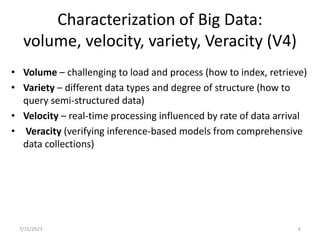
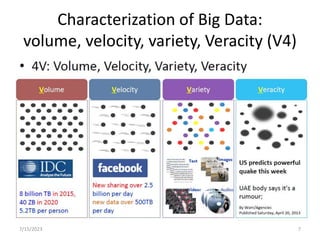
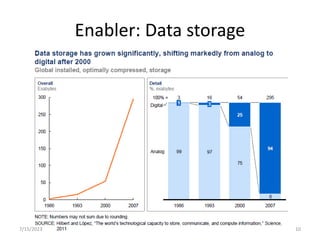
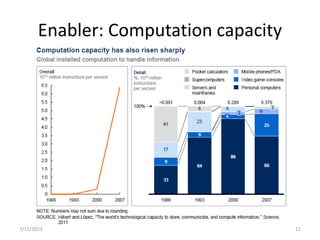
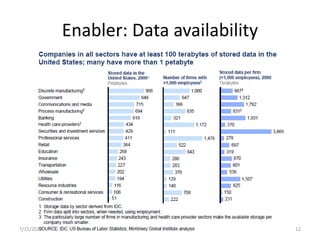
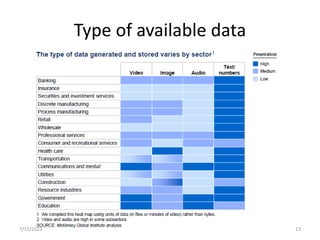
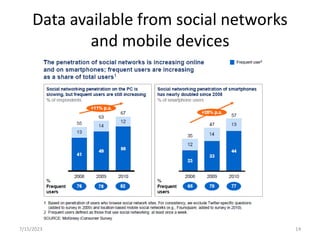
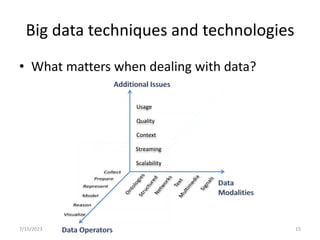
This document introduces the concept of big data by defining it as data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data processing tools to handle due to their volume, velocity and variety. It describes the four characteristics (4Vs) of big data as volume, velocity, variety and veracity. Additionally, it identifies key enablers that have contributed to the growth of big data, such as increases in data storage capacity, processing power, and data availability from various sources like social networks and mobile devices. Finally, the document discusses techniques for analyzing big data and provides examples of domains like healthcare, retail and manufacturing that are being transformed by its potential.