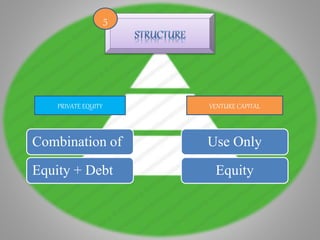
Venture capital is equity or equity-featured capital that seeks investments in new companies, products, processes or services that offer potential for high returns. Venture capital firms invest mostly in early stage companies focused on technology, biotech and cleantech. Venture capital acquires a minority stake, usually less than 50%, in companies. Private equity buys mature companies across all industries, acquiring 100% ownership. Private equity deals are larger, ranging from $100 million to $10 billion, compared to under $10 million for venture capital.