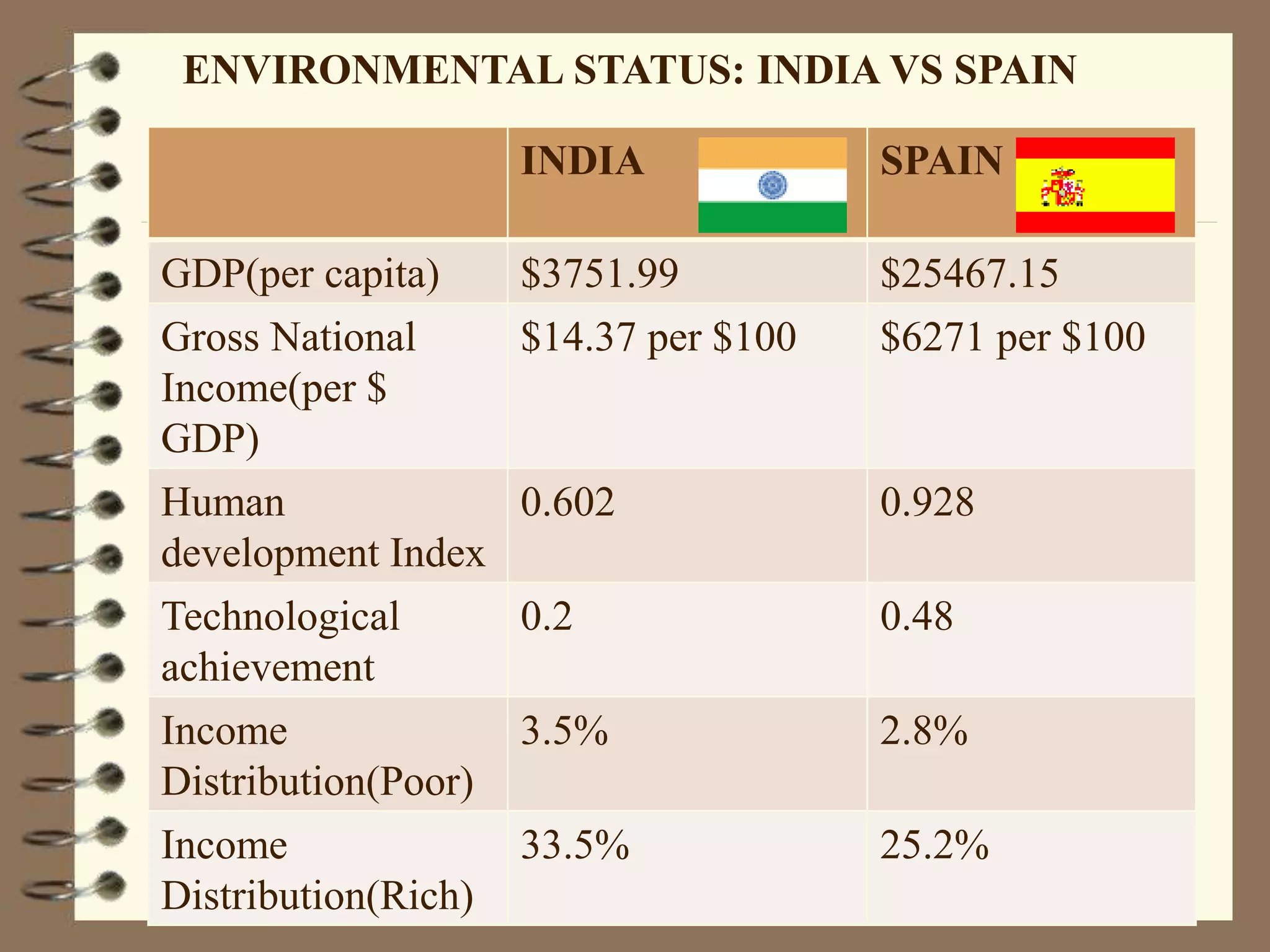
Spain is located on the Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe. It has a total area of 505,370 square kilometers and is bordered by Portugal, France, and the Mediterranean Sea. The country's terrain consists of mountainous central regions surrounded by coastal lowlands, with much of the population living in cities along the coast. Spain has a population of over 47 million people and its largest industries include tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing. Major environmental issues include pollution of the Mediterranean Sea and problems with water quality, supply, and pollution from various sources.