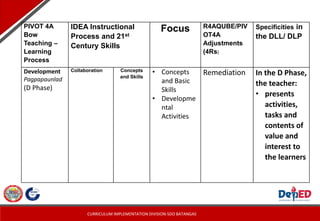
The document provides guidelines for teachers on developing PIVOT lesson exemplars using the IDEA framework. It outlines the key components of an exemplar, including objectives, content, learning resources, and procedures. The procedures section describes the four phases of instruction - introduction, development, engagement, and assimilation. Examples are provided for writing clear objectives and crafting activities for the different phases that develop 21st century skills. Overall, the document aims to guide teachers in creating student-centered exemplars aligned with the IDEA model for remote learning.