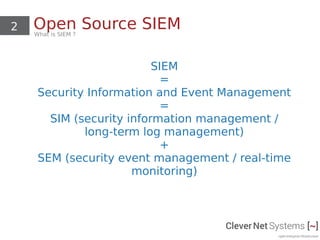
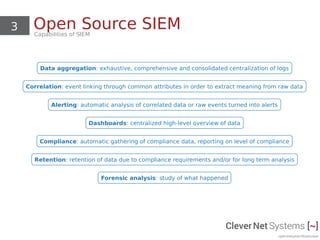
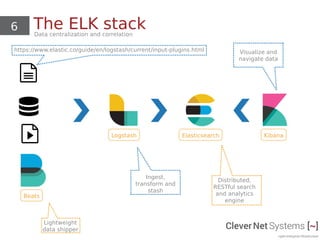
The document discusses open source Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, highlighting their capabilities such as data aggregation, correlation, alerting, and compliance monitoring. It focuses on the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), detailing its components and functionalities in handling logs and threat detection. Additionally, it covers hardware requirements for scaling and setup considerations for effectively utilizing SIEM solutions.





![9 The ELK stackParse Apache access logs with Logstash
Original logs
178.194.37.205 - - [10/Feb/2017:16:00:12 +0100] "POST /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php HTTP/1.1" 200 102
"https://www.clevernetsystems.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=5674&action=edit" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Fedora; Linux x86_64)
AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/55.0.2883.87 Safari/537.36"
54.205.244.176 - - [10/Feb/2017:16:00:23 +0100] "GET /monitoring-mysql-replication-with-munin/feed/ HTTP/1.1" 200 887
"http://www.google.com" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux i686) AppleWebKit/537.31 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/26.0.1410.43
Safari/537.31"
108.61.68.156 - - [10/Feb/2017:16:00:25 +0100] "GET /installing-rhel-packages-without-network-connection/ HTTP/1.1" 200
14379 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/39.0.2171.71
Safari/537.36"
198.27.68.101 - - [10/Feb/2017:16:00:50 +0100] "GET /recruitment/ HTTP/1.1" 200 9093 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1)
AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36"
198.27.68.101 - - [10/Feb/2017:16:00:50 +0100] "GET /wp-content/themes/enfold/css/grid.css?ver=2 HTTP/1.1" 200 2050
"https://www.clevernetsystems.com/recruitment/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)
Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36"
198.27.68.101 - - [10/Feb/2017:16:00:51 +0100] "GET /wp-content/themes/enfold/css/base.css?ver=2 HTTP/1.1" 200 3990
"https://www.clevernetsystems.com/recruitment/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)
Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36"
198.27.68.101 - - [10/Feb/2017:16:00:51 +0100] "GET /wp-content/themes/enfold/js/aviapopup/magnific-popup.css?ver=1
HTTP/1.1" 200 1914 "https://www.clevernetsystems.com/recruitment/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36
(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationelksiem-170718122705/85/Presentation-ELK-SIEM-et-demo-Wazuh-9-320.jpg)






