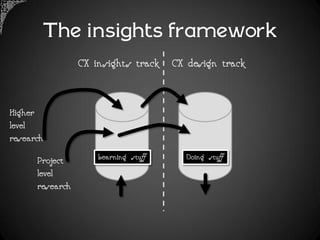
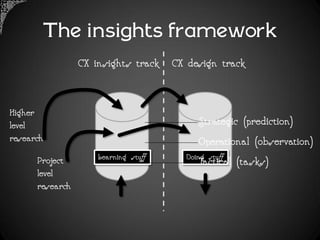
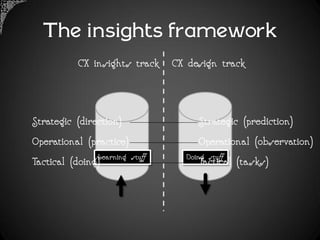
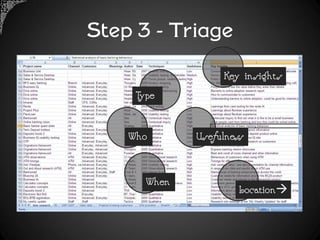
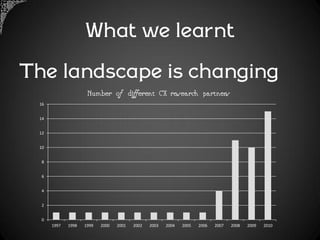
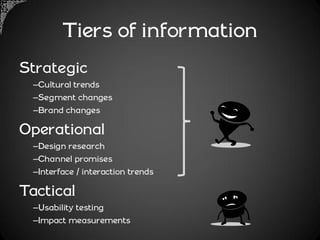
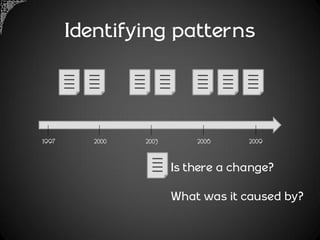
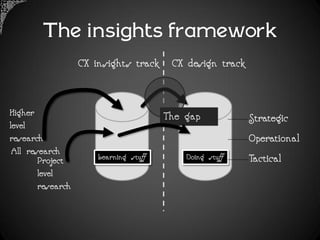
The document outlines a framework for analyzing historical data to identify changes in consumer behavior, particularly relating to online banking, and emphasizes the importance of building long-term research relationships. It presents a structured approach involving finding questions, gathering data, and analyzing insights while highlighting the necessity of raw data for meaningful interpretations. The piece concludes with steps for researchers to reflect and plan for future studies, underscoring the cumulative nature of knowledge in science.