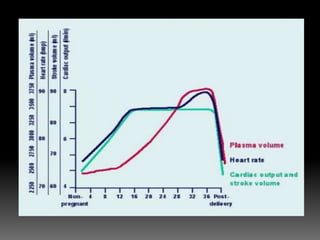
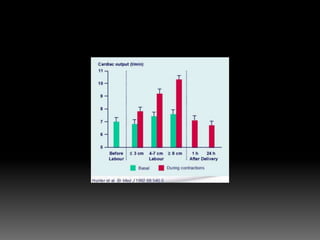
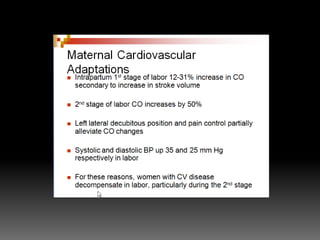
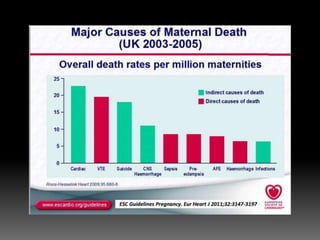
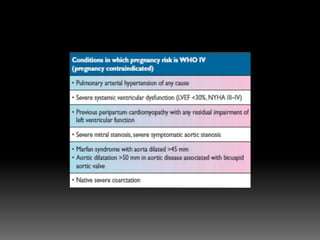
The document discusses various cardiovascular conditions and risks during pregnancy. It provides guidance on:
1) Conducting pre-pregnancy risk assessments for conditions like DVT, cardiomyopathy, and congenital heart disease.
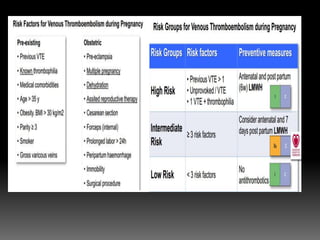
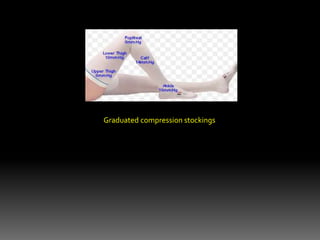
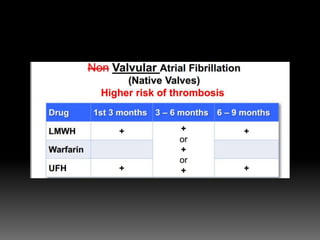
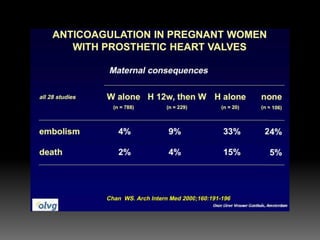
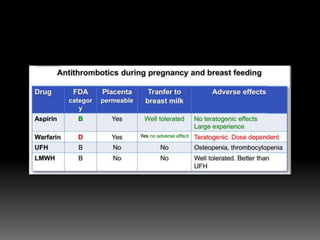
2) Managing risks of thromboembolism which increase during pregnancy. Low molecular weight heparin or compression stockings can help.
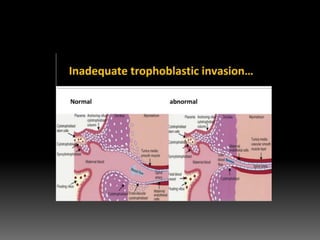
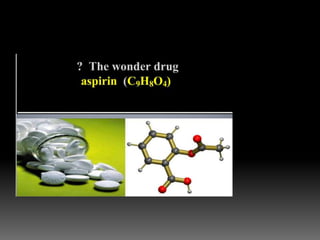
3) Administering low-dose aspirin before 16 weeks to reduce preeclampsia risk, especially for those with multiple risk factors.
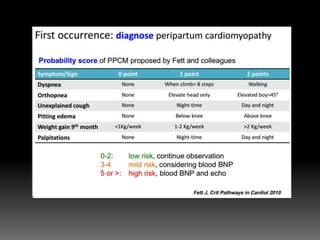
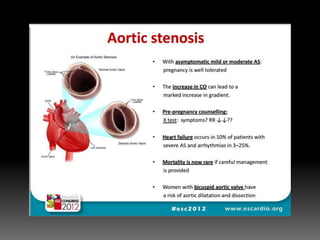
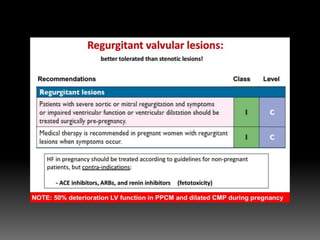
4) Evaluating dyspnea with BNP and echocardiography to identify valve lesions or heart failure.
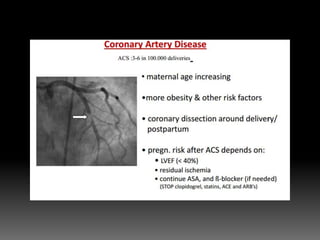
5) Exercising caution but not prohibiting pregnancy for conditions like CAD, with stress ech