Digestive System of Non-Ruminant animals.pptx
- 1. Biochemistry of Digestion and Absorption of Feedstuffs in Non-Ruminants
- 2. Outline • Digestion and Absorption • Non-Ruminant digestion and Absorption parts and Functions • Non –Ruminant Carbohydrate Digestion • Absorption of Nutrients-CHO • Digestion of Proteins • Absorption of protein • Lipid Digestion • Absorption of Lipid • Summary
- 3. Digestion and Absorption The process of digestion includes: –The prehension of food or feed –The mechanical chewing and grinding –Mixing with digestive acids and enzymes to chemically break down feedstuffs The process of absorption includes: –Transport of the digested foods across the intestinal mucosa to the blood or lymph system
- 4. Non-Ruminant • Simple digestive system -Monogastric -Feed must be highly quality concentrates -Cannot digest large amounts of fiber Some examples are: Human Dogs Cats Pigs Poultry
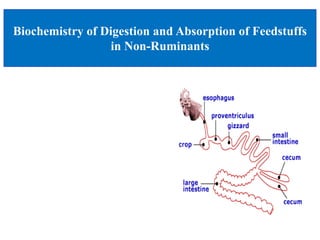
- 5. Non-ruminant digestive system • Mouth • Esophagus • Stomach - Enzymes acts on feed -Churns and mixes • Small intestine • Large intestine • Accessory System -Liver ( produces bile that acts on fat) -Pancreas(produces insulin) • Anus -End of the digestive tract
- 6. Non –Ruminant Carbohydrate Digestion Mouth: initial opening of alimentary canal Salivary Glands • secrete juices that contain enzymes to help break up the food Mastication • chewing, crushing, preparing food for swallowing Mouth Salivary amylase
- 7. Stomach • Stomach is extremely elastic bag • Acid and pepsin to unfold proteins • Extensive microbial populations to breakdown anaerobically ferment feed. Stomach
- 8. Continued…. • Pancreas Pancreatic amylase Hydrolyzes alpha 1-4 linkages Produces mono-saccharides , disaccharides and polysaccharides Major importance in hydrolyzing starch and glycogen to maltose Amylase Polysaccharides Disaccharides
- 9. Digestion in Small Intestine • Digestion mediated by enzymes synthesized by cells lining the small intestine (brush border) Brush Border Enzymes Disaccharides Mono-saccharides • Exception is β-1,4 bonds in cellulose
- 10. Digestion in Small Intestine Sucrose Glucose + Fructose Ruminants do not have sucrase Maltase Maltose Glucose + Glucose Lactase Lactose Glucose + Galactose Sucrase
- 11. Digestion in Large Intestine Large Intestine 3 Sections –cecum –colon –rectum •Active in water reabsorption •Secretion of some minerals •*Bacterial Fermentation*
- 12. Overview of CHO Digestion • Location Enzymes Form of Dietary CHO • Mouth Salivary Amylase Starch Maltose Sucrose Lactose • Stomach (amylase from saliva) Dextrin→ Maltose • Small Intestine Pancreatic Amylase Maltose Brush Border Enzymes Glucose Fructose Galactose + + + Glucose Glucose Glucose • Large Intestine None Bacterial Micro-flora Ferment Cellulose
- 13. Nutrient Absorption – CH0 • Active transport for glucose and galactose • Glucose and Galactose enter epithelial cells via - Sodium-linked secondary active transport across the apical membrane. • Facilitated transport for Fructose • The sugars exit the cells across the basolateral membrane by facilitated diffusion
- 14. Villi in the small intestine All the nutrients including carbohydrates must be come in contact with villi of small intestine to be absorbed. Munna
- 15. Carbohydrates uptake by small intestine Monosaccharides are mainly absorbed by the small intestine. Munna
- 16. Absorption Villi-expand absorptive surface Most nutrients absorbed here Nutrients move from the villi to the blood to be transported all over the body Absorption in Small Intestines
- 17. Absorption in Small Intestines • Mechanism of Absorption – Pores; carriers; pumps; pinocytosis (“drinking in”) • Not just a process of diffusion • Active “shuttle” transport • Pores are selective • Carriers are specific – Takes energy (kcal) for digestion • Dietary induced thermo genesis
- 18. Carbohydrates from small intestine to liver The absorption of monosaccharides from the small intestine to the liver via the portal vein is an essential step in our digestive process. The portal vein is a blood vessel that carries blood from the abdomen to the liver. The capillaries in the small intestine join to the portal vein, which transports mono saccharides directly to the liver. Munna
- 19. Selective carbohydrates absorption by liver Liver doesn't actively absorb nutrients like monosaccharides from the bloodstream. Instead, it selectively takes up nutrients, including monosaccharides, from the blood through specific transporters located on its cell membranes (hepatocytes). Munna
- 20. Carbohydrates absorption in large intestine • Almost all of the carbohydrates (95%), except for dietary fiber and resistant starches, are efficiently digested and absorbed into the small intestine. Some of the remaining indigestible carbohydrates are broken down by enzymes released by bacteria in the large intestine. • While the large intestine contributes a smaller percentage in absorption, the Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) it produces offer various health benefits, including promoting gut health and potentially protecting against certain diseases. Munna
- 21. Continued… • Limited absorption: Only a small amount of indigestible carbohydrates and resistant starches reach the large intestine. • Types of carbohydrates absorbed: Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced by gut bacteria fermenting these remaining carbohydrates are the main source of energy absorbed. • Mechanisms of absorption: SCFAs are directly absorbed into the epithelial cells of the colon and enter the bloodstream. Munna
- 22. Absorption from Large Intestines • Site of water, salt, vitamin absorption (leaving a mass in a semi-solid state) • Almost everything of nutritional value has been utilized by time it reaches the large intestines -- leaving only waste • Feces contains some water, dead intestinal cells, bacteria, non- absorbed remains of digestion • Helpful bacteria in the large intestine feed on the “leftovers” and make vitamins like vitamin K and B.
- 23. Digestion of proteins The protein load received by the gut is derived from two primary sources: o 70-100 g dietary protein, and o 35-200 g endogenous protein The latter either as secreted enzymes and proteins in the gut or from intestinal epithelial cell turnover In healthy adults, only 1-2 g nitrogen, equivalent to 6-12g protein, are lost in the feces on a daily basis Thus, the digestion and absorption of protein is extremely efficient
- 24. Digestion of proteins The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach, which secretes gastric juice, a unique solution containing hydrochloric acid and the pro-enzyme pep-sinogen: 1. Hydrochloric acid: Stomach acid is too dilute (pH 2-3) to hydrolyze proteins; however, the acid functions to kill some bacteria and to denature proteins, making them more susceptible to subsequent hydrolysis by proteases
- 25. Continued…. 2. Pepsin: This acid-stable endopeptidase is secreted by the serous cells of the stomach as an inactive zymogen (or pro-enzyme), pep- sinogen. Digestion of proteins by pancreatic enzymes On entering the small intestine, large polypeptides produced in the stomach by the action of pepsin are further cleaved to oligopeptides and amino acids by a group of pancreatic proteases These enzymes, like pepsin, are synthesized and secreted as inactive zymogens
- 26. Overview of protein digestion
- 27. Absorption of Protein Amino acids enter the absorptive epithelial cells via sodium-linked secondary active transport across the apical membrane. Amino acids are then transported across the basolateral membrane by facilitated diffusion
- 28. Absorption of Amino Acids Amino acids are absorbed from the lumen of the small intestine principally by semi- specific Na+-dependent transport proteins in the luminal membrane of the intestinal cell brush border, similar to that already seen for carbohydrate transport. Munna
- 29. Lipid Digestion Fat breakdown about 50 % of energy in liver, kidney and skeletal muscles up to 95 % of energy cardiac muscle Fats are the major source of energy for fasting animal organism in diabetes Digestion – Mainly occur in small intestine. Enzyme – pancreatic lipase. Lipase catalyzes hydrolysis at the C1 and C3 positions of TGs producing free fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerol.
- 30. DIGESTION OF DIETARY LIPIDS
- 31. Lipid Digestion: Sites and Enzymes Sites: • The stomach • The small intestine Enzymes: 1. Act in stomach: Mouth: Lingual lipase Stomach: Gastric lipase 2. Act in small intestine: Pancreatic enzymes Lipase and co-lipase Cholesterol esterase Phospholipase A2 Lysophospholipase
- 32. Hormonal control of digestion in small intestine The digestion in small intestine is hormonally controlled. Two small peptide hormones are released from cells of the upper part of small intestine: 1. Cholecystokinin (CCK) 2. Secretin
- 33. Hormonal control of digestion in small intestine • Cholecystokinin (CCK): 1. Secretion of pancreatic enzymes 2. Bile secretion 3. Slow release of gastric contents • Secretin: 1. Release of watery solution 2. Rich in bicarbonate by pancreas
- 34. Fatty acids and monoglycerides enter the enterocytes by simple diffusion. Inside the enterocytes the molecules are reassembled into triglycerides and are packaged into large particles called chylomicrons. The chylomicrons are secreted across the basolateral membrane by exocytosis. The chylomicrons enter the lymphatic capillaries. The flow of lymphatic fluid carries the chylomicrons to the bloodstream Absorption of Lipid
- 35. Continued… • Lipids within the digestive system will tend to hydrophobically aggregate to form large fat globules. • Bile salts, secreted from the gall bladder, emulsify these fat globules and break them up into smaller droplets. • Hydrolytic enzymes called lipases then digest the fats into their component parts. • When the fatty acids are absorbed into the epithelial cells of the intestinal lining, they are combined to form triglycerides. • The triglycerides are combined with proteins inside the Golgi apparatus to form chylomicrons. Munna
- 36. Continued… Munna
- 37. Absorption of vitamins • Vitamins are organic molecules necessary for normal metabolism in animals, but either are not synthesized in the body or are synthesized in inadequate quantities and must be obtained from the diet. Essentially all vitamin absorption occurs in the small intestine. • Most water soluble vitamins are available for intestinal absorption from two sources: 1) the diet, and 2) synthesis by microbes in the large intestine or, in the case of ruminants, the rumen. Munna
- 38. Continued.… • The fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K are absorbed from the intestinal lumen using the same mechanisms used for absorption of other lipids. • In short, they are incorporated into mixed micelles with other lipids and bile acids in the lumen of the small intestine and enter the enterocyte largely by diffusion. • Within the enterocyte, they are incorporated into chylomicrons and exported via exocytosis into lymph. Munna
- 39. Absorption of Minerals • Mineral absorption is normally proportional to dietary intake • The vast bulk of mineral absorption occurs in the small intestine. • Minerals are clearly required for health, but most also are quite toxic when present at higher than normal concentrations. • The small intestine, with its villi and intricate epithelial cell lining, serves as the main stage for mineral absorption. Each mineral has its own unique entrance strategy, a testament to the exquisite adaptability of the bodies. Munna
- 41. Absorption of Water The specific mechanisms animals use to absorb water differ depending on their physiology and environment: • Intestinal absorption: Similar to humans, many animals absorb water through their intestines. The small intestine in particular is equipped with specialized cells and transporters that facilitate water uptake. • Skin absorption: Amphibians like frogs and toads are masters of skin absorption, drawing water directly through their permeable skin. Some reptiles also utilize skin absorption to a lesser extent. Munna
- 42. • Cloacal reabsorption: Birds excrete a concentrated form of urine and feces combined, called a cloaca. In many birds, the cloaca reabsorbs water from this waste before expulsion, maximizing water conservation. Continued.… Munna
- 43. Summary of Digestion & Absorption in Non-Ruminant • Consists of starches , glycogen, sucrase, lactose , glucose , fructose • Polysaccharides broken down to mono-saccharides • Mono-saccharides taken up by active transport or facilitated diffusion and carried to liver. • Glucose is transported to cells requiring energy. • Dietary lipids are relatively hydrophobic • Lipid digestion begins in stomach • Emulsification of lipids occurs in duodenum, helped by peristalsis and bile salts
Editor's Notes
- This slide is Digestion and absorption of non ruminant animal. The term Prehension: to take into the mouth .
- Non-ruminants are also called "monogastrics"--animals with a single-compartment stomach. (Ruminant stomachs have four compartments.) Examples of mongastric animals are humans, primates, swine, dogs, cats, and even horses.
- These are the main parts of non ruminant digestive systems. these are Mouth , esophagus , stomach, SI, LI .
- Breaks starches down to maltose and Salivary amylase enzyme are present in this system Plays only a small role in breakdown because of the short time food is in the mouth Ruminants do not have this enzyme
- Than this is the part of CHO digestion .Stomach is extremely elastic bag. Gastric Gland are present in stomach wall. Pepsin , Renin , and gastric lipase are present in Gastric juice. Gastric lipase begins the digestion of fat.
- Pancreas is a leaf like digestive system . It secrets pancreatic amylase .Maltase – specifically removes a single glucose from the no reducing end of a linear a1-4 glucose chain…breaking down maltose into glucose. (exosaccharidases)
- Than digestion in SI and Digestion mediated by enzymes synthesized by cells lining the small intestine (brush border enzymes).
- Continue this slide and sucrose , Maltose , lactose are breakdown into digestion of SI.
- It consists of the Cecum , colon , Rectum and Anus. No enzyme secretion in large Intestine.
- Lumen: This is the hollow space inside the small intestine, surrounded by the villi. Think of it as a narrow tunnel lined with these finger-like projections, where the magic of digestion and absorption takes place. The lumen serves as the passageway for digested food, a rich concoction of broken-down carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. This "nutrient soup" bathes the villi, allowing them to readily access and absorb the dissolved molecules. Lacteals: These are blind-ended lymphatic vessels located at the core of each villus. Lacteals are responsible for absorbing fatty acids and glycerol, the building blocks of fats, from the digested food in the intestinal lumen. After being absorbed, these molecules are packaged into chylomicrons, lipoprotein particles that help transport fats via the lymphatic system to the bloodstream. Capillary Bed: A dense network of tiny blood vessels crisscrosses throughout the villus, forming a miniature transportation system. Think of it as a web of miniature highways ready to ferry the absorbed nutrients to their destinations. The capillary bed absorbs sugars, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals from the epithelial cells lining the villi. These molecules then hop onto the blood vessels and get whisked away to various tissues and organs throughout the body for utilization.
- Glucose and galactose are taken up by the sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1, active carrier transport). Fructose is taken up by facilitated diffusion through glucose transporter (GLUT) 5. There are 12 glucose transporters that are named GLUT 1-12, and all use facilitated diffusion to transport monosaccharides. Monosaccharides, inside the enterocyte ( Intestinal absorptive cells, these are simple columnar epithelial cells that line small intestines), all three are then transported out of the enterocyte into the capillary (absorbed) through GLUT2.
- Most absorption takes place in the small intestine. Small intestine’s inner surface looks smooth, but viewed through a microscope, it turns out to be wrinkled into hundreds of folds. Each fold is covered with thousands of fingerlike projections called villi. A single villus, magnified still more, turns out to be composed of several hundred cells, each covered with microscopic hairs called microvilli. Absorptive system Once a molecule has entered a cell in a villus, the next step is to transmit it the bloodstream and the lymphatic system. Both systems supply vessels to each villus. Through these vessels, the nutrients leave the cell and enter either the lymph or the blood. In either case, the nutrients end up in the blood. The water- soluble nutrients (and the smaller products of fat digestion) are released directly into the bloodstream by way of the capillaries, but the larger fats and the fat-soluble vitamins find direct access into the capillaries impossible because these nutrients are insoluble in water (and blood is mostly water). They require some packaging before they are released. The intestinal cells assemble the products of fat digestion into larger molecules called triglycerides, which then packaged for transport. They cluster together with special proteins to form chylomicrons, one kind of lipoproteins. Finally, the cells release the chylomicrons into the lymphatic system.
- Monosaccharides (primarily glucose, fructose, and galactose) are absorbed from the small intestine into the bloodstream via the hepatic portal vein. The hepatic portal vein directly transports this nutrient-rich blood to the liver. Hepatocytes have specific transporters on their surface membrane that bind to different monosaccharides. Glucose, the main energy source for most cells, utilizes GLUT2 transporters for preferential uptake into the liver. Fructose and galactose use different transporters (GLUT5 and GLUT8, respectively) and undergo dedicated metabolic pathways within the liver.
- The protein load received by the gut is derived from two primary sources: thease are 70-100 g dietary protein, and 35-200 g endogenous protein. Than In healthy adults, only 1-2 g nitrogen, equivalent to 6-12g protein, are lost in the feces on a daily basis. Digestion of proteins by pancreatic enzymes.
- The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach, which secretes gastric juice, a unique solution containing hydrochloric acid and the proenzyme pepsinogen.
- Than Pepsinogen (MW=40,000) is activated by the enzyme and pepsin present already in the stomach and the stomach acid. Pepsinogen cleaved off to become the enzyme pepsin (MW=33,000) and a peptide fragment to be degraded. Pepsin partially digests proteins by cleaving the peptide bond formed by aromatic amino acids: Phe, Tyr, Trp
- Amino acids are then transported across the basolateral membrane by facilitated diffusion.
- As these protein fragments flood the intestinal lumen, specialized enzymes like trypsin and chymotrypsin meticulously break them down into individual amino acids. These free amino acids, eager to find their new homes, have different ways to enter the enterocytes: Cotransport with Sodium: Like savvy shoppers using conveyor belts, some amino acids hitch a ride with sodium ions through specific transporters. This "sodium-coupled cotransport" ensures efficient uptake against the concentration gradient. Facilitated Diffusion: Other amino acids, smaller and nimbler, take a more leisurely route. They pass through dedicated transporters like GLUTs, navigating the membrane like expert shoppers browsing for the perfect fit. Active Transport: Some rarer amino acids require a more exclusive entrance. Using pumps powered by ATP, the energy currency of cells, they are actively transported against the concentration gradient, ensuring no valuable molecule is left behind.
- This slide is the lipid digestion . Triacylglycerols (TGs) and glycogen - two major forms of stored energy. TGs which are more efficient energy stores because: (1) They are stored in an anhydrous form (2) Their fatty acids are more reduced than monosaccharides
- Digestion – Mainly occur in small intestine. Enzyme – pancreatic lipase. Lipase catalyzes hydrolysis at the C1 and C3 positions of TGs producing free fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerol
- Fatty acids and monoglycerides enter the enterocytes by simple diffusion. Inside the enterocytes the molecules are reassembled into triglycerides and are packaged into large particles called chylomicrons. The chylomicrons are secreted across the basolateral membrane by exocytosis.
- Chylomicrons are released from the epithelial cells and are transported via the lacteals to the liver. While in the liver, chylomicrons may be modified to form a variety of lipoproteins. Low density lipoproteins will transport lipids via the bloodstream to cells. High density lipoproteins will scavenge excess lipids from the bloodstream and tissues and return them to the liver.
- Active Transport: Sodium, potassium, calcium, and iron, the VIPs of the mineral world, often require active transport. Imagine tiny pumps, fueled by ATP, pushing these minerals uphill against the concentration gradient, ensuring their delivery even when numbers are scarce. Channel-mediated diffusion: Some minerals, like chloride and magnesium, find their way through dedicated channels in the cell membrane, like guests with special passes to a VIP lounge. Carrier-mediated diffusion: Other minerals, like zinc and copper, rely on specific carrier proteins that bind them and ferry them across the membrane, ensuring selective passage and efficient uptake.
- Absorption and excretion of water. If the Daily Meal (DM) contains 5.0 kg of water, the small and large intestines will absorb a large amount of this water (approximately 4.5 kg), and only a small amount of water (0.5 kg) will be excreted from the body with feces.
- Now summary of digestion and absorption in non-ruminant.
- That’s all about me. Thank you very much for your patience.