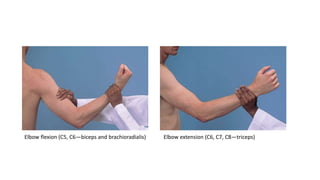
This document provides guidance on performing a physical exam to assess muscle strength. It describes how to test individual muscle groups, including those in the upper and lower extremities. A 5-point scale is presented for grading muscle strength from 0 (no contraction) to 5 (full strength against resistance). Proximal and distal weakness are defined, and tips are provided for identifying each, such as asking about difficulty with certain movements. The various methods of testing major muscle groups like the biceps, triceps, hips and knees are outlined as well.