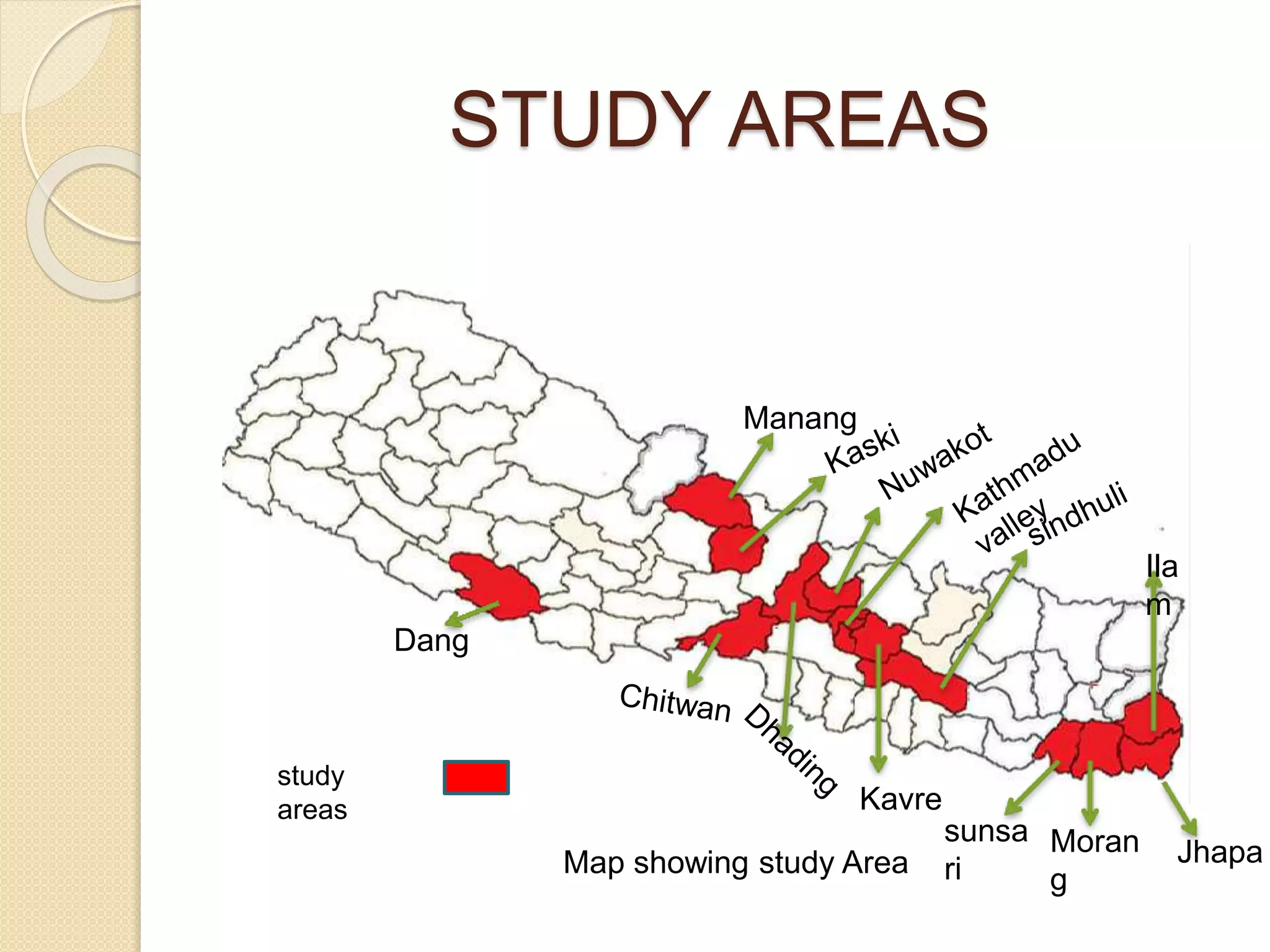
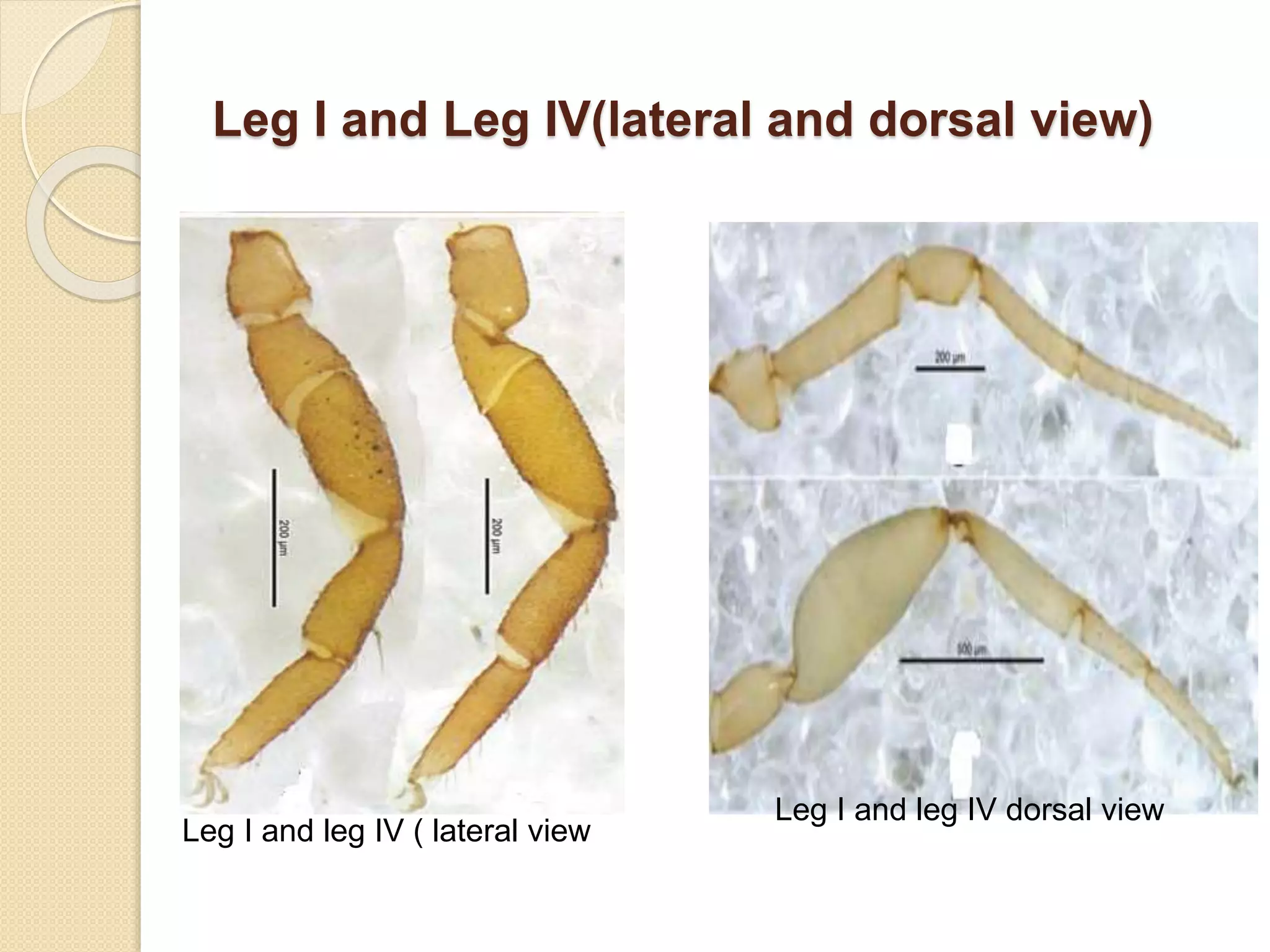
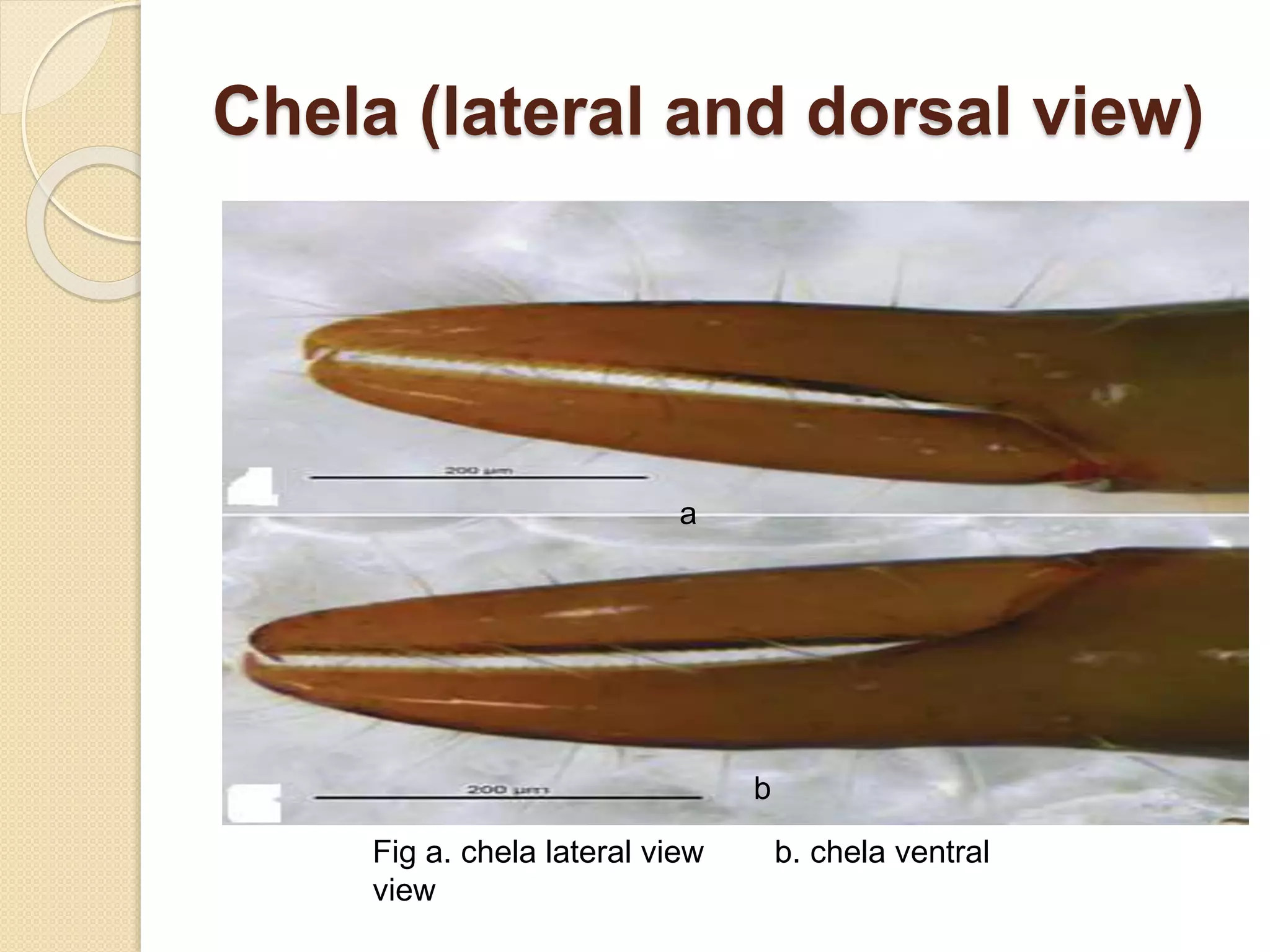
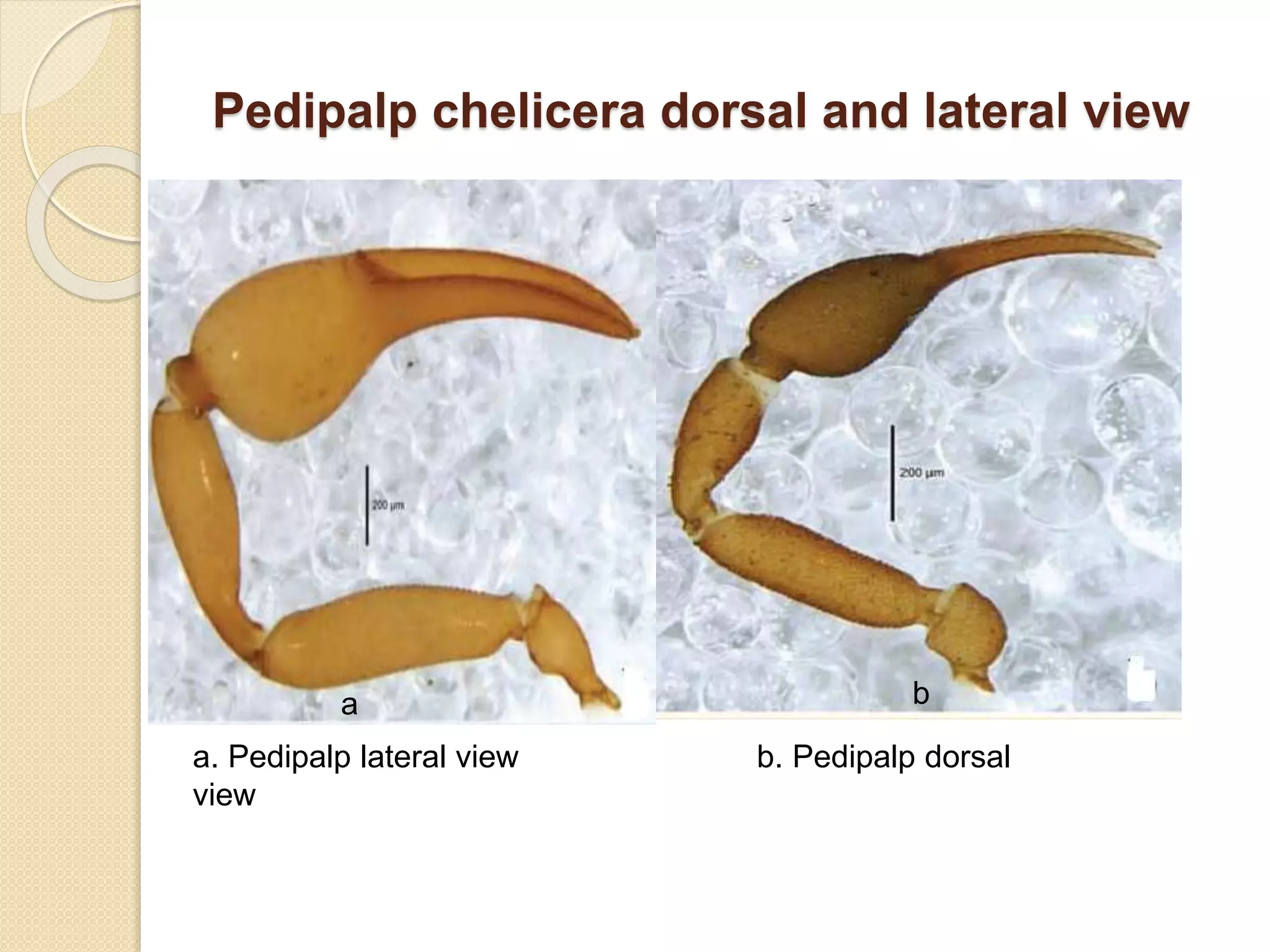
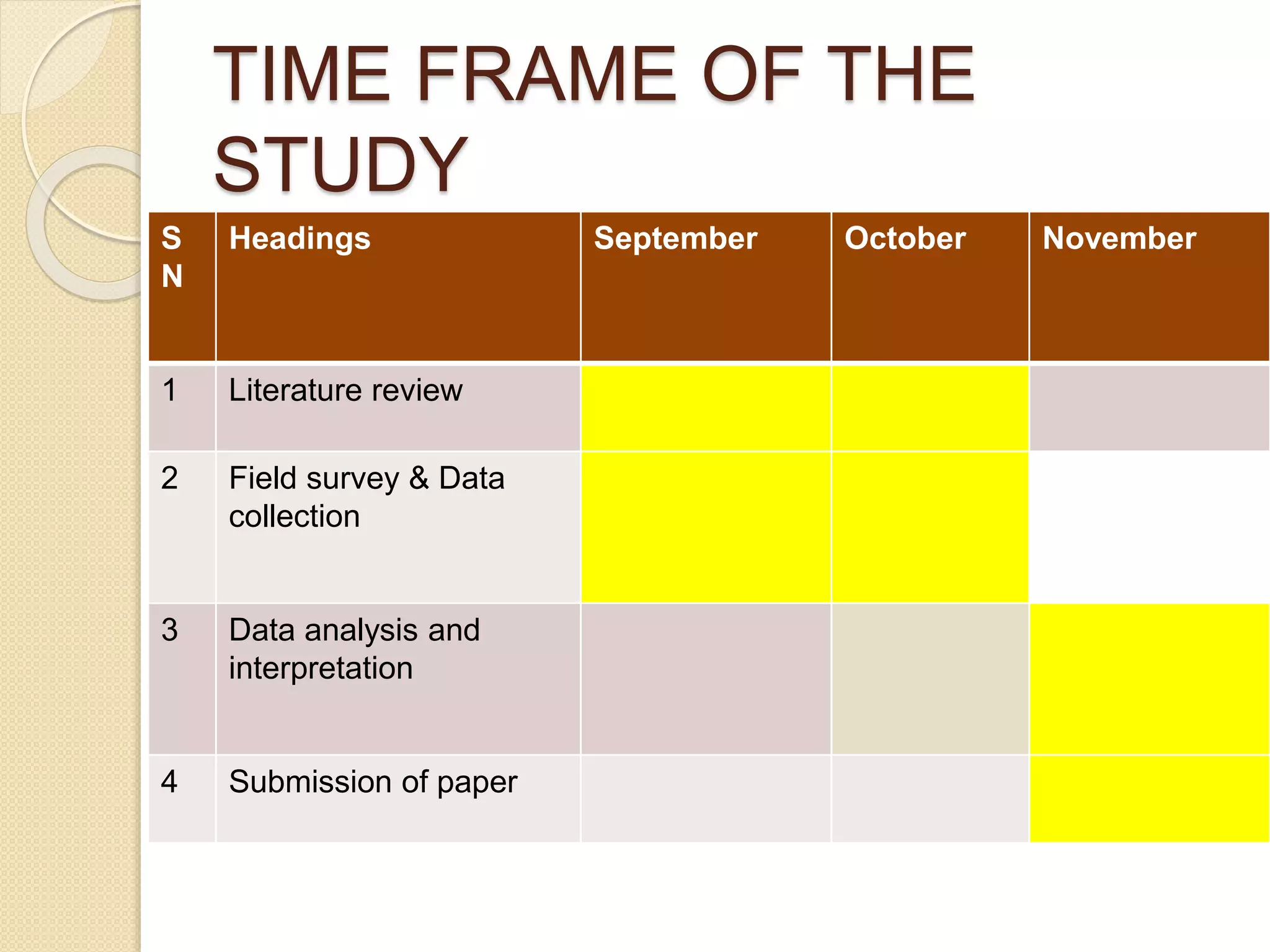
This document presents a study on the distribution of pseudoscorpions in honey bee colonies in Nepal. Pseudoscorpions are small arachnids that can be found in bee hives. The study aims to determine if pseudoscorpions associate symbiotically with honey bee colonies. Field surveys will be conducted at 15 districts across Nepal to search for pseudoscorpions in Apis cerena and Apis melifera hives. Any pseudoscorpions found will be collected and identified. The distribution patterns of pseudoscorpions in honey bee colonies across Nepal will be developed. The results of this study may show whether or not pseudoscorpions associate symbiotically with honey bee colonies.