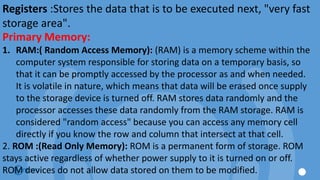
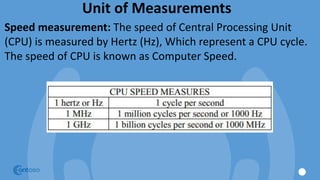
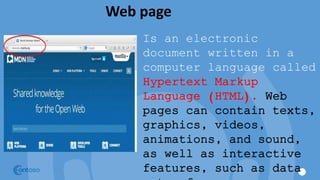
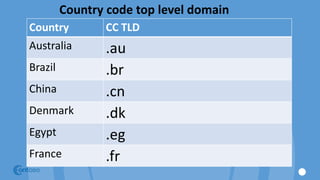
The document outlines the principles and structure of Don Bosco Technical Institute in Victorias, emphasizing a blend of spiritual guidance and technical education. It provides details on computer lab rules, computer components, functionalities, and the history and evolution of computers, along with an overview of software types and internet navigation. The document serves as an introductory guide to understanding computers, their components, and their applications in modern society.