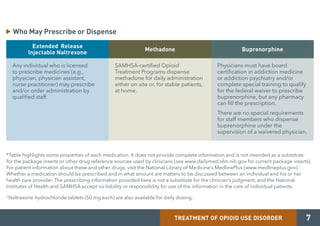
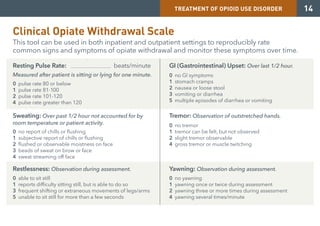
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is an effective response to opioid use disorder that combines medications with behavioral therapies. Nearly 80% of individuals with an opioid use disorder do not receive treatment. Screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment (SBIRT) can help identify substance use disorders and refer individuals to appropriate care. There are three medications approved for treating opioid use disorder - extended release injectable naltrexone, methadone, and buprenorphine. These medications work through different mechanisms but must be combined with counseling and social support for effective treatment.