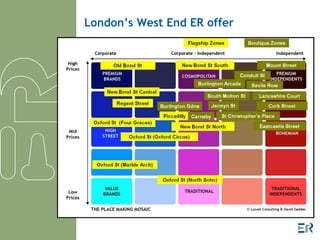
The document discusses experience retail as a key factor in attracting tourists, emphasizing the need for innovative and planned retail developments to enhance destinations. It explores how combining shopping with entertainment and leisure activities can increase footfall and spending in areas such as London's West End, Milan, and Dubai. The document outlines key lessons for tourism development, including the importance of a balanced mix of attractions and effective marketing strategies.