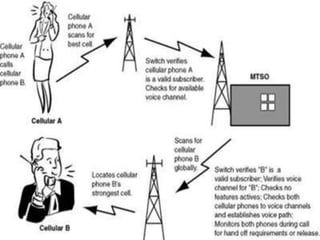
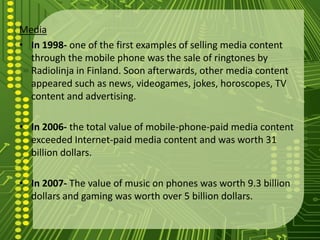
The document traces the evolution of cellphones from their early development in the 1950s to the present day. It discusses the progression from 1G analog networks to 2G digital networks to 3G and 4G networks utilizing increasing digital technologies and data capabilities. The document also outlines the impact of cellphones on society through their use in commerce, social connections, media, and both benefits and restrictions to health and privacy.