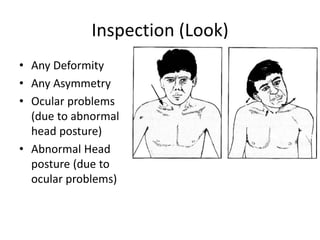
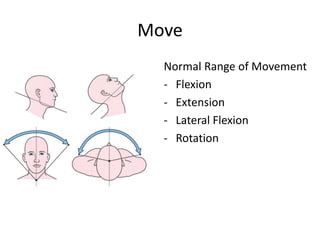
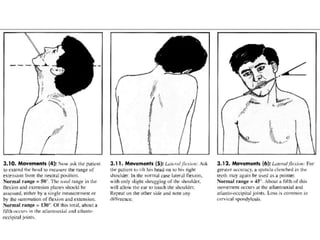
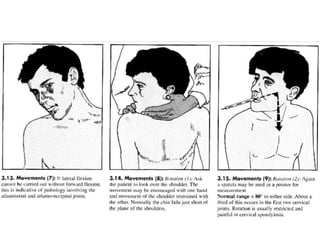
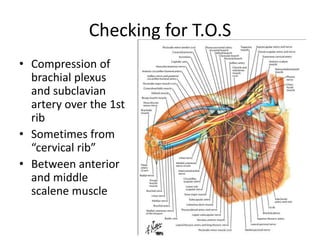
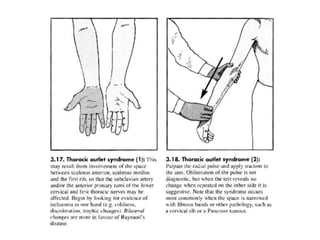
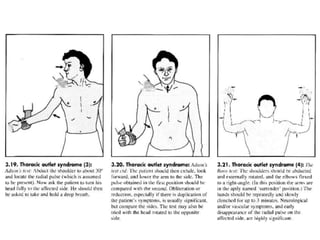
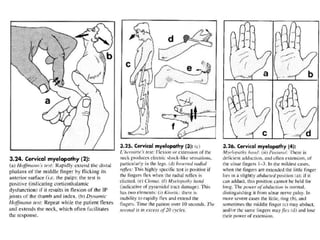
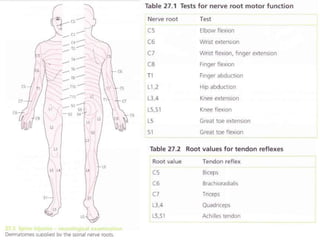
This document provides information on performing a physical examination of the cervical spine (neck). It lists the most common symptoms as pain, stiffness, deformity, numbness/tingling in the upper limbs, headache, and tension. Common neck problems mentioned include torticollis, cervical spondylosis, spinal stenosis, and myelopathy. The physical examination involves inspection for deformities, asymmetry, and head posture, palpation of the neck in prone or sitting positions, and assessing the range of motion through flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation. Special tests check for issues like foraminal compression, cord compression, and thoracic outlet syndrome.