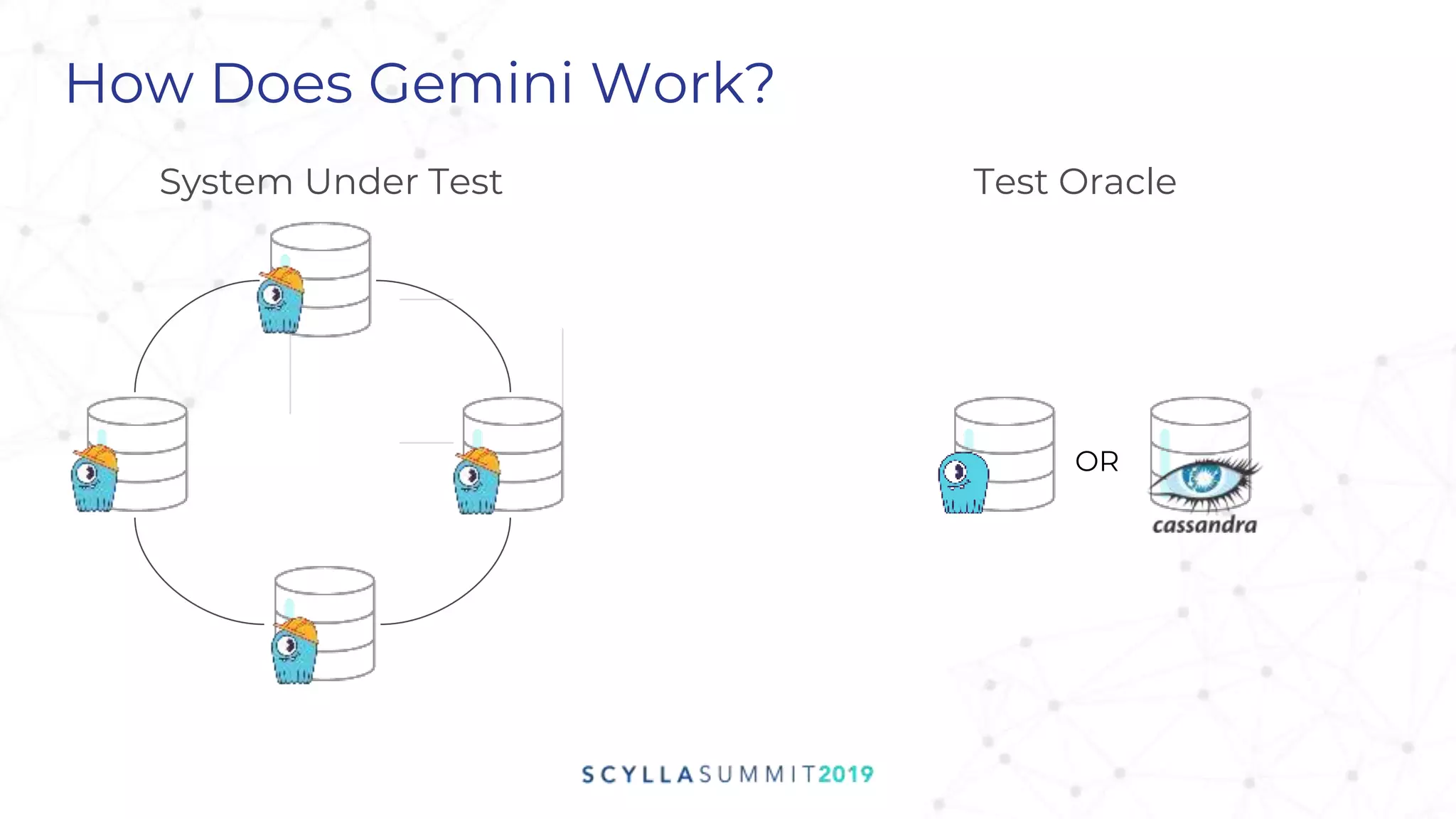
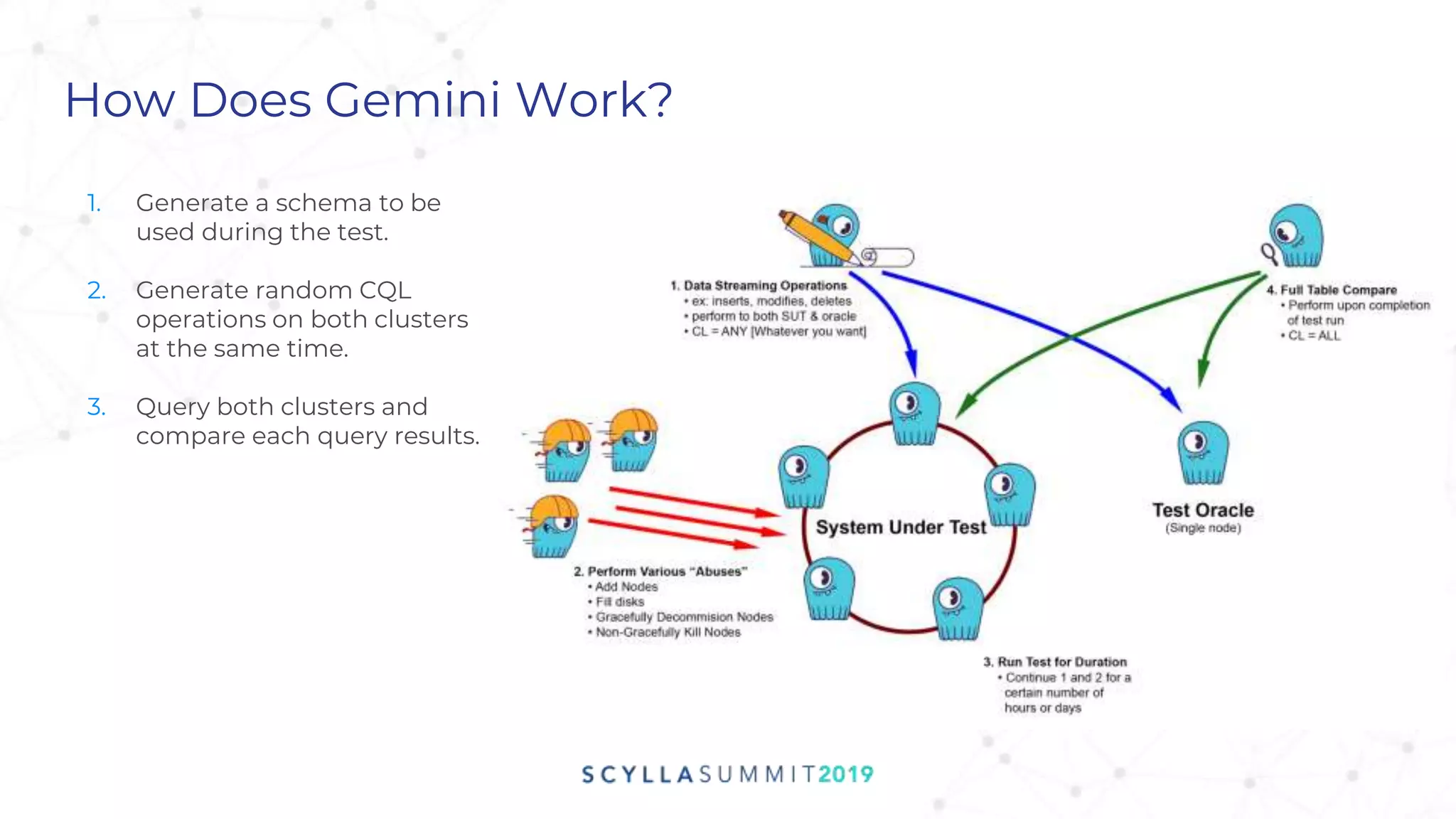
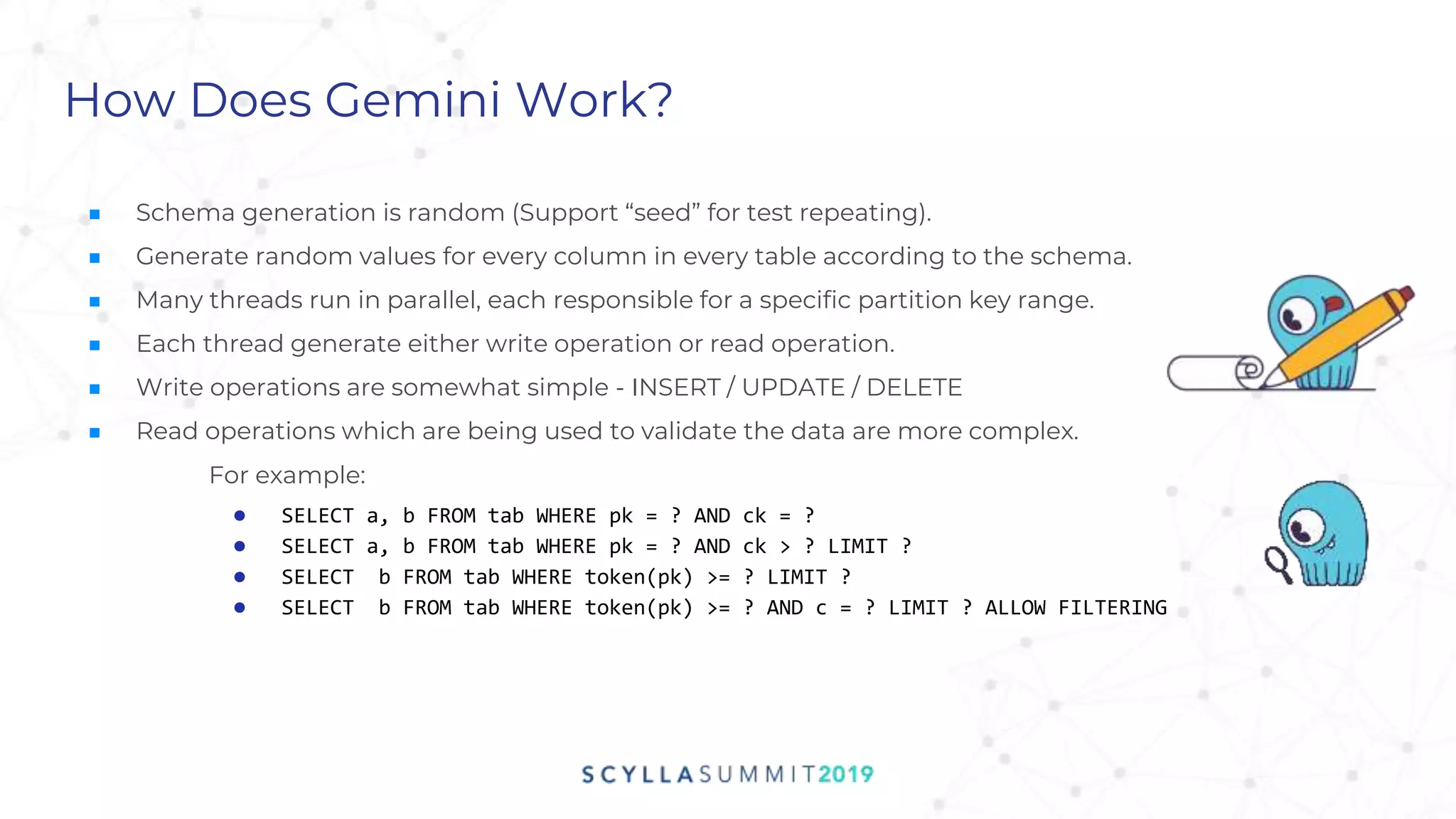
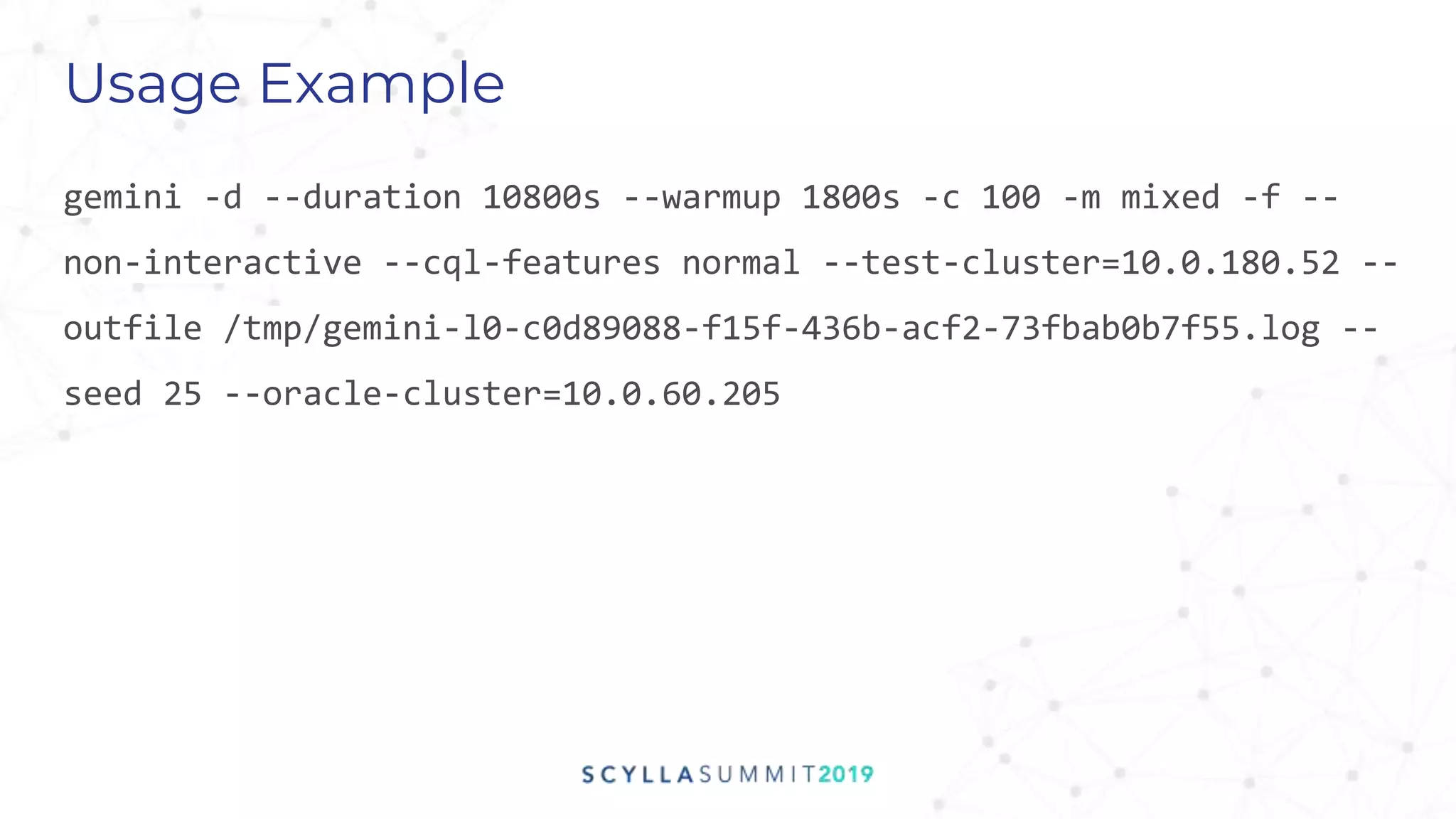
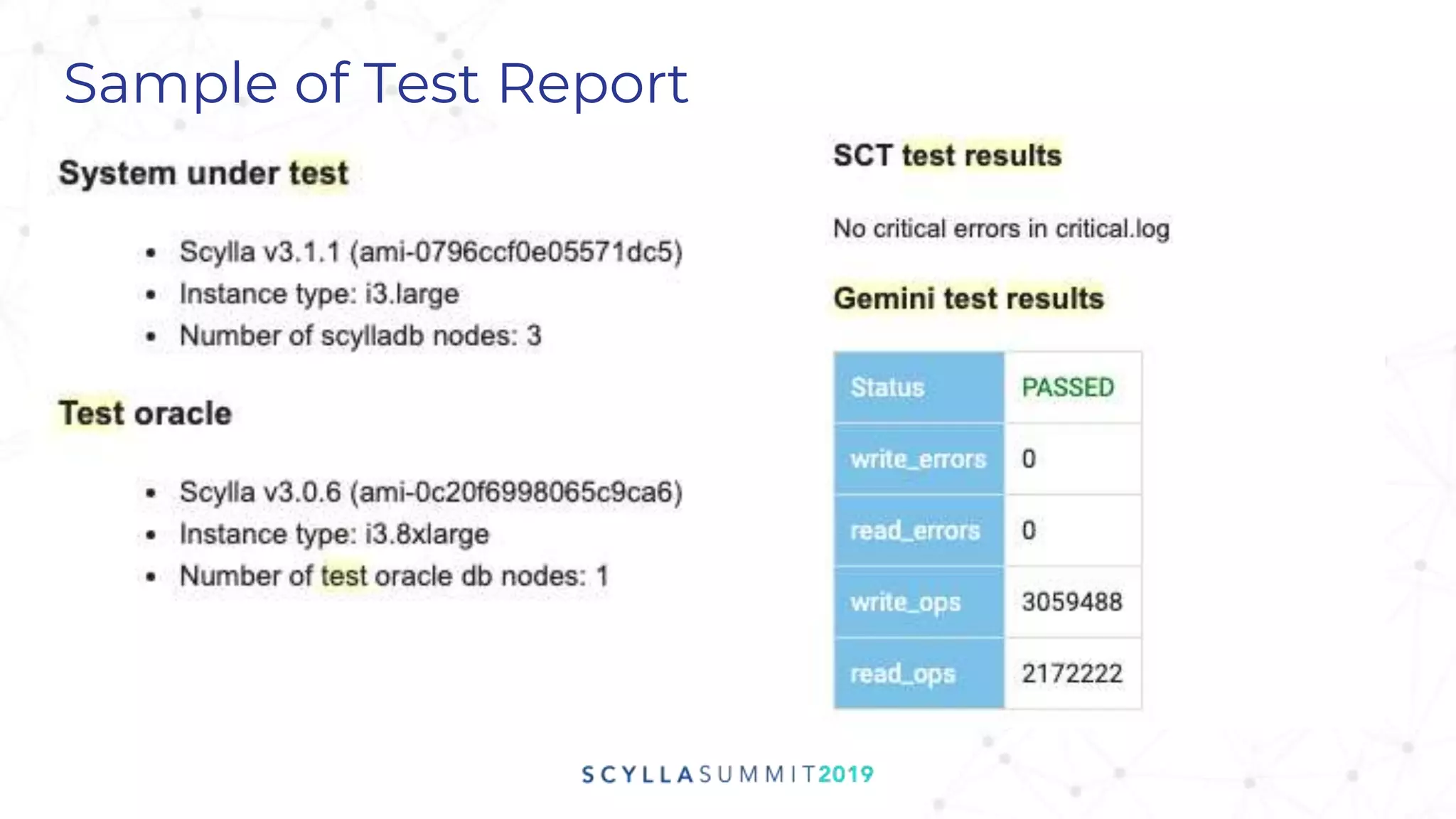
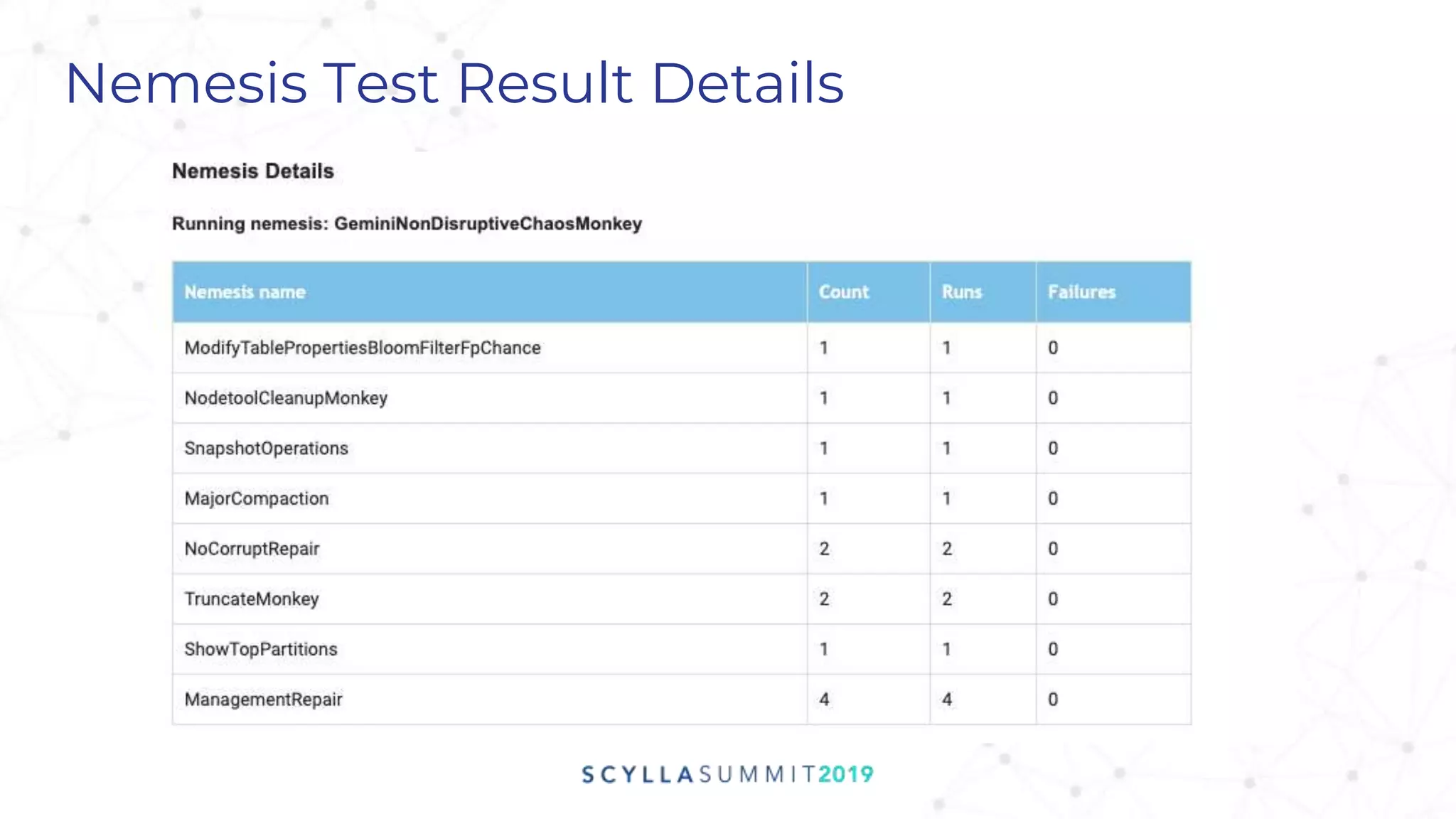
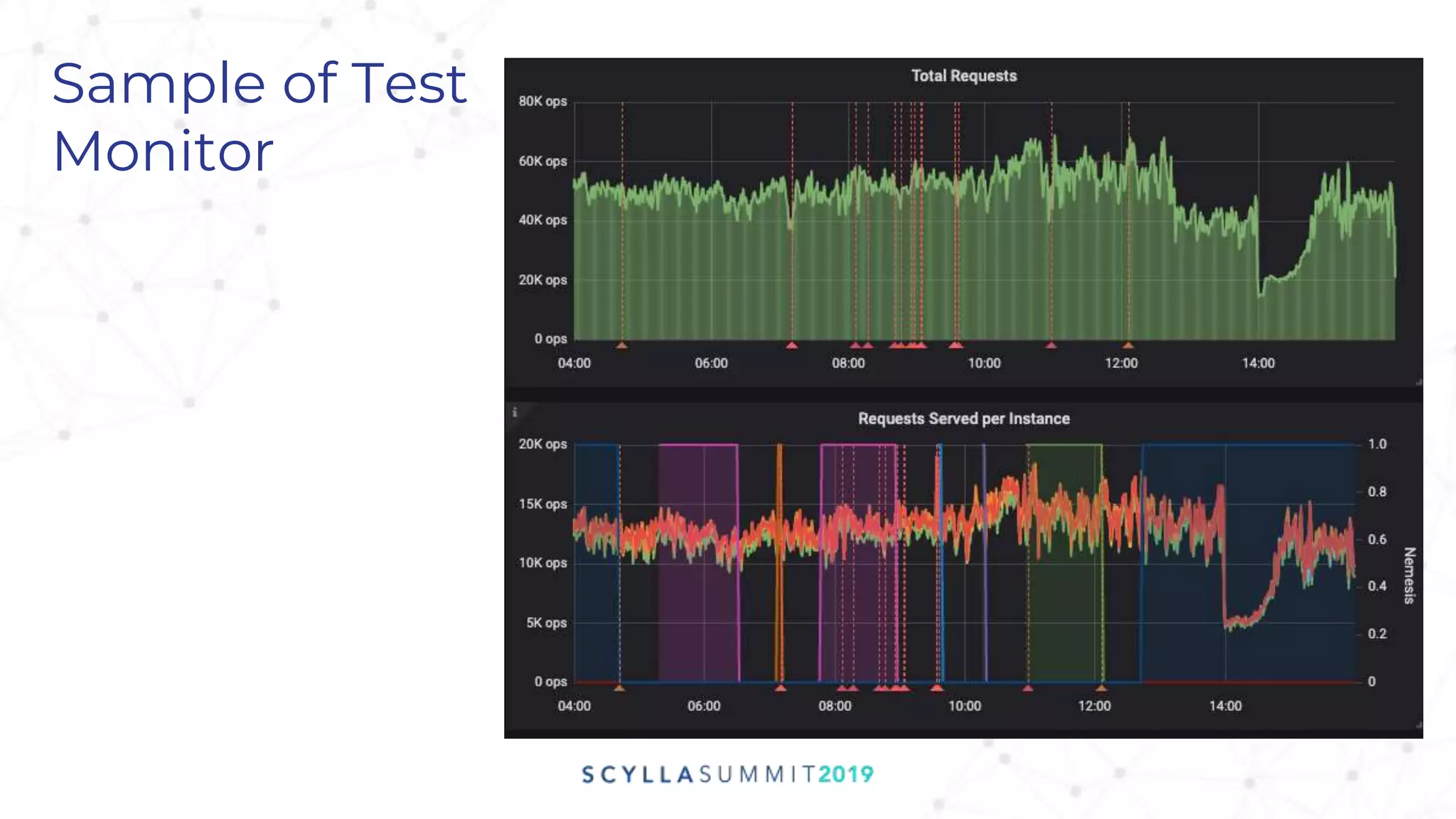
Project Gemini is a testing tool designed by Pekka Enberg, Larisa Ustalov, Henrik Johansson, and Alex Bykov in 2017 to detect data integrity issues like data loss and data corruption in databases. It accomplishes this by applying random testing to a system under test and validating the results against a test oracle. QA manager Roy Dahan discusses how Gemini works by generating random operations on clusters and comparing query results to find differences.