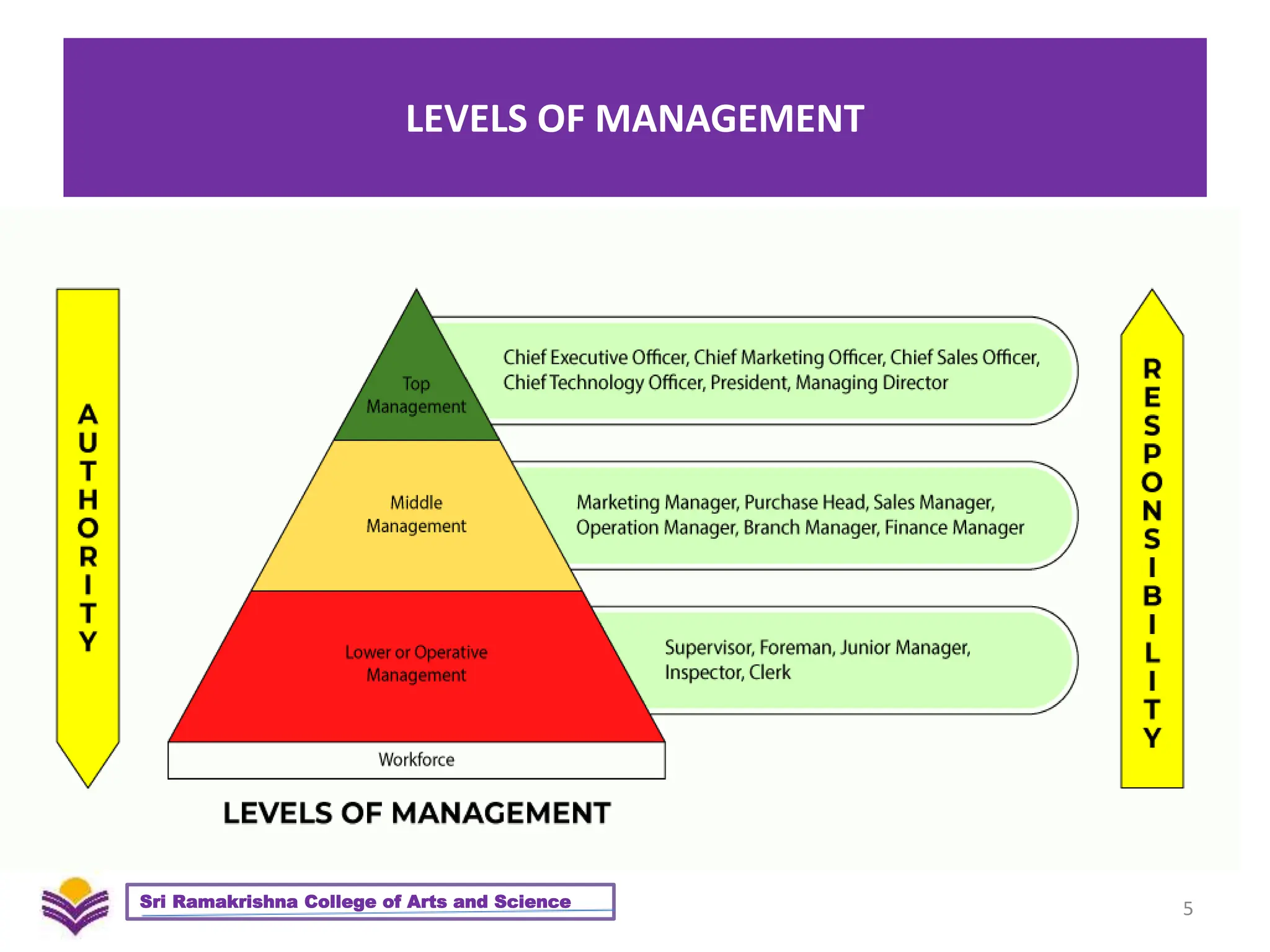
The document provides an overview of management, defining it and discussing its characteristics, scope, skills, and roles of managers. It also outlines various management theories including classical, neo-classical, and modern approaches. Key functions of management and qualities of effective managers are highlighted as essential to the practice of management.