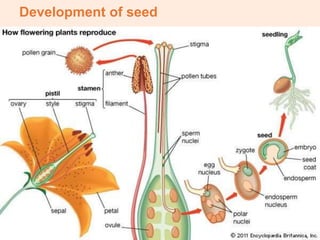
The document discusses seed propagation and germination. It describes the three main parts of seeds - the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The seed coat protects the seed and prevents germination until conditions are suitable. For germination to occur, the seed must be viable, internal conditions must be favorable, and external environmental conditions like water, temperature, oxygen, and light must be present. Seed dormancy can be caused by unfavorable external conditions or internal inhibitory factors in the seed coat or embryo. The document also discusses various growing media that can be used like soil, coco peat, perlite and vermiculite.