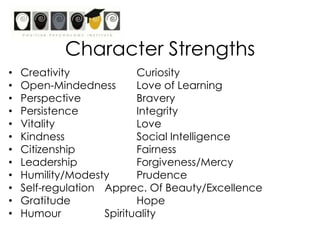
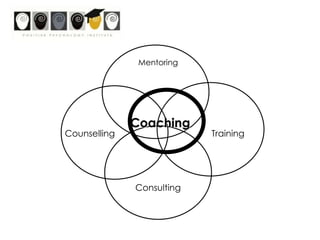
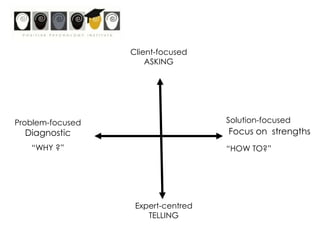
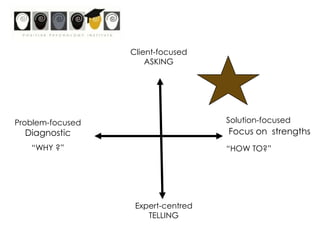
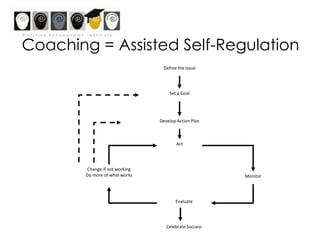
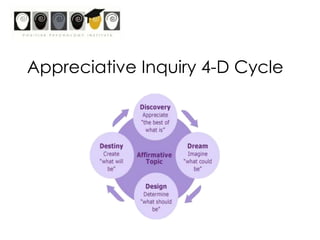
This workshop introduces school psychologists to the principles of Appreciative Inquiry and Positive Psychology. The workshop aims to help participants apply these principles to optimize their own functioning, their students' functioning, and their school. The workshop covers topics like character strengths, strengths-based approaches, and evidence-based coaching. It guides participants through an Appreciative Inquiry 4D cycle of Discovery, Dream, Design, and Deliver to help envision positive changes and develop plans to implement them. The overall goal is for school psychologists to learn how to incorporate Positive Psychology approaches into their work through strength-spotting, goal-setting, and collaborative team efforts.