This document provides an overview of polynomials including:
- Classifying polynomials by the number of terms they contain such as one term, two terms, etc.
- Defining monomials as numbers, variables, or products of numbers and variables and the degree of monomials and polynomials.
- Explaining how to order variables in ascending and descending order.
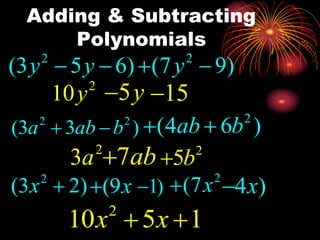
- Covering how to add, subtract, and multiply polynomials including examples of each operation.