherry’, ‘orange’, ‘kiwi’)
print(t[:4]) o/p=>(‘apple’,’banana’,’cherry’,’orange’)
print(t[2:]) o/p=>(‘cherry’,’kiwi’,’melon’,’mango’)
print(t[-4:-1]) o/p=>(‘orange’,’kiwi’,’melon’)
Update Tuple
Once a tuple is created, you cannot change its values. Tuples are unchangeable,
or immutable as it also is called.
It can convert the tuple into a list, change the list, and convert the list back into a tuple
Add Items
thistuple=("apple", "banana", "cherry")
y= list(thistuple)
y.append("orange")
thistuple= tuple(y)
o/p (‘apple’, ‘banana’, ‘cherry’, ’orange’)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-47-638.jpg)
![48 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Update Items
x=("apple", "banana", "cherry")
y= list(x)
y[1]= "kiwi"
x= tuple(y)
print(x)
o/p(‘apple’, ‘kiwi’, ‘cherry’)
Remove Item
thistuple=("apple", "banana", "cherry")
y= list(thistuple)
y.remove("apple")
thistuple = tuple(y)
print(thistuple)
o/p(‘banana’, ‘cherry’)
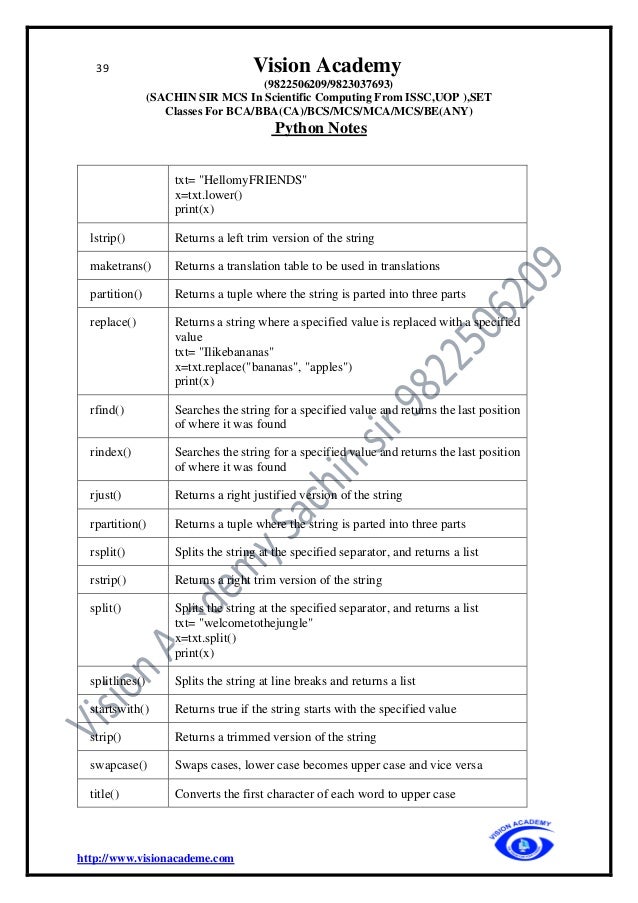
Packing Tuple
When we create a tuple, It normally assign values to it. This is called "packing" a tuple
fruits = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(fruits)
Unpacking Tuple
It allowed to extract the values back into variables. This is called "unpacking"
fruits=("apple", "banana", "cherry")
(green,yellow,red)=fruits
print(green) o/p=>apple](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-48-638.jpg)
![50 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Iteration The for loop is used to iterate over the
tuple elements.
for i in T1:
print(i)
Output
1
2
3
4
5
Length It is used to get the length of the tuple. len(T1) = 5
Build In function
Sr.No. Function with Description Eg
1 cmp(tuple1, tuple2)
Compares elements of both tuples.
It return following result
list1 = [ 1, 2, 4, 3]
list2 = [ 1, 2, 5, 8]
list3 = [ 1, 2, 5, 8, 10]
list4 = [ 1, 2, 4, 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-50-638.jpg)
![51 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
If T1>T2 return(1)
If T1=T2 return(0)
If T1<T2 return(-1)
print cmp(list2, list1) o/p 1
print cmp(list2, list3) o/p -1
print cmp(list4, list1) o/p 0
2 len(tuple)
Gives the total length of the tuple.
t(1,2,3)
print len(t) o/p 3
3 max(tuple)
Returns item from the tuple with max
value.
t(1,2,3)
print max(t) o/p 3
4 min(tuple)
Returns item from the tuple with min
value.
t(1,2,3)
print min(t) o/p 1
5 tuple(seq)
Converts a list into tuple.
aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc']
aTuple = tuple(aList)
print aTuple
o/p
(123,’xyz’,’zara’)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-51-638.jpg)
![52 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Sr.no List Tuple
1 The literal syntax of list is
shown by the [].
The literal syntax of the tuple is
shown by the ().
2 The List is mutable. The tuple is immutable.
3 The List has the a variable
length.
The tuple has the fixed length.
4 The list provides more
functionality than a tuple.
The tuple provides less
functionality than the list.
5 List iteration is slower and is
time consuming
Tuple iteration is faster
6 The lists are more memory The tuples are less memory.
7. L=[1,2,3] T=(1,2,3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-52-638.jpg)




![57 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
print(thislist[x])
3.both keys and values, by using the items() method:
for x,y in thisdict.items():
print(x, y)
Access Value from Dictionary
thisdict ={
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
print ("thisdict[brand]:",thisdict["brand"]);
print ("thisdict[model]:",thisdict["model"]);
print ("thisdict[year]:",thisdict["year"]);
Update Dictionary
1.Add a Item
thisdict ={ "brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
thisdict["color"] = "red"
print(thisdict)
2.Update Item](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-57-638.jpg)
![58 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
The update() method will update the dictionary with the items from a given argument. If the
item does not exist, the item will be added.
The argument must be a dictionary, or an iterable object with key:value pairs.
thisdict =
{
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
thisdict.update({"color": "red"})
3.Remove Item
1.Using del method
thisdict= {
"brand": "Ford", "model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
del thisdict["model"]
print(thisdict)
2.The del keyword can also delete the dictionary completely
thisdict= {
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
del thisdict
print(thisdict)
2.The clear() method empties the dictionary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-58-638.jpg)




![63 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
return c;
a = 10
b = 20
print("The sum is:",sum(a,b)) # calling sum() function in print statement
Function Argument
There are 2 ways passing argument to the function
1.Call by Reference
It pass as address as parameter to the function
def change_list(list1):
list1.append(20)
list1.append(30)
print("list inside function = ",list1)
#defining the list
list1 = [10,30,40,50]
#calling the function
change_list(list1)
print("list outside function = ",list1)
o/p list inside function = [10, 30, 40, 50, 20, 30]
list outside function = [10, 30, 40, 50, 20, 30]
2. Call By value
It pass as value as parameter to the function
Types of arguments
There may be several types of arguments which can be passed at the time of function call.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-63-638.jpg)




![68 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
(filter(),map(),reduce())
Map()
The map() function in Python takes in a function and a list as an argument. The function is
called with a lambda function and a list and a new list is returned which contains all the
lambda modified items returned by that function for each item
Syntax
Map(finction,list)
li = [5, 7, 22, 97, 54, 62, 77, 23, 73, 61]
final_list = list(map(lambda x: x*2, li))
print(final_list)
o/p
[10, 14, 44, 194, 108, 124, 154, 46, 146, 122]
Filter()
The filter() function in Python takes in a function and a list as arguments. This offers an
elegant way to filter out all the elements of a sequence “sequence”, for which the function
returns True.
Syntax
Filter(function,list)
li = [5, 7, 22, 97, 54, 62, 77, 23, 73, 61]
final_list = list(filter(lambda x: (x%2 != 0) , li))
print(final_list)
o/p
[5, 7, 97, 77, 23, 73, 61]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-68-638.jpg)
![69 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
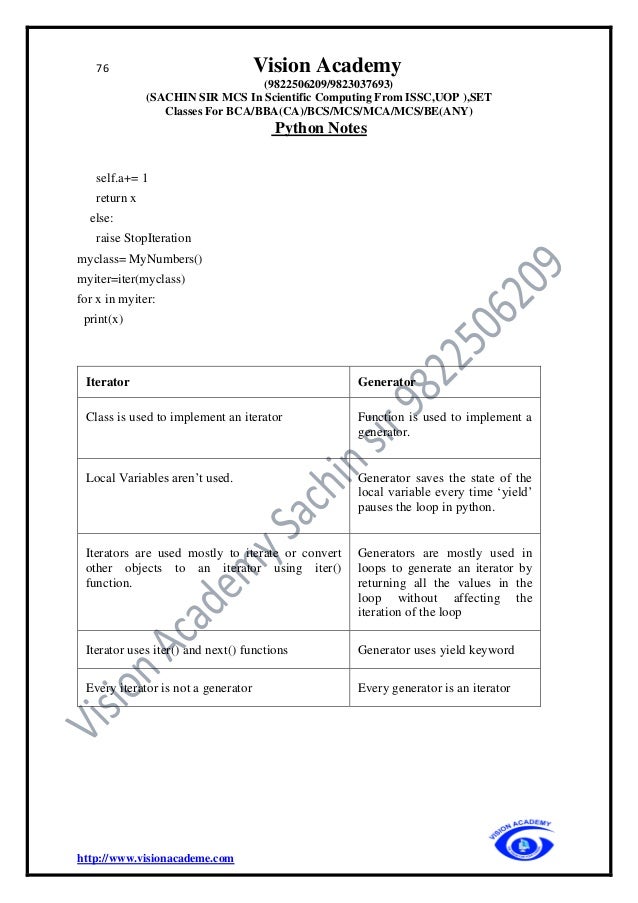
Reduce()
The reduce() function in Python takes in a function and a list as an argument. The function
is called with a lambda function and an iterable and a new reduced result is returned. This
performs a repetitive operation over the pairs of the iterable. The reduce() function belongs
to the functools module.
Syntax
reduce(function, sequence[, initial])
from functools import reduce
li = [5, 8, 10, 20, 50, 100]
sum = reduce((lambda x, y: x + y), li)
print (sum)
o/p 193
Q.Packing and Unpacking Arguments
1.args*
• It can use * to unpack the list so that all elements of it can be passed as different
parameters
• The single asterisk(*) form of *args can be used as parameter to send non keyworded
Variable-length argument list to a functions.
• * used for tuple
def fun(a, b, c, d):
print(a, b, c, d)
# Driver Code
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
# Unpacking list into four arguments
fun(*my_list)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-69-638.jpg)








![80 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
self.name=name
self.age = age
p1 = Person("amol", 36)
Garbage collection
• Python deletes unwanted objects (built-in types or class instances) automatically to free
the memory space. The process by which Python periodically frees and reclaims blocks
of memory that no longer are in use is called Garbage Collection.
• Python's garbage collector runs during program execution when an object's reference
count reaches zero.
• An object's reference count increases when it is assigned a new name or placed value.
The object's reference count decreases when it's deleted with del, its reference is
reassigned, or its reference goes out of scope. When an object's reference count reaches
zero, Python collects it automatically.
a = 40 # Create object <40>
b = a # Increase ref. count of <40>
d=b # Increase ref. count of <40>
c = [b] # Increase ref. count of <40>
del a # Decrease ref. count of <40>
b = 100 # Decrease ref. count of <40>
c[0] = -1 # Decrease ref. count of <40>
d=none # Decreases ref. count of <40>
Destructor
• The __del__() method is a known as a destructor method in Python.
• when the object is destroyed, due to garbage collection, then _del_ method is called.
• This method might be used to clean up any non memory resources used by an instance
Syntax
def __del__(self):
# body of destructor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-80-638.jpg)






![96 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Syntax
try:
You do your operations here;
......................
except ExceptionI:
If there is ExceptionI, then execute this block.
except ExceptionII:
If there is ExceptionII, then execute this block.
......................
else:
If there is no exception then execute this block.
e.g
try:
x=int(input('Enter a number: '))
y=int(input('Enter another number: '))
z=x/y
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Division by 0 not accepted")
else:
print("else block")
e.g 2 Handles all types of exception
try:
x=int(input('Enter a number: '))
y=int(input('Enter another number: '))
z=x/y
except Exception:
print("Division by 0 not accepted")
else:
print("else block")
except Clause with Multiple Exceptions
Syntax
try:
You do your operations here;
......................
except(Exception1[, Exception2[,...ExceptionN]]]):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-96-638.jpg)

![98 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Raise an exception
Python also provides the raise keyword to be used throw an exception to be explicitly.
Syntax
raise [Exception [, args]
Where
Exception :It is the type of exception (for example, NameError)
Argument: It is a value for the exception argument.
try:
x=int(input('Enter a number upto 100: '))
if x > 100:
raise ValueError(x)
except ValueError:
print(x, "is out of allowed range")
else:
print(x, "is within the allowed range")
User-defined Exceptions
e.g
class Myerror(Exception):
def __init__(self,arg):
self.arg=arg
try:
n=int(input("enter value"))
if(n<0):
raise Myerror("no is negative")
else:
print("postive value")
except Myerror as e:
print (e.arg)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-98-638.jpg)

![101 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
Q.Python Modules
A python module can be defined as a python program file which contains a python code
including python functions, class, or variables. In other words, we can say that our python
code file saved with the extension (.py) is treated as the module
module to be the same as a code library
To creation of User Defined package
1.To create module
def show(name):
print("Hello, " + name)
Note: save as mymodule.py
2. The import Statement
It can use any Python source file as a module by executing an import statement in some other
Python source file.
syntax −
import module1[, module2[,... moduleN]
import mymodule
mymodule.show("om")
e.g To add some part in above module
person1={
"name": "om",
"age": 22,
"country": "india"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-101-638.jpg)
![102 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
save above code in mymodule.py
import mymodule
a=mymodule.person1["age"]
print(a)
Import From Module
It can choose to import only parts from a module, by using the from keyword.
from modname import name1[, name2[, ... nameN]]
def show(name):
print("Hello," +name)
person1={
"name": "om",
"age": 22,
"country": "india"
}
Import only the person1 dictionary from the module
from mymodule import person1
print (person1["age"])
from...import * Statement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-102-638.jpg)
![103 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
It is also possible to import all names from a module into the current namespace by using the
following import statement
from mymodule import *
print (person1["age"])
show("om")
Re-naming a Module
It can create an alias when it import a module, by using the as keyword
import mymodule as mx
a=mx.person1["age"]
print(a)
Pre defined module
import calendar
cal = calendar.month(2021, 1)
print ("Here is the calendar:")
print (cal)
#current date & time
import datetime
x = datetime.datetime.now()
print(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-103-638.jpg)





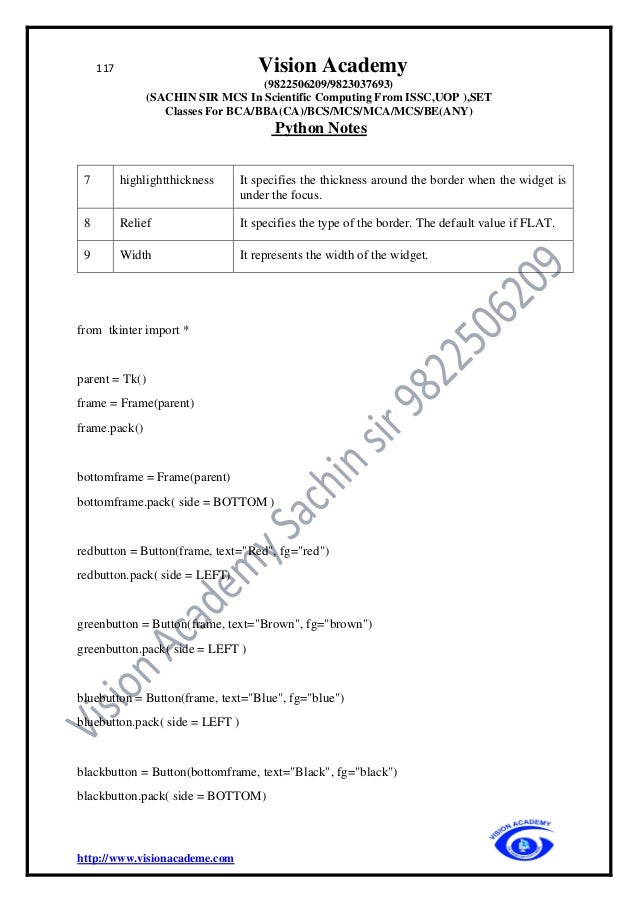
![118 Vision Academy
(9822506209/9823037693)
(SACHIN SIR MCS In Scientific Computing From ISSC,UOP ),SET
Classes For BCA/BBA(CA)/BCS/MCS/MCA/MCS/BE(ANY)
Python Notes
http://www.visionacademe.com
parent.mainloop()
4.messagebox
The messagebox module is used to display the message boxes in the python applications. There
are the various functions which are used to display the relevant messages depending upon the
application requirements.
Syntax
messagebox.function_name(title, message [, options])
Parameters
o function_name: It represents an appropriate message box function.
o title: It is a string which is shown as a title of a message box.
o message: It is the string to be displayed as a message on the message box.
o options: There are various options which can be used to configure the message dialog
box.
The two options that can be used are default and parent.
1. default
o The default option is used to mention the types of the default button, i.e. ABORT,
RETRY, or IGNORE in the message box.
2. parent
o The parent option specifies the parent window on top of which, the message box is to
be displayed.
You could use one of the following functions with dialogue box .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonfinalprintvisonacademy9822506209-220405041642/95/Python_final_print_vison_academy_9822506209-pdf-118-638.jpg)