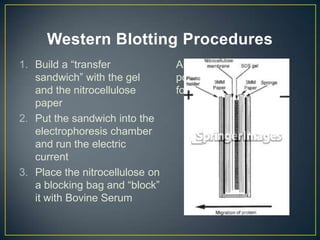
POU5F1 is a transcription factor required for embryo development. The document describes growing E. coli colonies at different pH levels to determine which pH produces the most authentic POU5F1 protein when used to express the POU5F1 gene. Western blotting was used to analyze protein expression, and showed that E. coli grown at pH 4.5 expressed the most POU5F1, near the expected molecular weight of 38,571 Da. Possible sources of error include incubating the nitrocellulose membrane for too long or incomplete washing of antibodies.