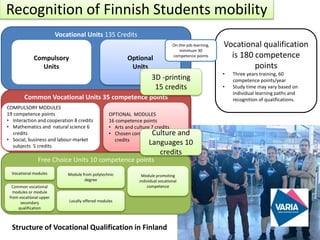
The document discusses ECVET (European Credit system for Vocational Education and Training) cooperation between Finland and South Korea. It explains that ECVET aims to facilitate student mobility across Europe and recognition of learning outcomes achieved abroad.
The ECVET process involves several steps before, during, and after student mobility. Before mobility, partners develop understanding through a Memorandum of Understanding to identify learning outcomes and discuss assessment. During mobility, students receive learning activities and assessment with results documented. After mobility, partners validate and recognize learning outcomes and evaluate the process.
As part of an ECVET project, Finland and South Korea implemented this process for welding and machinery qualifications. Finnish students' mobility periods were recognized as part of