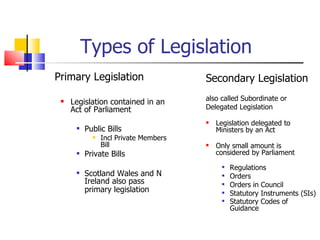
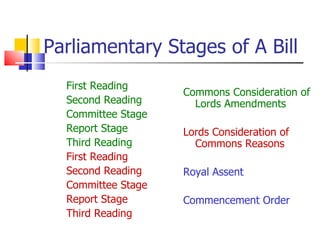
The document provides an overview of the functions and processes of Parliament regarding public bills, including types of legislation, stages of a bill, and the role of private members' legislation. It highlights the difference between government bills and private members' bills, the importance of scrutiny, and the influence of devolution on legislation in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Additionally, it explains how legislation is influenced by outside bodies and emphasizes the complexities of the legislative process within the UK Parliament.