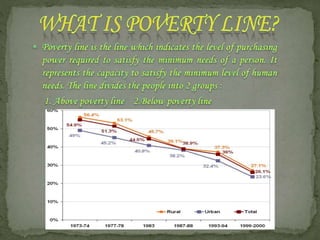
This document discusses poverty in India. It defines poverty as the inability to meet minimum living standards for health, food, and efficiency. The document outlines the poverty line in India and trends showing poverty has decreased but many remain in poverty. Causes of poverty include rapid population growth, lack of capital and jobs, agricultural issues, social factors like the caste system, and unequal distribution of resources. The government has implemented various measures to reduce poverty such as employment programs, programs to acquire productive assets like loans for small businesses, and other programs focused on basic needs, education, housing, and infrastructure development.