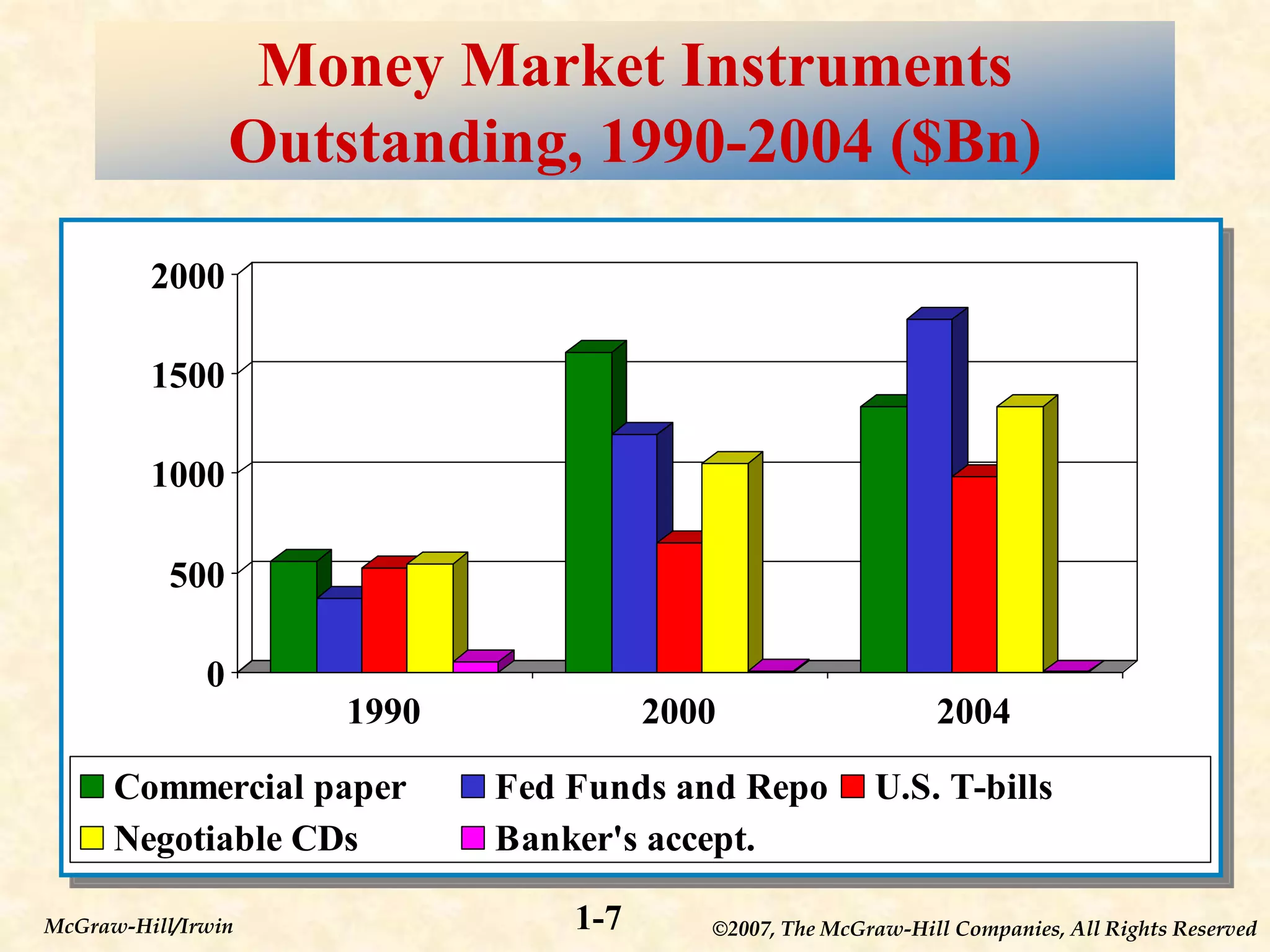
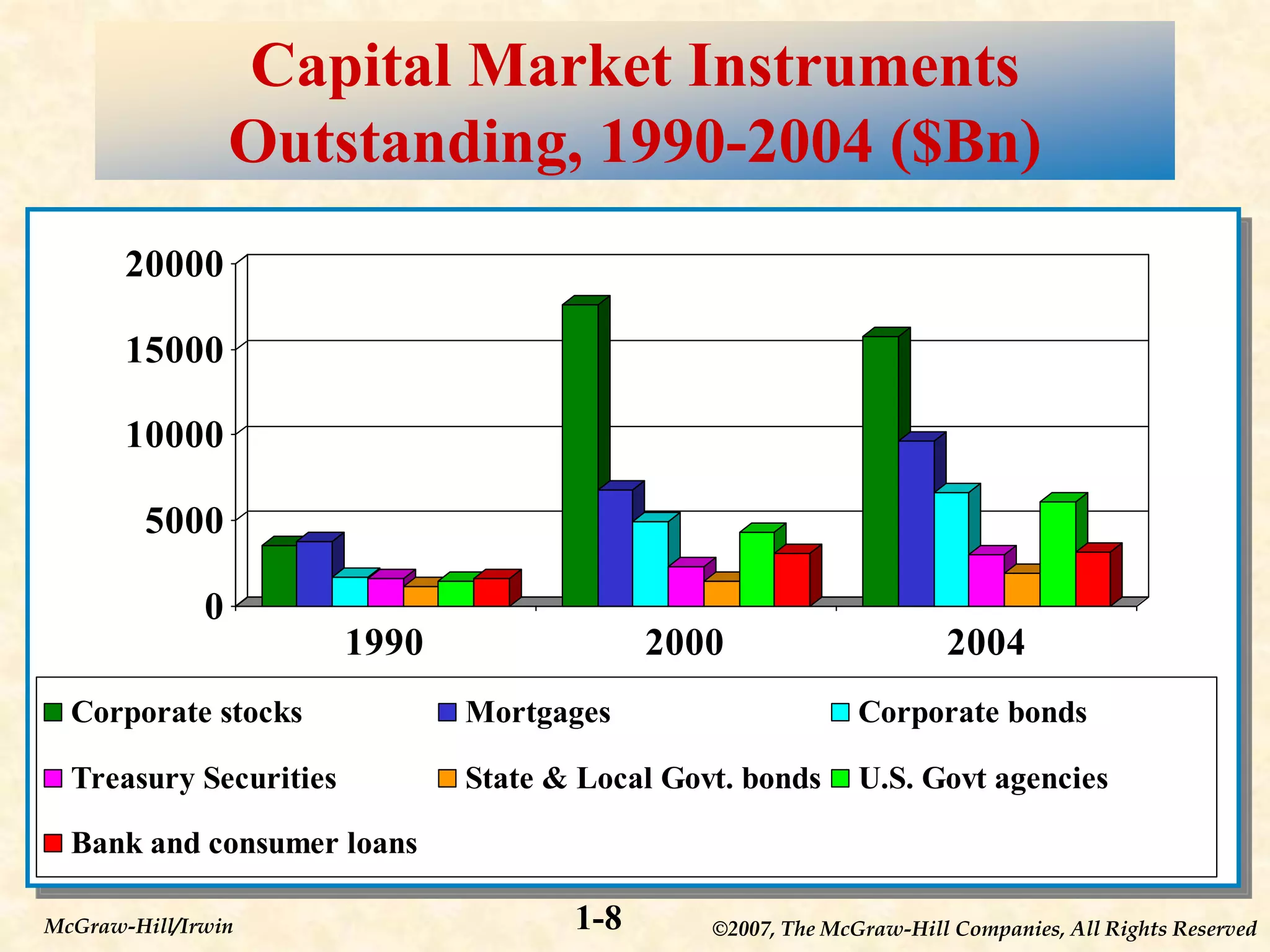
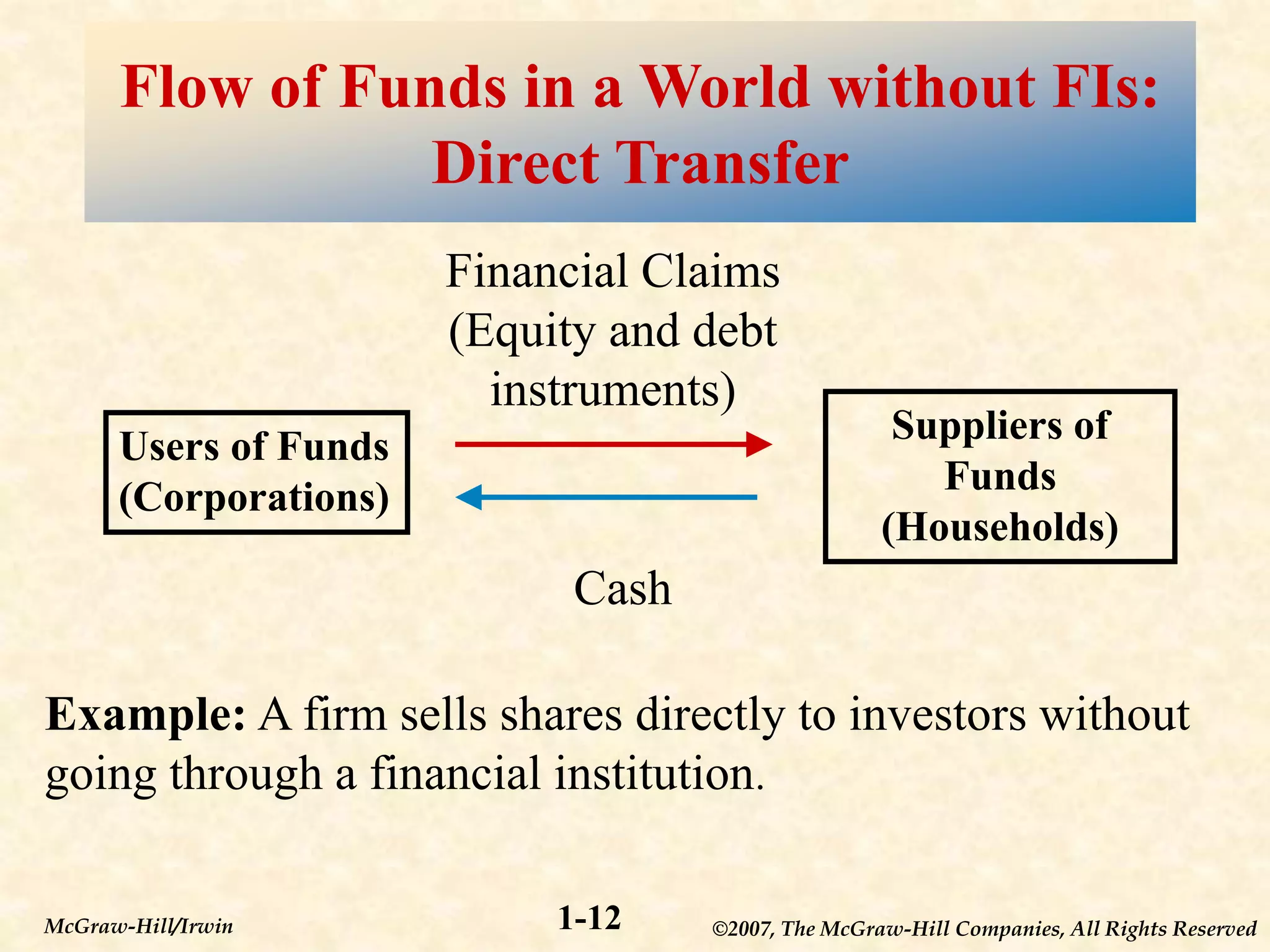
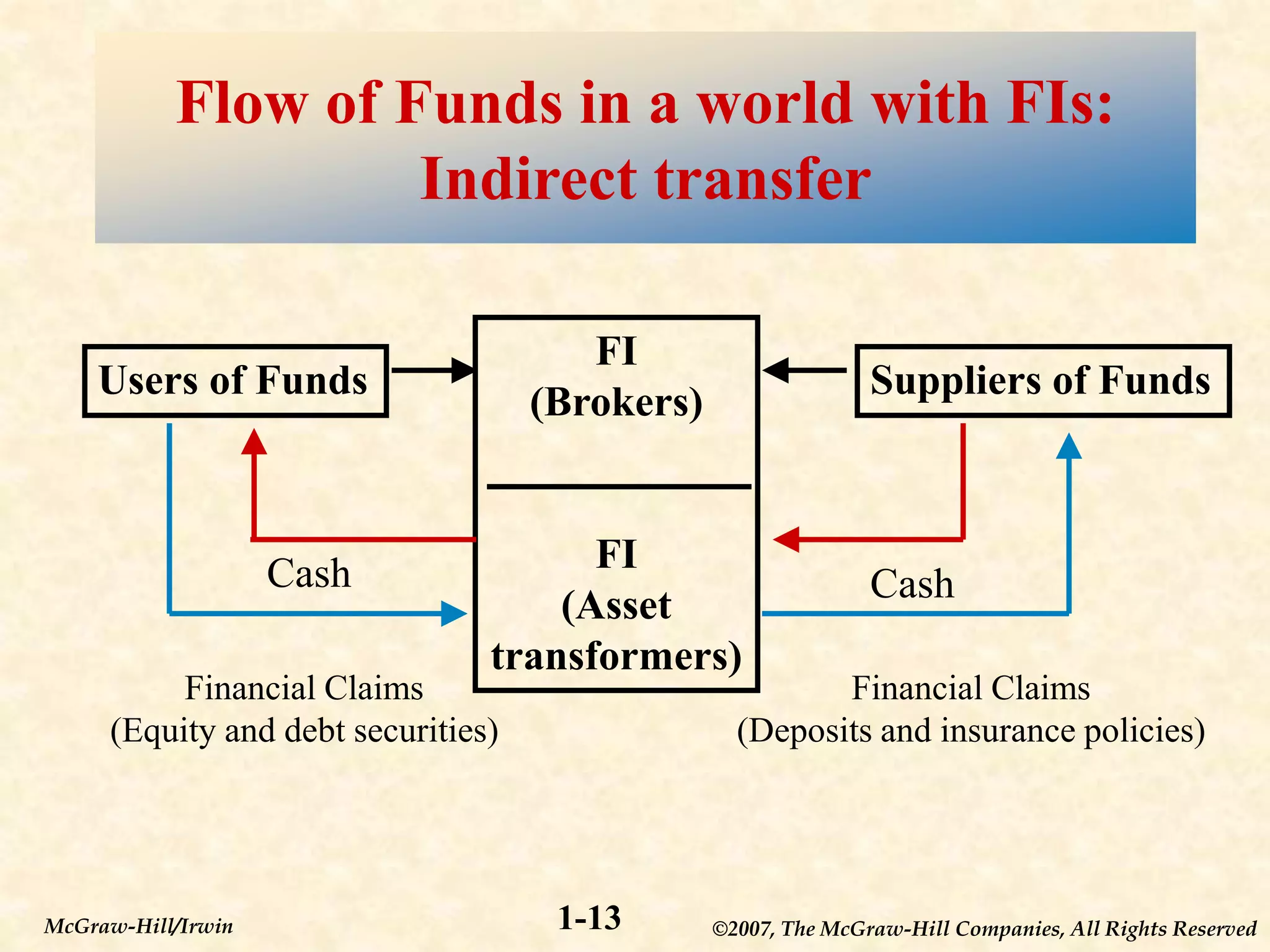
This document provides an overview of financial markets and institutions. It defines key terms like primary and secondary markets, money and capital markets, and different types of financial institutions. The document also discusses why these markets and institutions are important, as they allow individuals and organizations to invest or obtain financing, and help channel funds from savers to borrowers in the economy. Risks to these institutions are also covered.