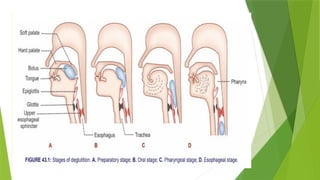
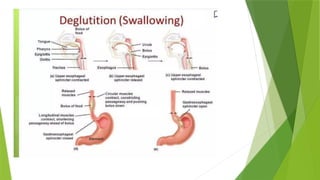
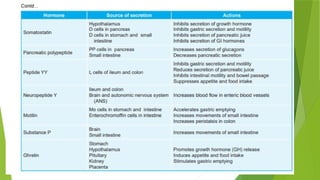
The document discusses the processes of digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the gastrointestinal tract. It outlines how carbohydrates are broken down into monosaccharides mainly in the jejunum and ileum, and how fats are digested with the help of pancreatic lipase and bile salts. Additionally, it describes the absorption mechanisms for these nutrients, including simple diffusion and active transport.