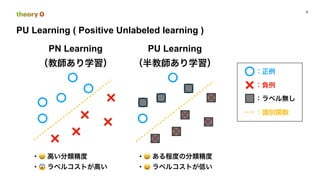
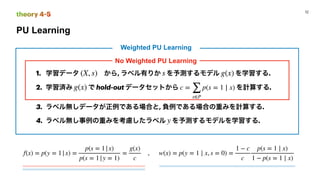
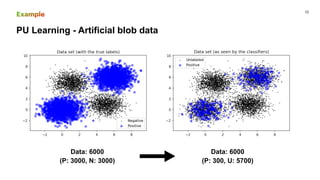
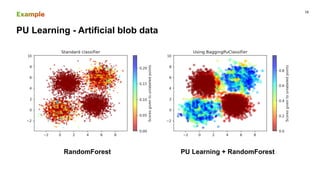
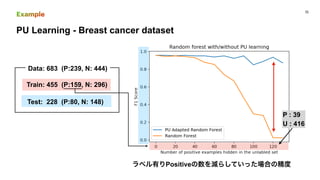
This document discusses PU (positive unlabeled) learning for image segmentation. It presents the theory of PU learning, which involves estimating a classifier from labeled positive and unlabeled data where the unlabeled data contains both positive and negative samples. The theory shows how to estimate the probability of positive samples being in the unlabeled data and how to train classifiers on labeled positive and unlabeled data. It also provides an example applying PU learning to segment blobs in artificial data and lesions in breast cancer images. Finally, it discusses extending PU learning theory to deep learning models for classification.








![PU Learning for DeepLearning
16
theory 5
:
: Positive
: Negative
:
: ,
X
πp = p(Y = + 1)
πn = p(Y = − 1)
g
ℓ(t, y) t y
Risk Estimator PU Learning
̂Rpu(g) = πp
̂R+
p (g) − πp
̂R−
p (g) + ̂R−
u (g)
R−
u (g) = 𝔼X∼p(x)[ℓ(g(X), − 1)]
R+
p (g) = 𝔼p[ℓ(g(X), + 1)], where 𝔼p[ ⋅ ] = 𝔼X∼pp
[ ⋅ ]
R−
p (g) = 𝔼p[ℓ(g(X), − 1)], where 𝔼p[ ⋅ ] = 𝔼X∼pp
[ ⋅ ]
∑
θ∈Θ
R(θ, δ)π(θ)
,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulearn-201110032056/85/PU-Learning-14-320.jpg)
![PU Learning for DeepLearning
17
theory 6
Risk Estimator PN Learning
̂Rpn(g) = πp
̂R+
p (g) + πn
̂R−
n (g)
R−
n (g) = 𝔼n[ℓ(g(X), − 1)], where 𝔼n[ ⋅ ] = 𝔼X∼pn
[ ⋅ ]
R+
p (g) = 𝔼p[ℓ(g(X), + 1)], where 𝔼p[ ⋅ ] = 𝔼X∼pp
[ ⋅ ]
Risk Estimator PU Learning
̂Rpu(g) = πp
̂R+
p (g) − πp
̂R−
p (g) + ̂R−
u (g)
R−
u (g) = 𝔼X∼p(x)[ℓ(g(X), − 1)]
R+
p (g) = 𝔼p[ℓ(g(X), + 1)], where 𝔼p[ ⋅ ] = 𝔼X∼pp
[ ⋅ ]
R−
p (g) = 𝔼p[ℓ(g(X), − 1)], where 𝔼p[ ⋅ ] = 𝔼X∼pp
[ ⋅ ]
{
πnpn(x) = p(x) − πppp(x)
πnR−
n (g) = R−
u (g) − πpR−
p (g)
,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulearn-201110032056/85/PU-Learning-15-320.jpg)