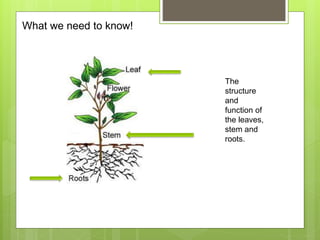
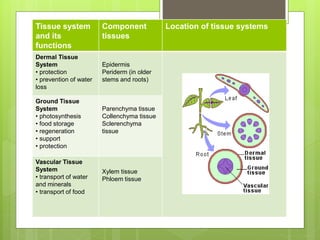
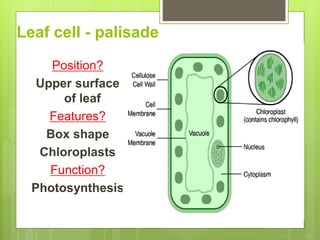
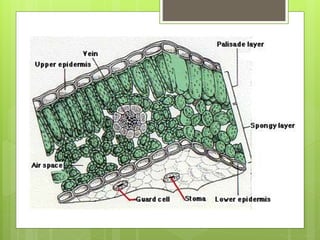
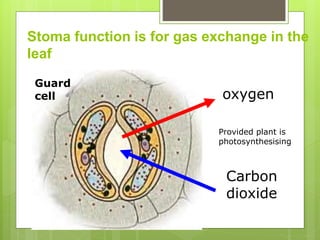
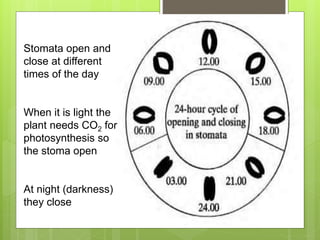
The document summarizes the structure and function of key plant tissues and organs involved in photosynthesis. It discusses the three main tissue systems - dermal, ground, and vascular - and key cell types like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. It focuses on the role of xylem and phloem in transporting water, minerals and glucose throughout the plant. Key plant organs like leaves, stems, and roots are also summarized. Leaves contain chloroplasts and stomata for gas exchange to facilitate photosynthesis. Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. The stem provides structure and uses xylem and phloem to transport throughout the plant.