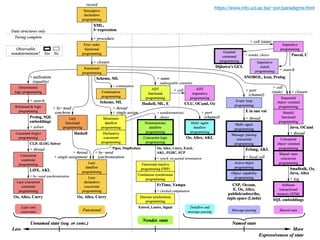
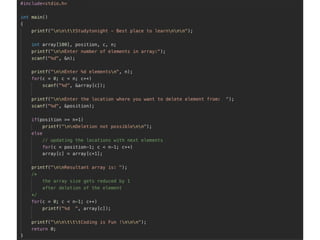
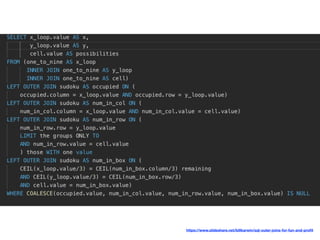
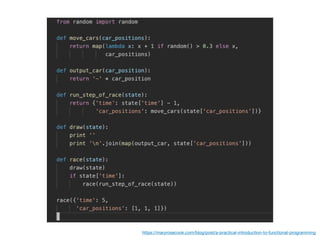
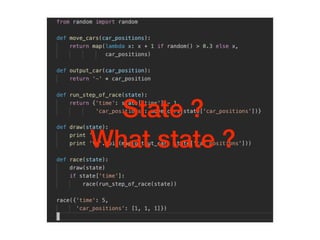
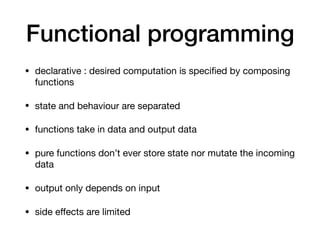
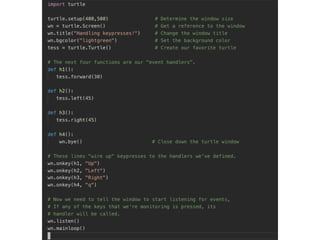
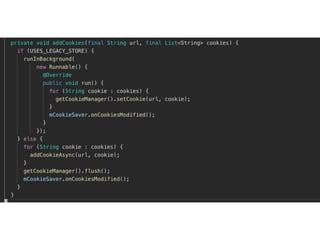
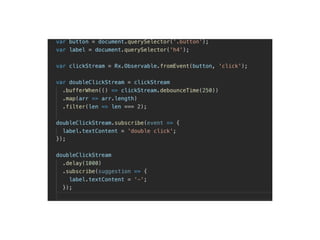
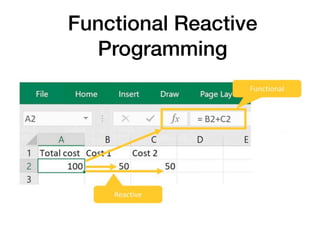
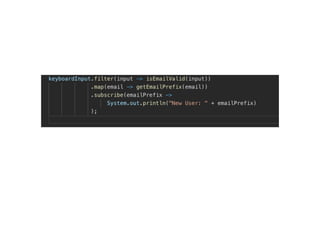
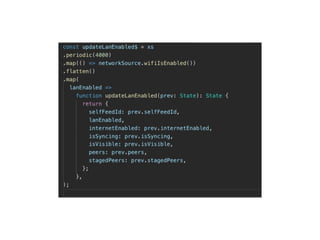
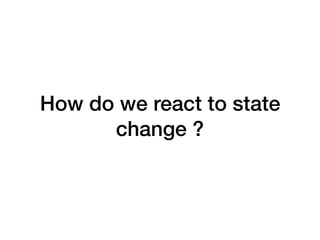The document discusses various programming paradigms, including object-oriented, functional, and declarative programming, defining each's fundamental characteristics and differences. Key components addressed include program flow decision-making, state storage and access, and reactions to state changes. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these paradigms for both general programming advancement and individual programmer skill enhancement.