The document discusses pointers in C++. It defines a pointer as a variable that holds the memory address of another variable. It provides examples of declaring and accessing variables using pointers, and demonstrates how to use pointers to change variable values, find the sum of array elements, calculate the square of a number, and swap two numbers. It also explains the difference between call by value and call by reference, and provides examples of functions that swap numbers using each approach.




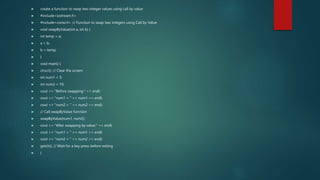
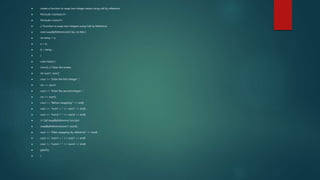
![ Write a C++ program to find the sum of elements in an array using pointer.
#include <iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main() {
clrscr(); // Clear the screen
int n;
cout << "Enter the number of elements in the array: ";
cin >> n;
if (n <= 0) {
cout << "Invalid input. Please enter a positive number of elements." << endl;
}
int arr[100]; // Assuming a maximum of 100 elements, adjust as needed
int *ptr = arr; // Pointer to the array
int sum = 0;
cout << "Enter the elements of the array:" << endl;
// Input the elements of the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> *ptr;
sum += *ptr;
ptr++;
}
cout << "Sum of elements in the array: " << sum << endl;
getch(); // Wait for a key press to close the console
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointer-240228183252-50165731/85/Pointers-in-c-programming-presentation-5-320.jpg)