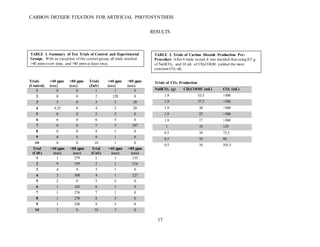
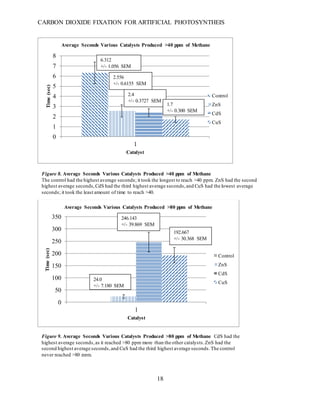
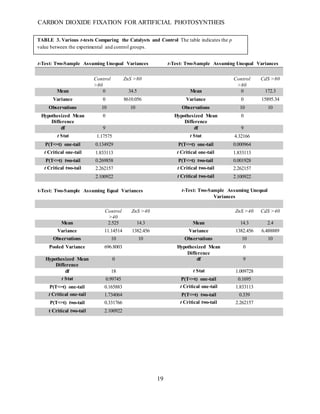
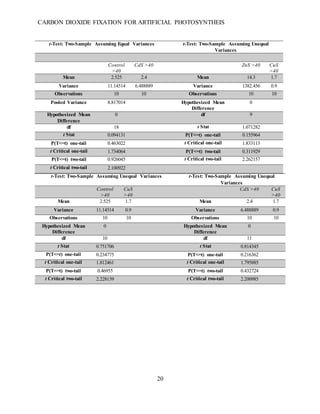
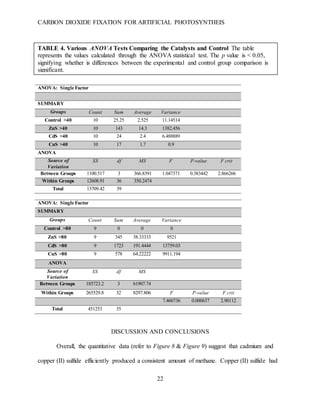
This document summarizes a student research project that aimed to develop a method for artificial photosynthesis to simultaneously reduce carbon dioxide levels and increase oxygen levels in the atmosphere. The student designed a solar-powered reaction using various sulfur-based catalysts (CdS, ZnS, CuS) to fix carbon dioxide into oxygen and methane through the reaction: CO2 + X + H2O → O2 + CH4, where X is the catalyst. Testing showed the production of methane was statistically significant, rejecting the null hypothesis. Therefore, the student concluded carbon fixation could produce both breathable oxygen and a renewable fuel source to address global warming. Further research is needed to harness the produced oxygen for industrial purposes.