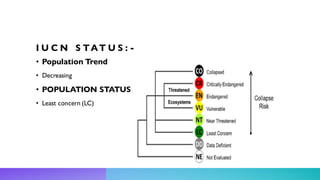
This document summarizes information about the Silver Pheasant bird species. It notes that the Silver Pheasant is found in forests of Southeast Asia, has a population status of least concern, and has a decreasing population trend. It provides details on the species' physical appearance, habitat, behavior, geographic distribution, diet, threats, and some interesting facts. For example, it states that the male is black and white while the female is mainly brown, they prefer forest edges with open areas, and their main threats are habitat degradation and loss.