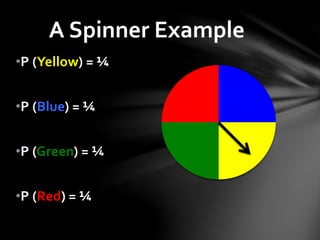
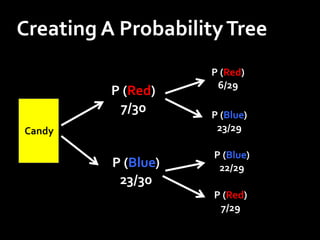
This document defines probability and provides examples of calculating probability using fractions, decimals, and percentages. It explains that probability is a measurement between 0 and 1 that indicates the likelihood of an event occurring. Examples are given showing how to convert between fractions, decimals, and percentages in probability calculations. The document also demonstrates calculating probability using examples like dice rolls, spinners, and drawing from jars without replacement to find the probability of different outcomes.