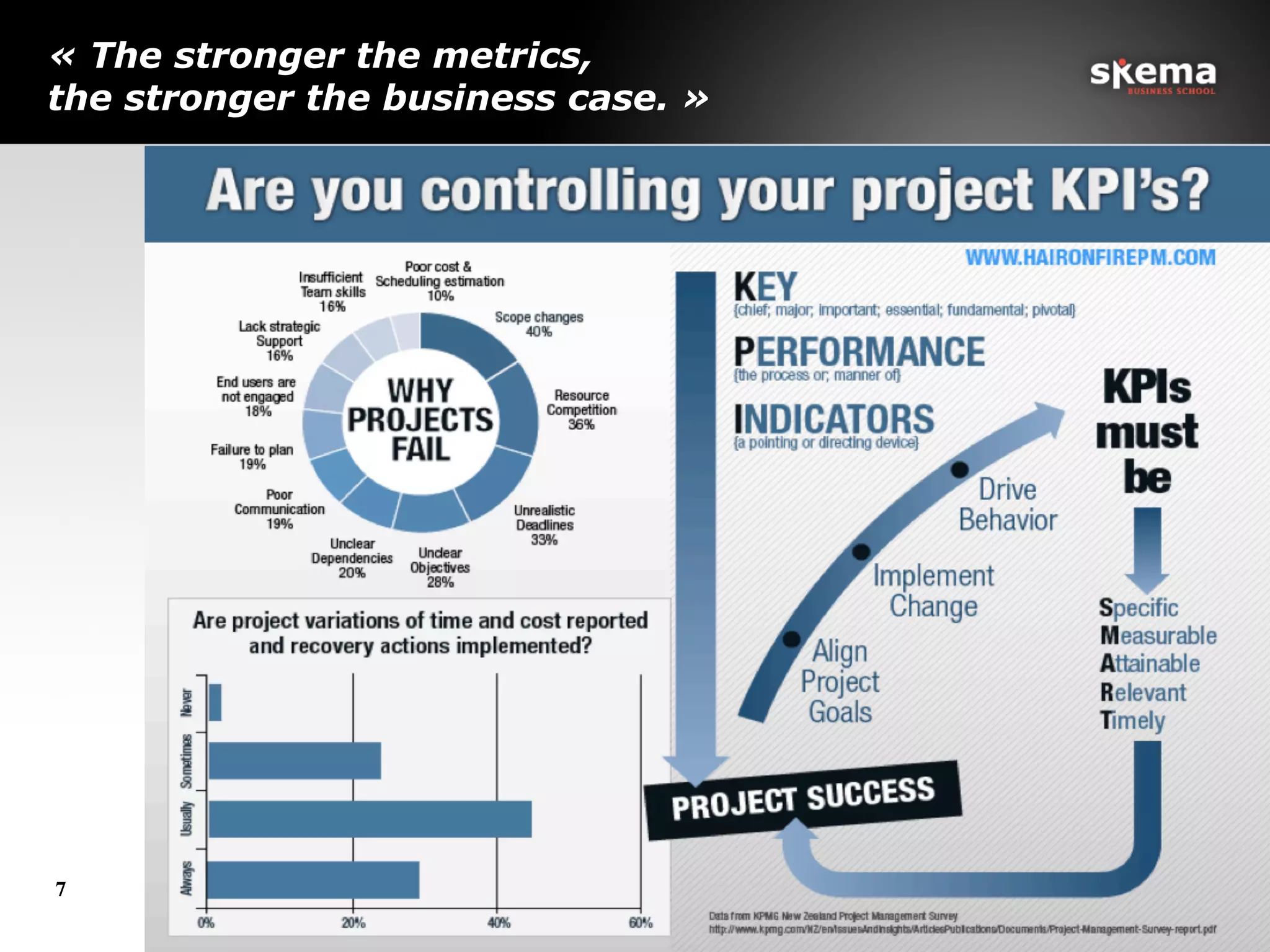
The document discusses the integration of sustainability into project performance measurement through the development of sustainable key performance indicators (KPIs). It outlines the importance of new metrics beyond traditional measures like cost and quality to assess project sustainability effectively. The conclusion emphasizes the need for a collaborative approach and new governance in project management to foster sustainability.