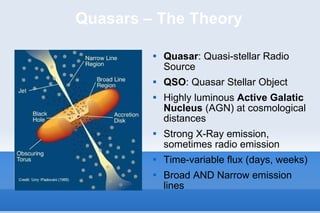
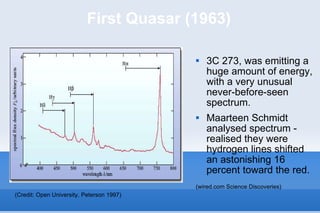
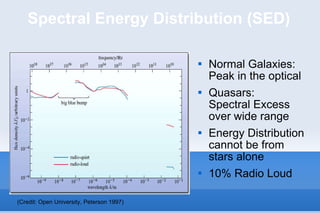
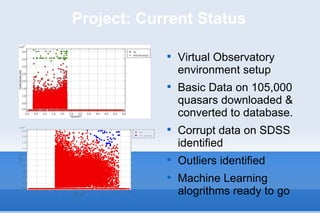
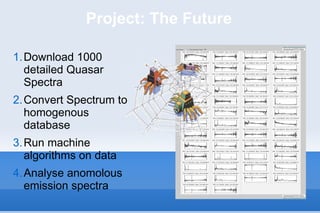
This document discusses the field of astroinformatics, which uses machine learning algorithms and computational tools to analyze large astronomy datasets. It summarizes that quasars are extremely luminous celestial objects located far from Earth that emit unusually large amounts of energy. The document also notes that analyzing detailed spectra of thousands of quasars using machine learning could help identify anomalous emission patterns. Finally, it predicts that astroinformatics will be crucial for making sense of the huge volumes of data that will be produced by next-generation telescopes.