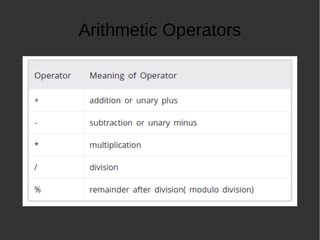
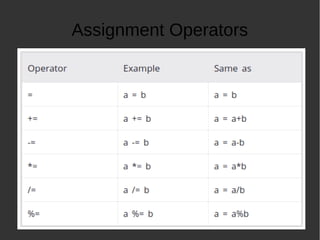
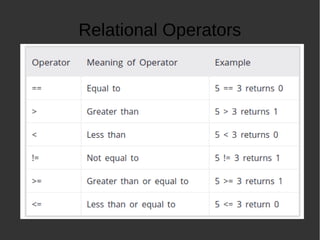
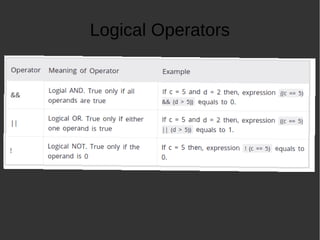
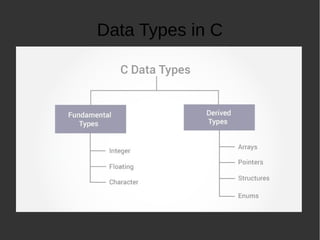
The document provides an introduction to programming basics in C language. It discusses key concepts like how a program runs using compile and execute steps, IDE vs compilers, basic structure of a C program including main function and return statement. It also covers data types in C like integer, floating point and characters. Additionally, it explains various operators, decision making using if-else and loops, functions and input/output operations in C programming.










![Character types
● Keyword char is used for declaring such
variables.
● char test = 'h';
● test is a character variable.
● The value of test is 'h'.
● No string type in C . alternative = char array
● Eg: char num[ ] = “hello”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingbasics-171220101047/85/Programming-basics-13-320.jpg)