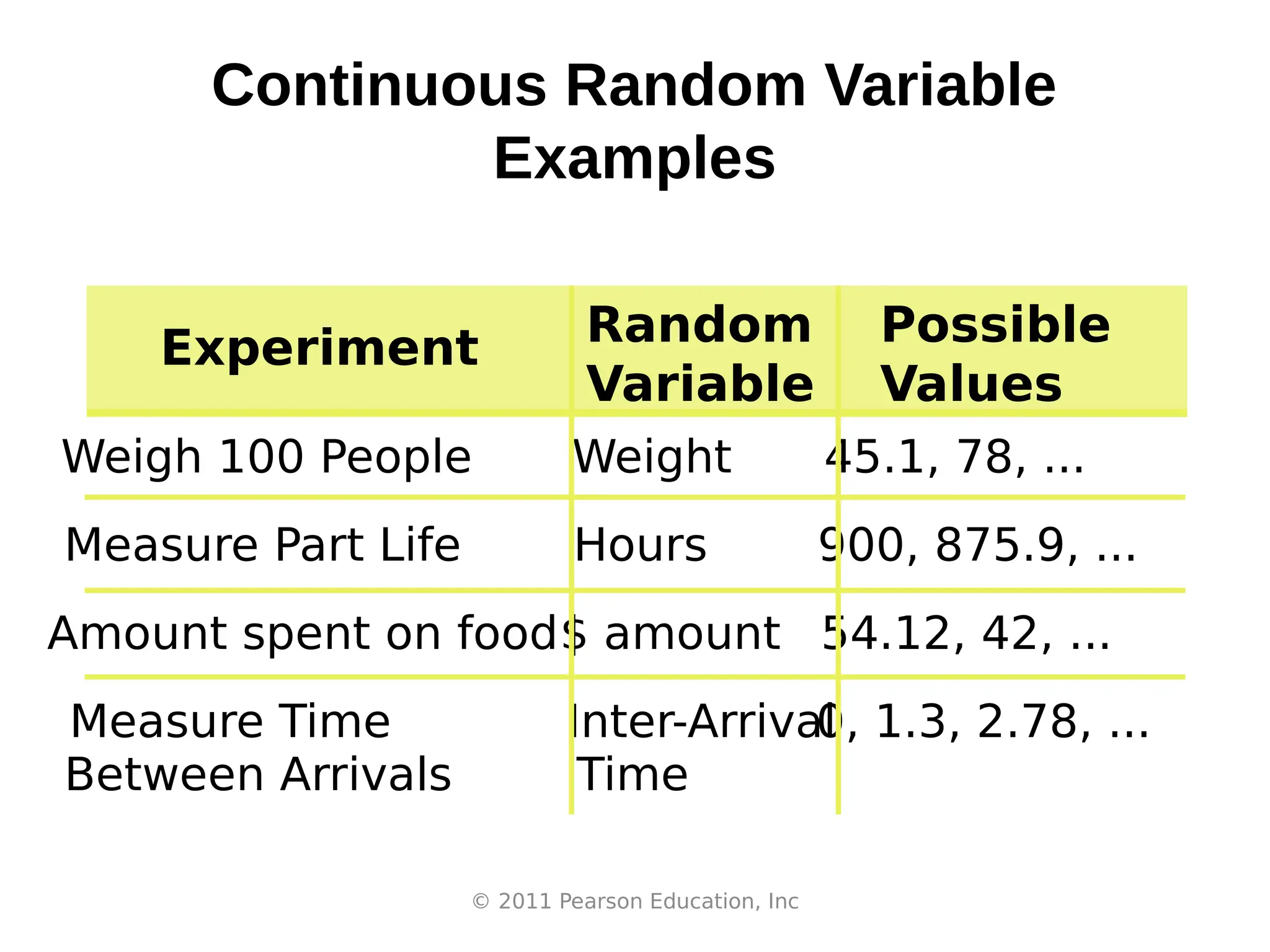
The document outlines a statistics and probability course, emphasizing the understanding of random variables, sampling techniques, hypothesis testing, and data analysis. It introduces two types of random variables: discrete, which assumes countable values, and continuous, which can take any value within an interval. Various examples and assessments guide students in classifying different types of variables.