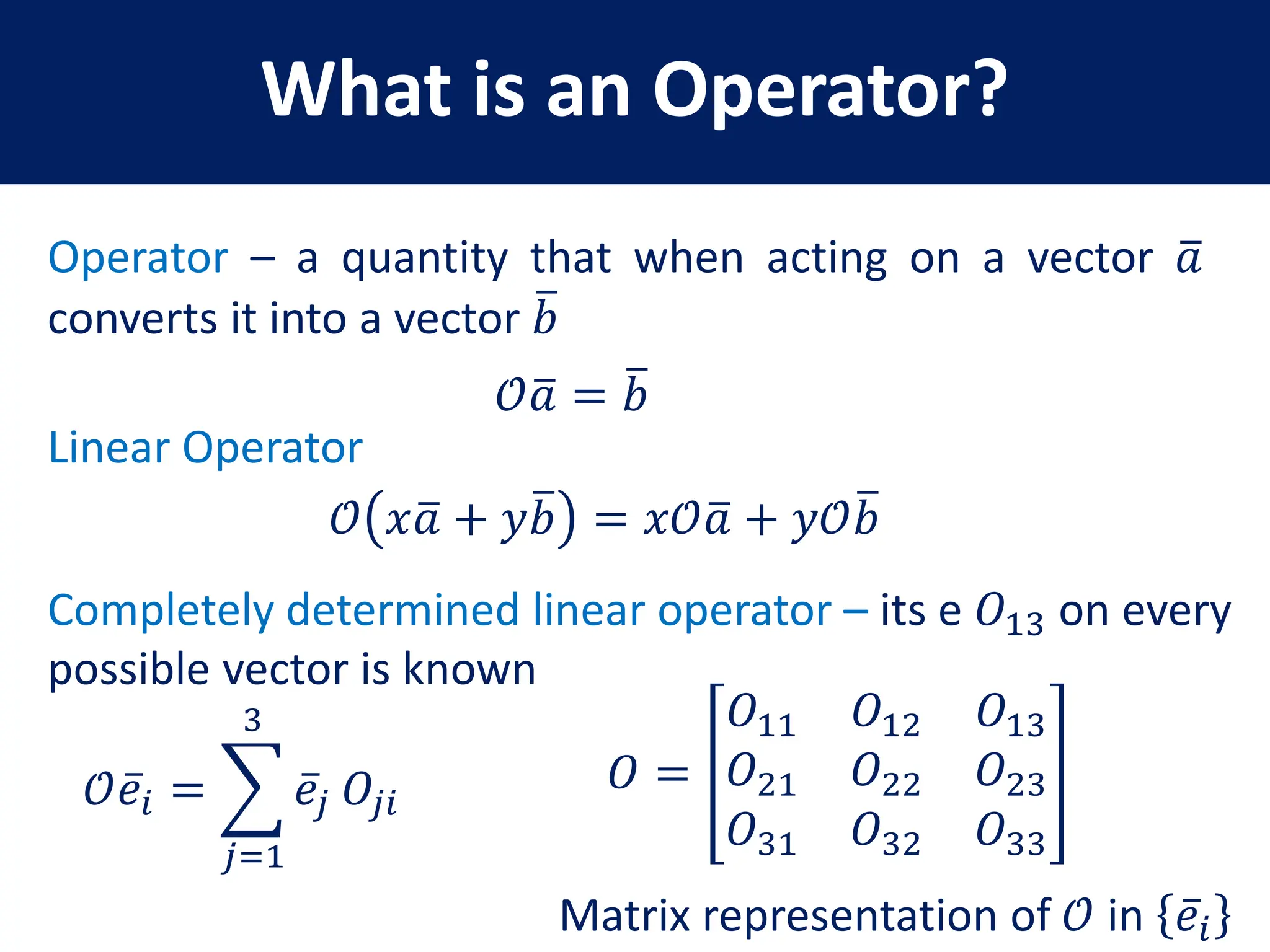
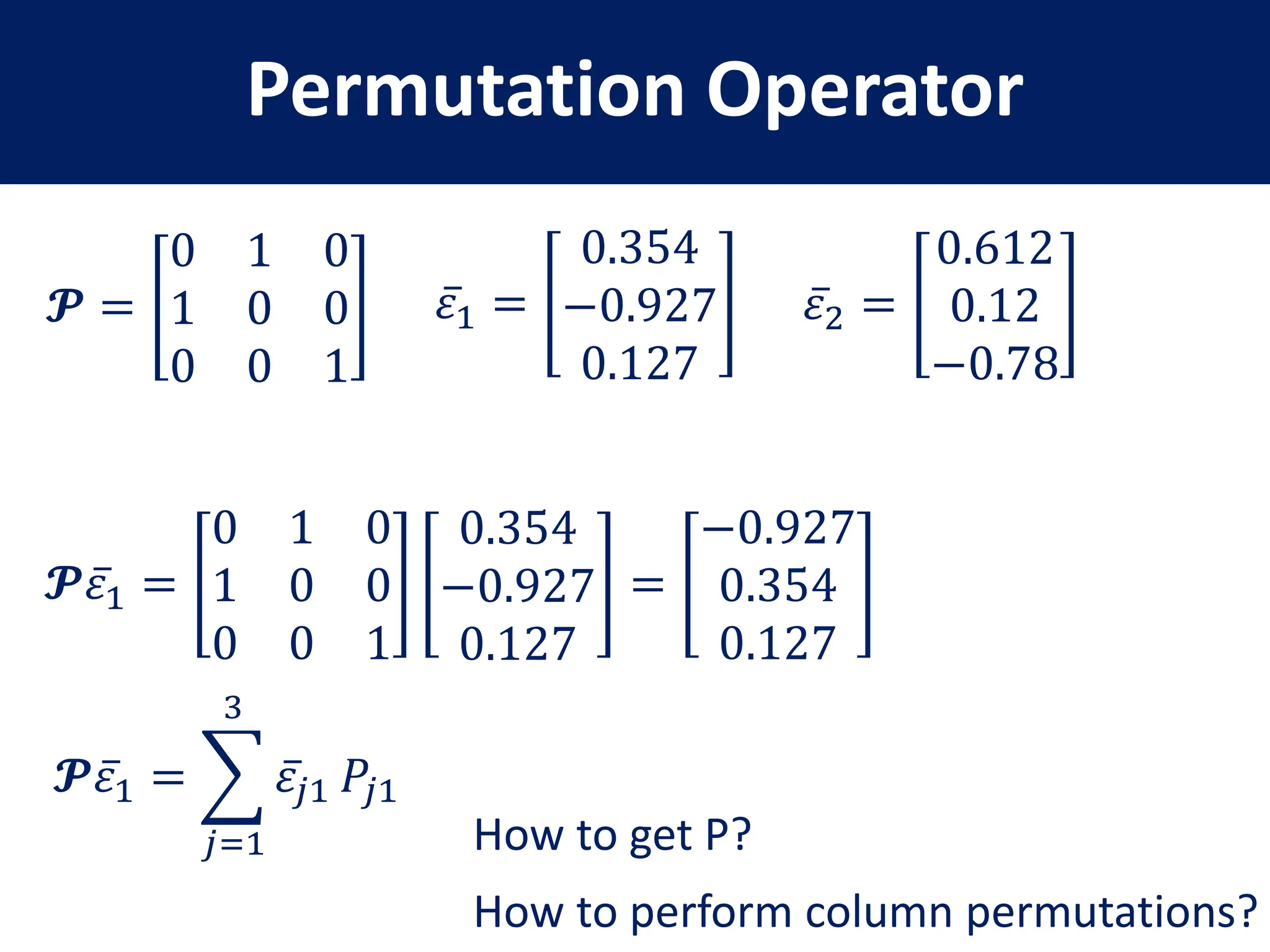
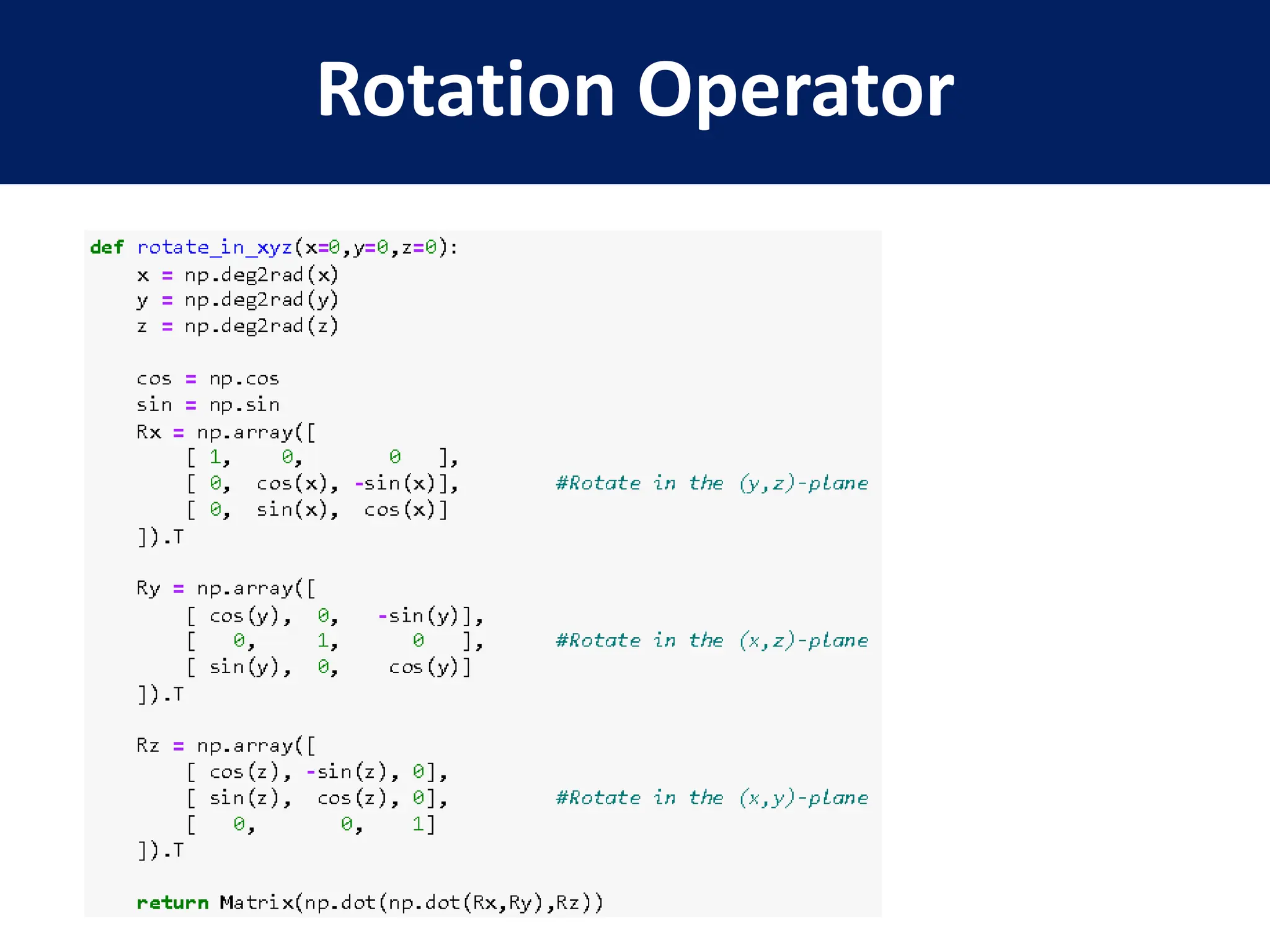
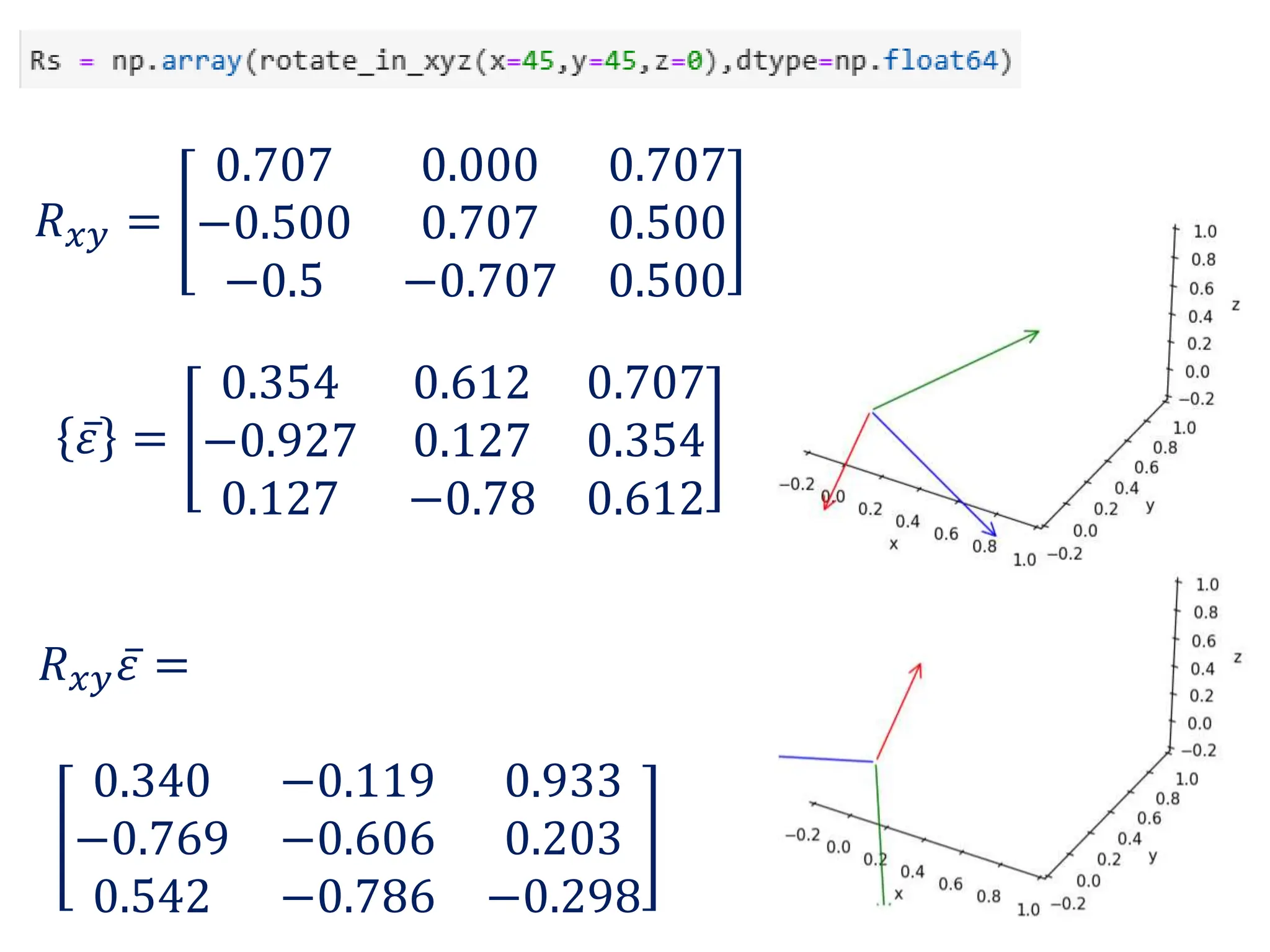
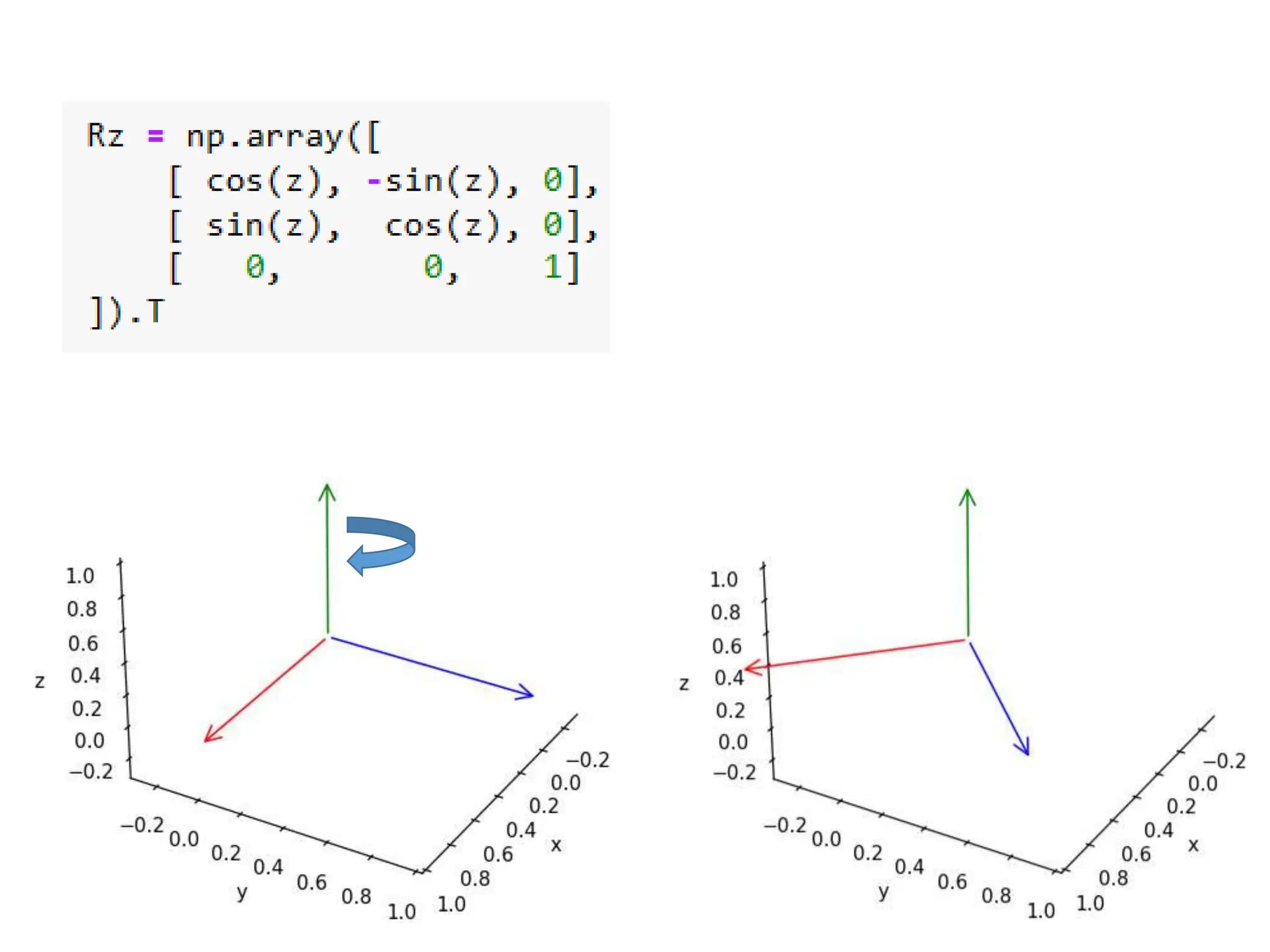
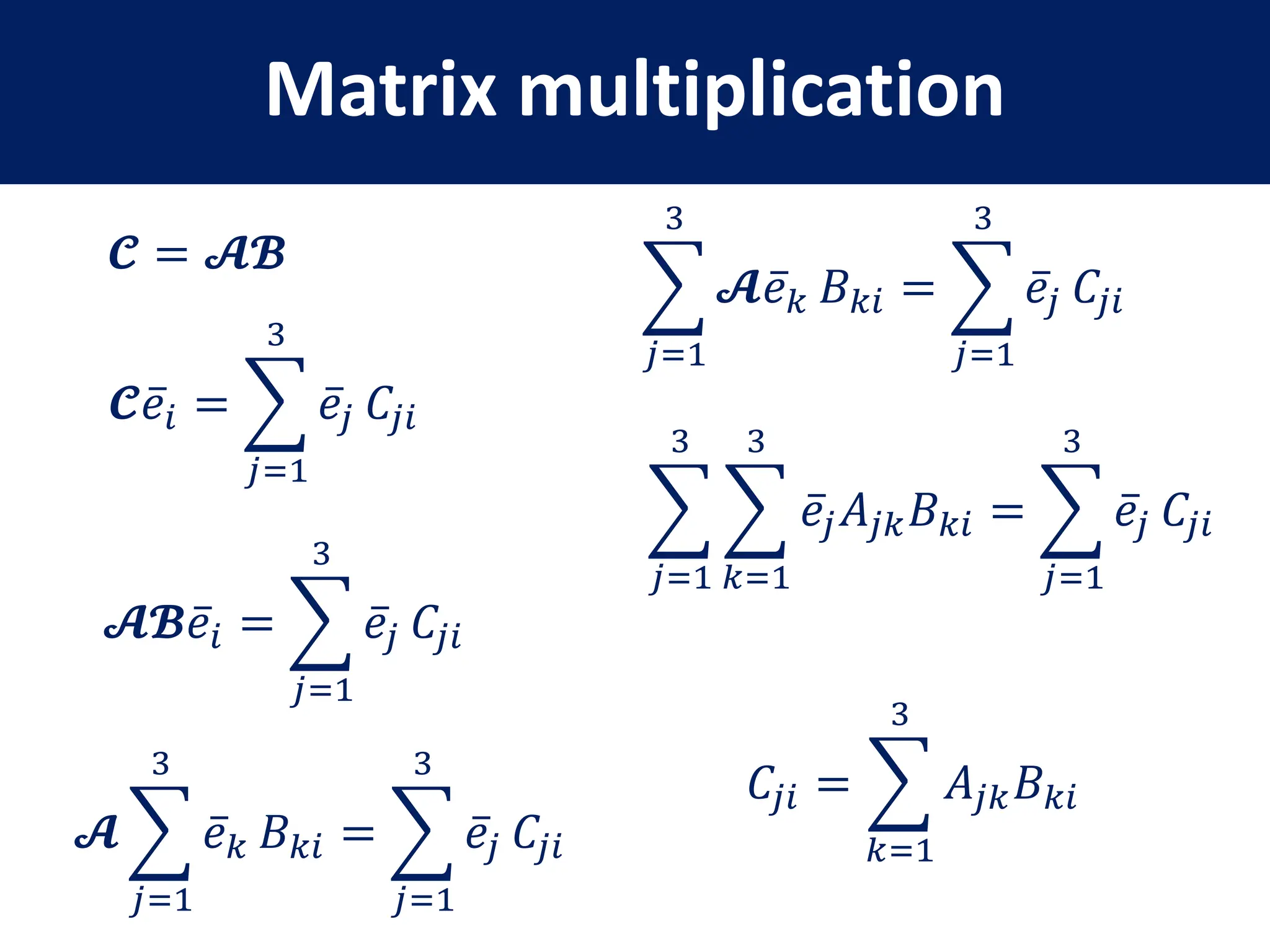
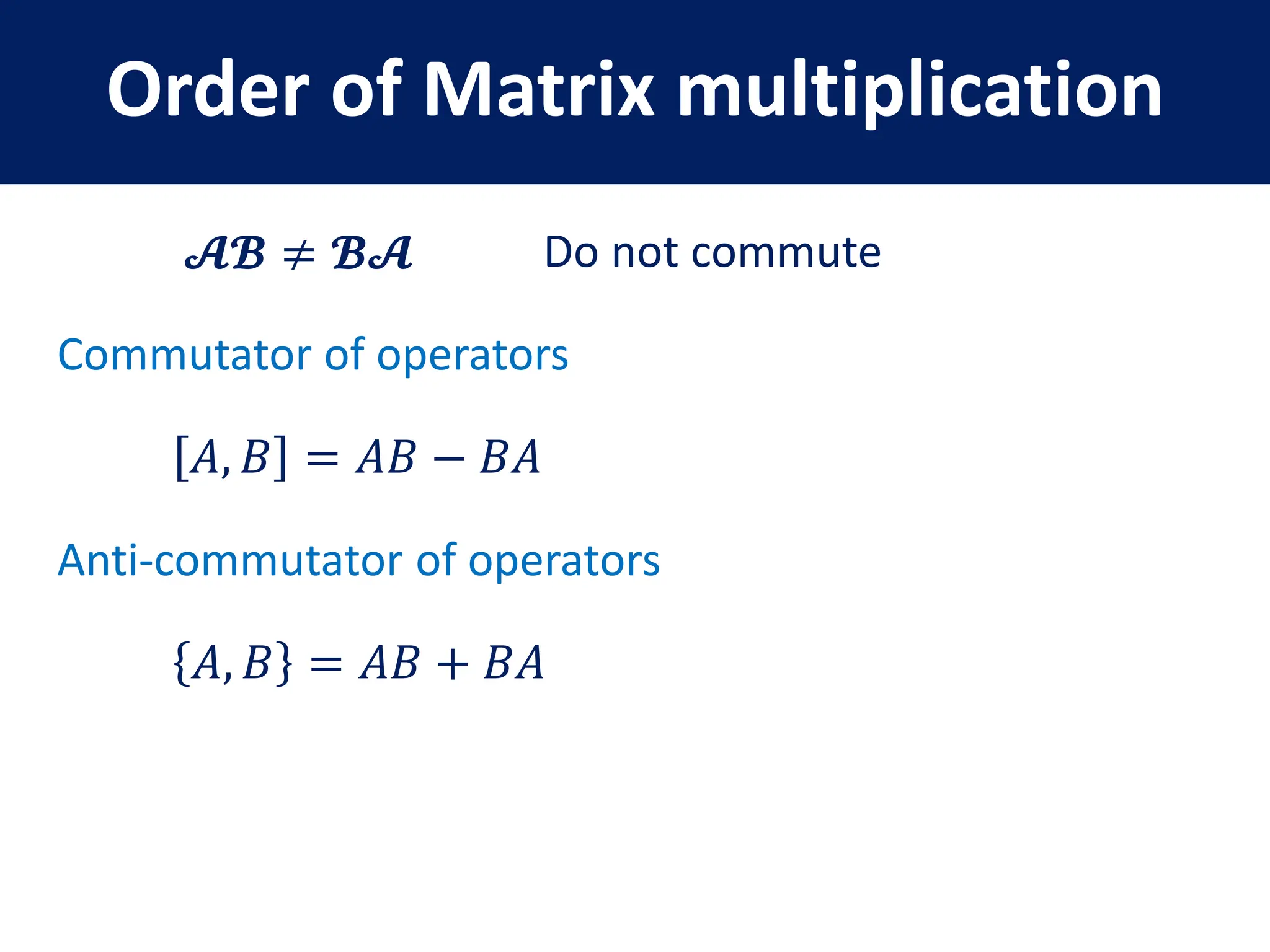
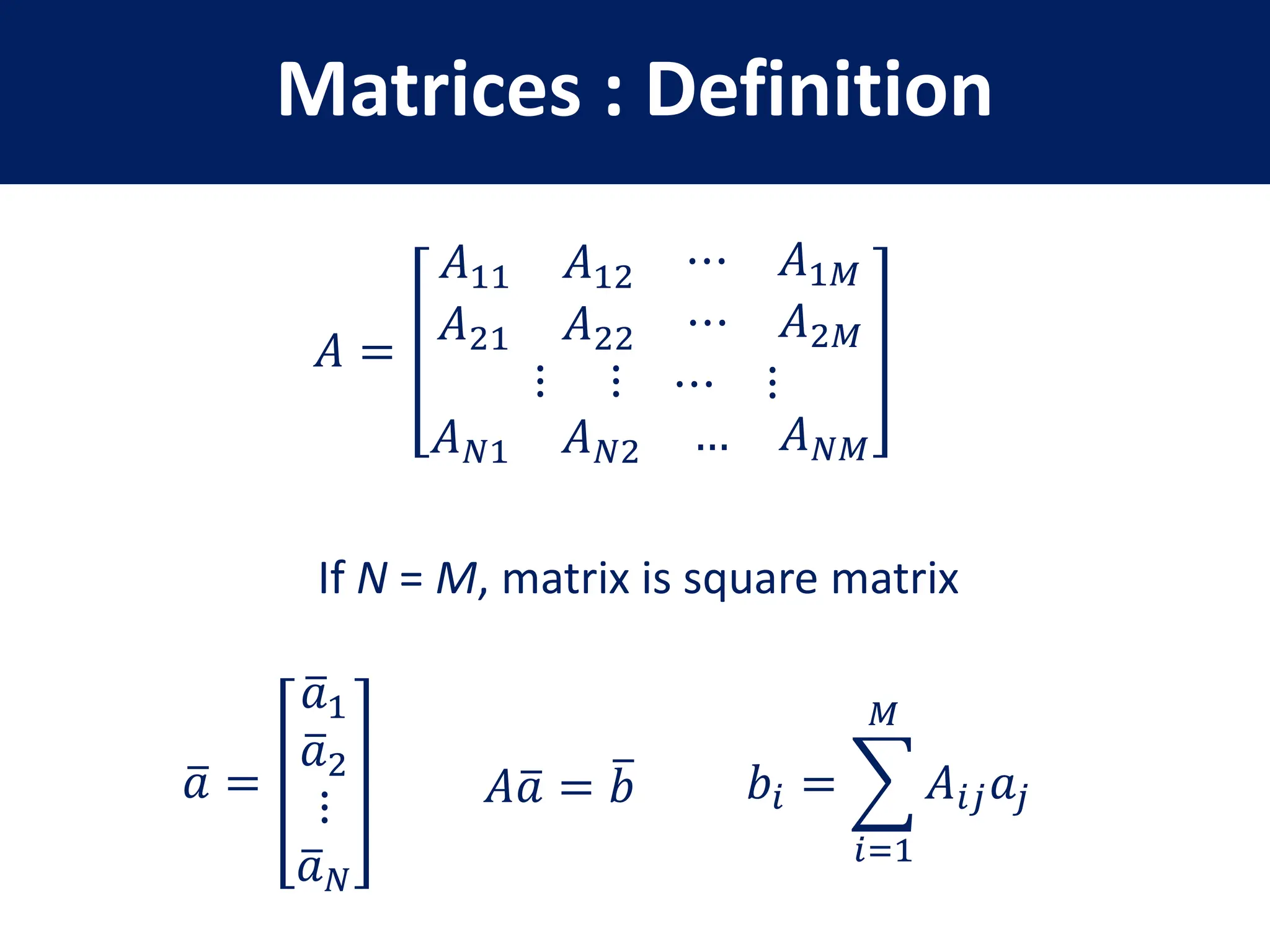
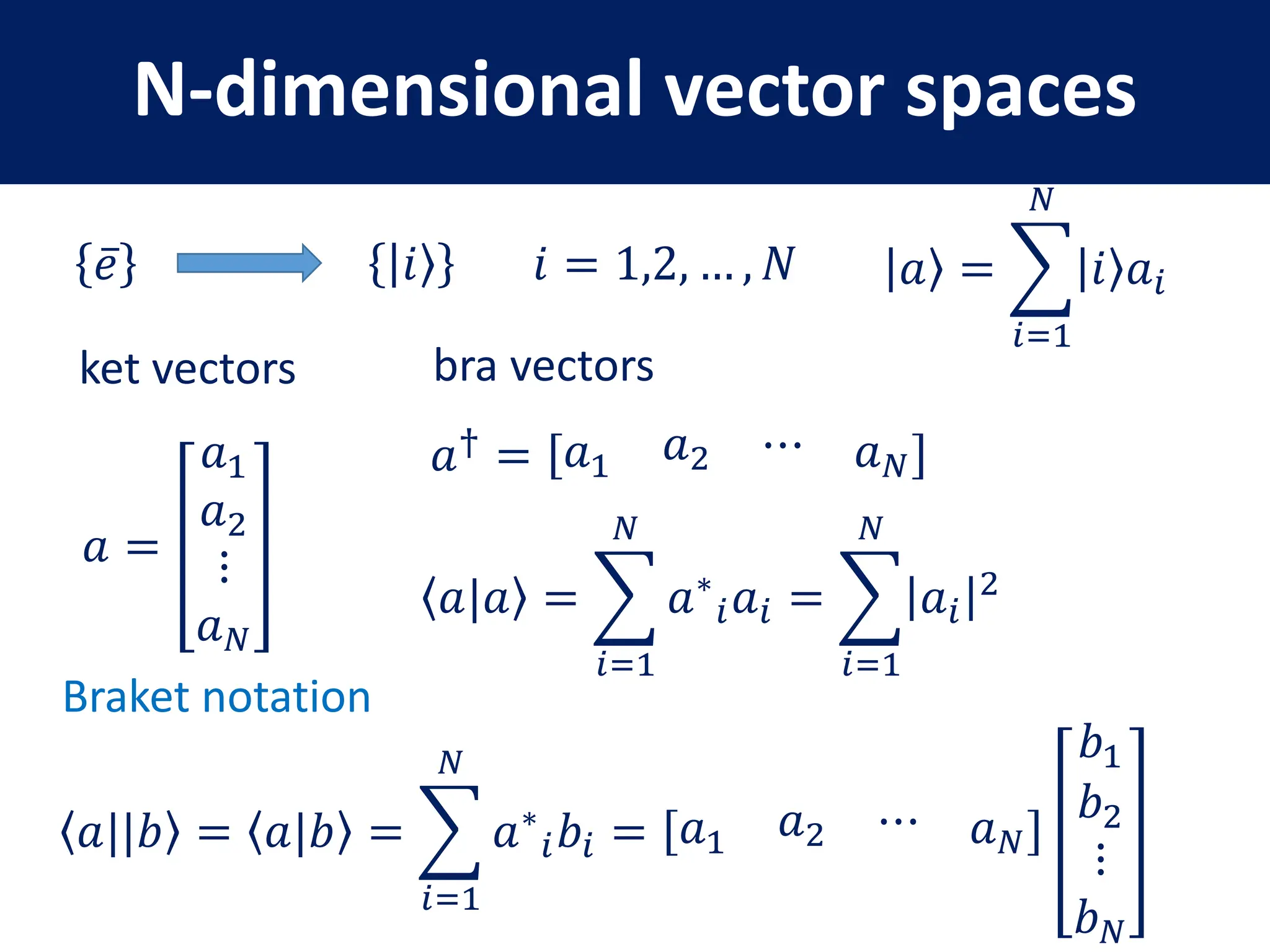
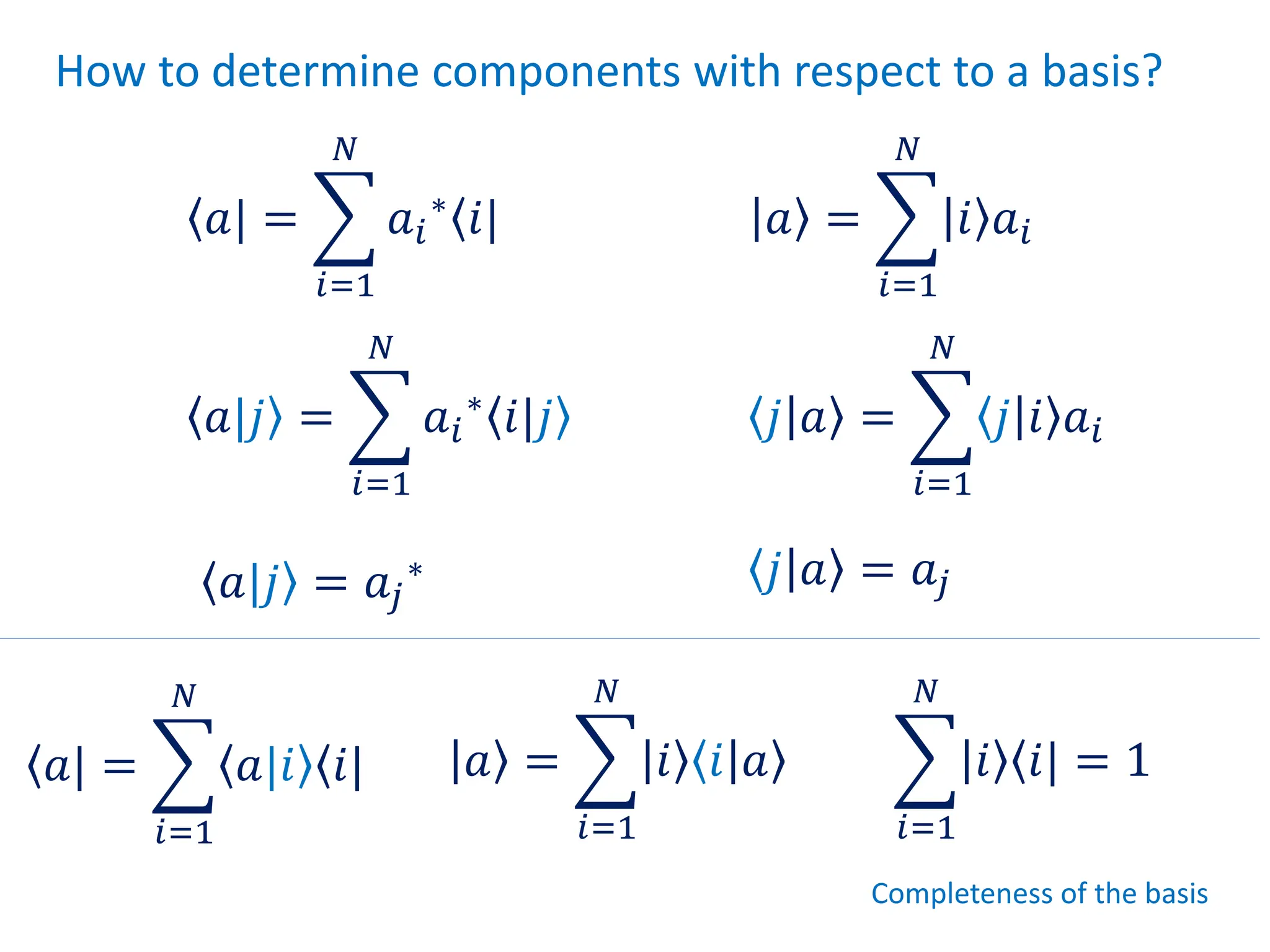
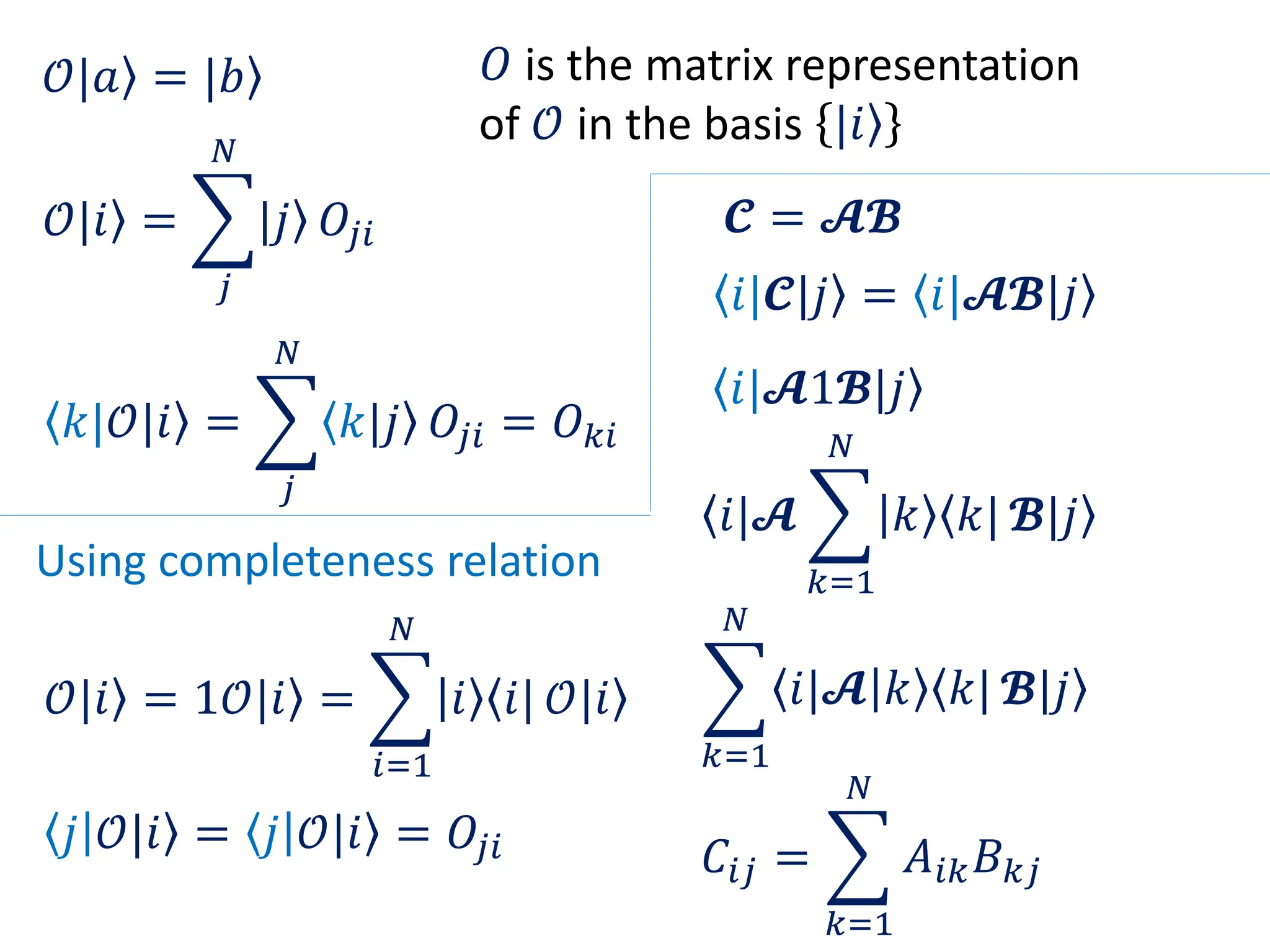
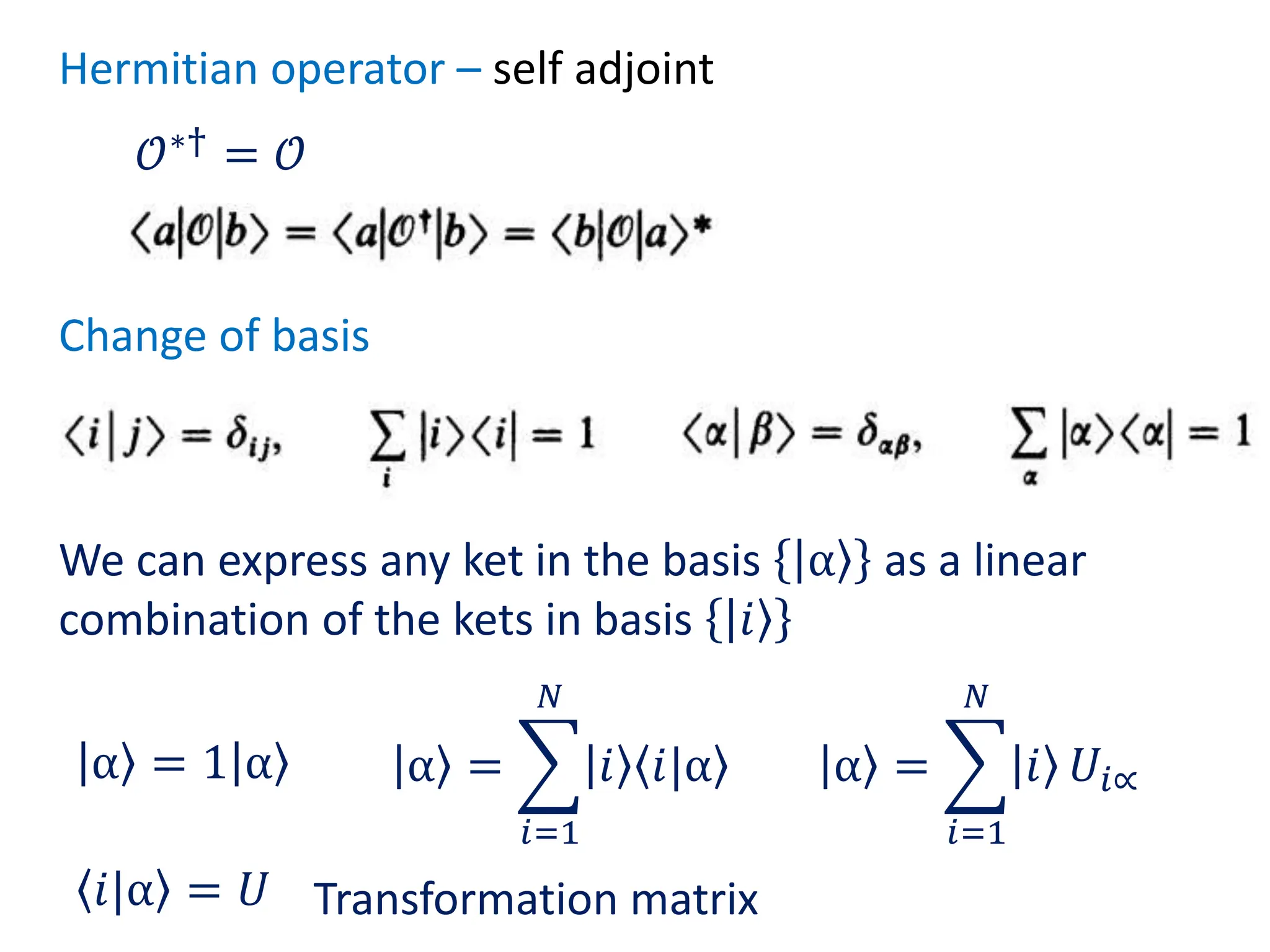
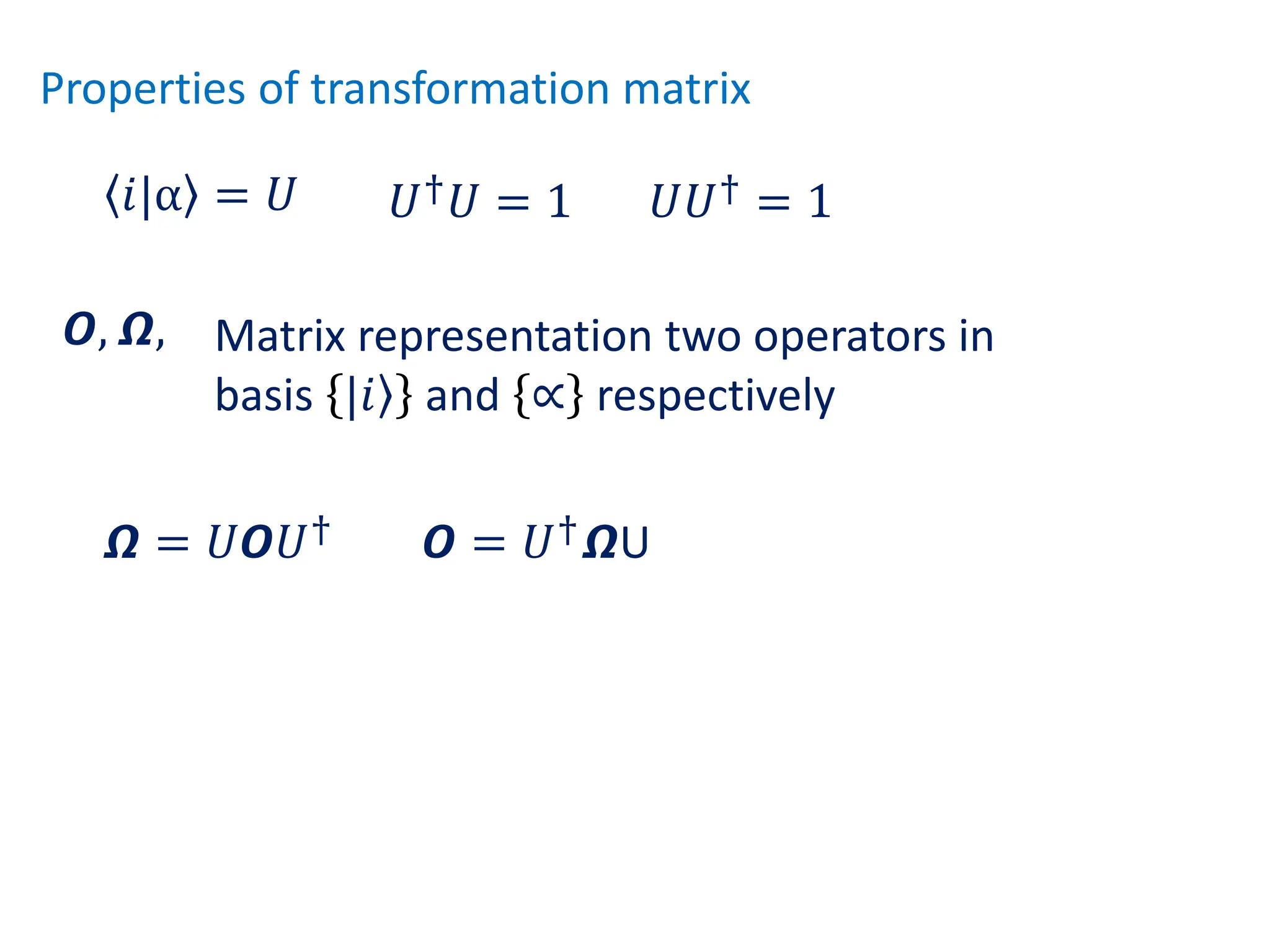
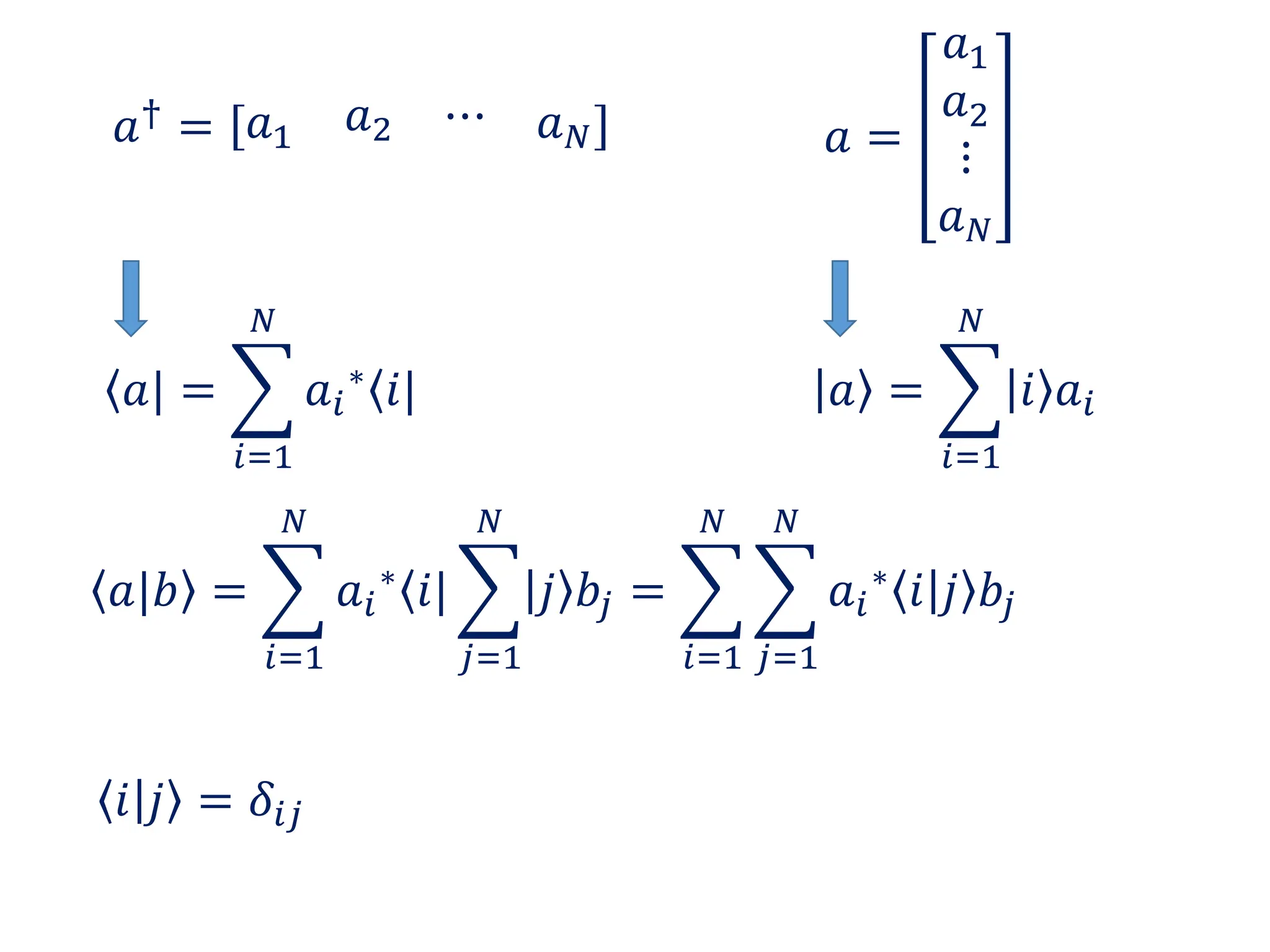This document provides a review of mathematical concepts relevant to physical chemistry, including:
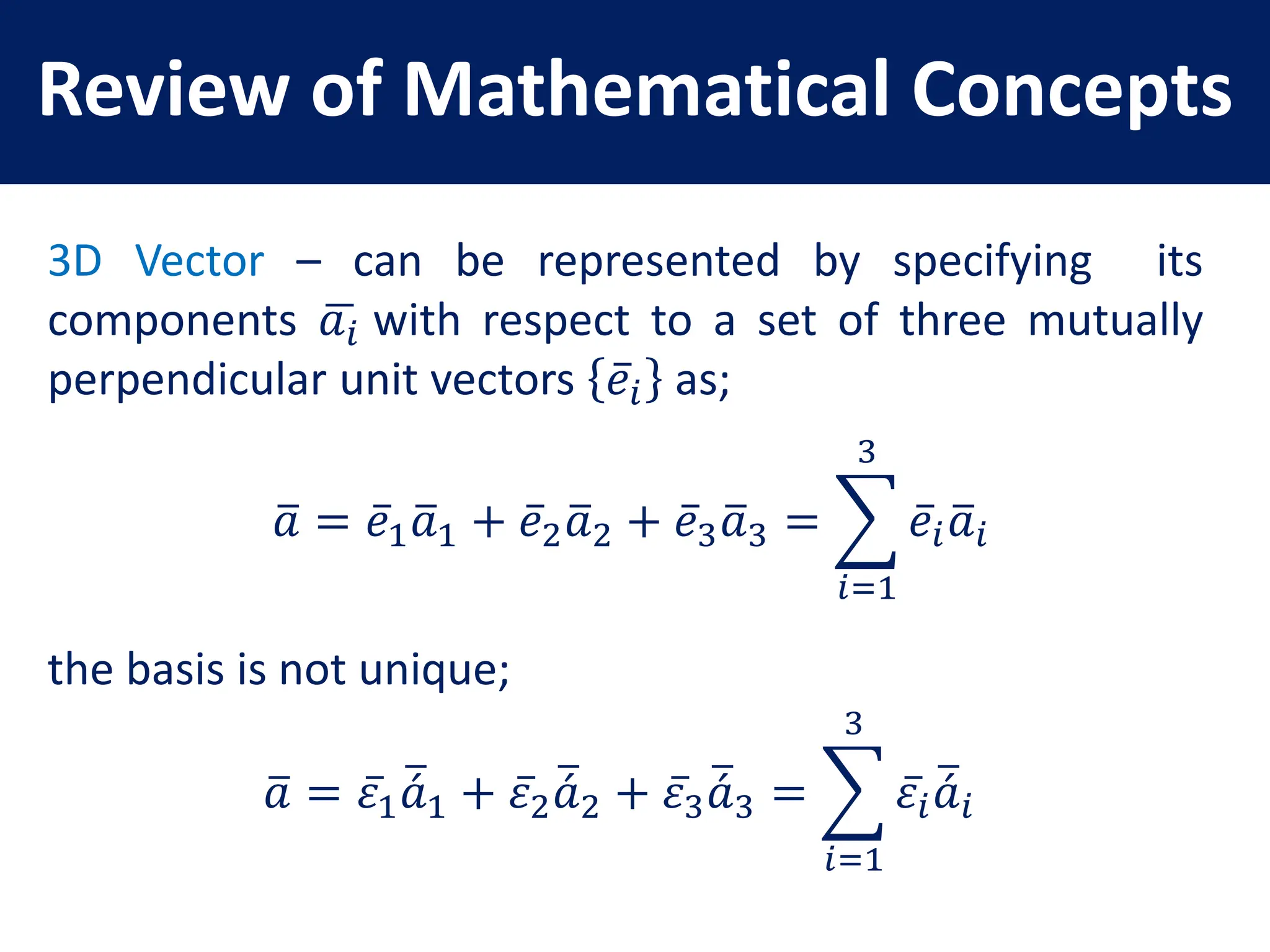
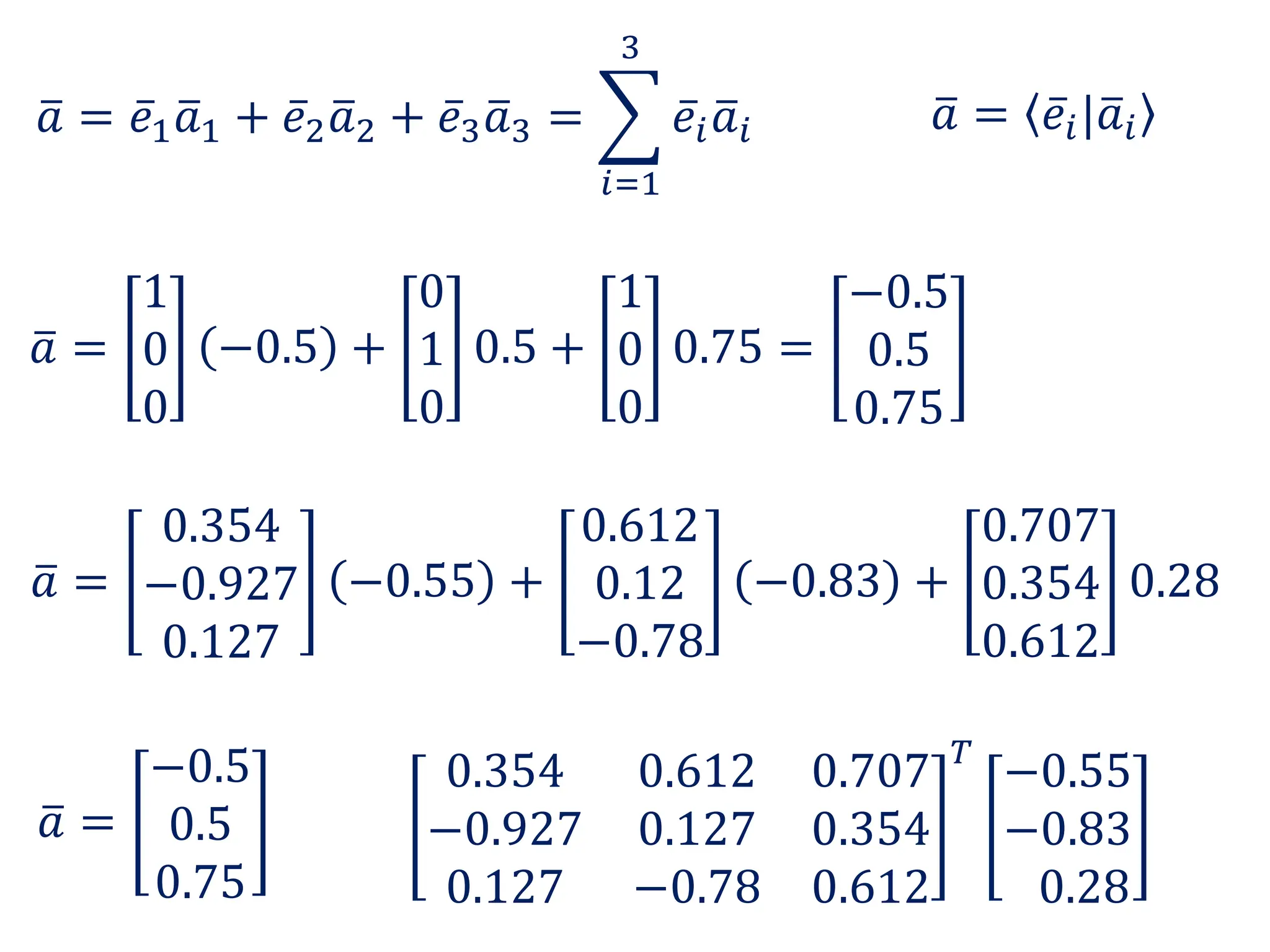
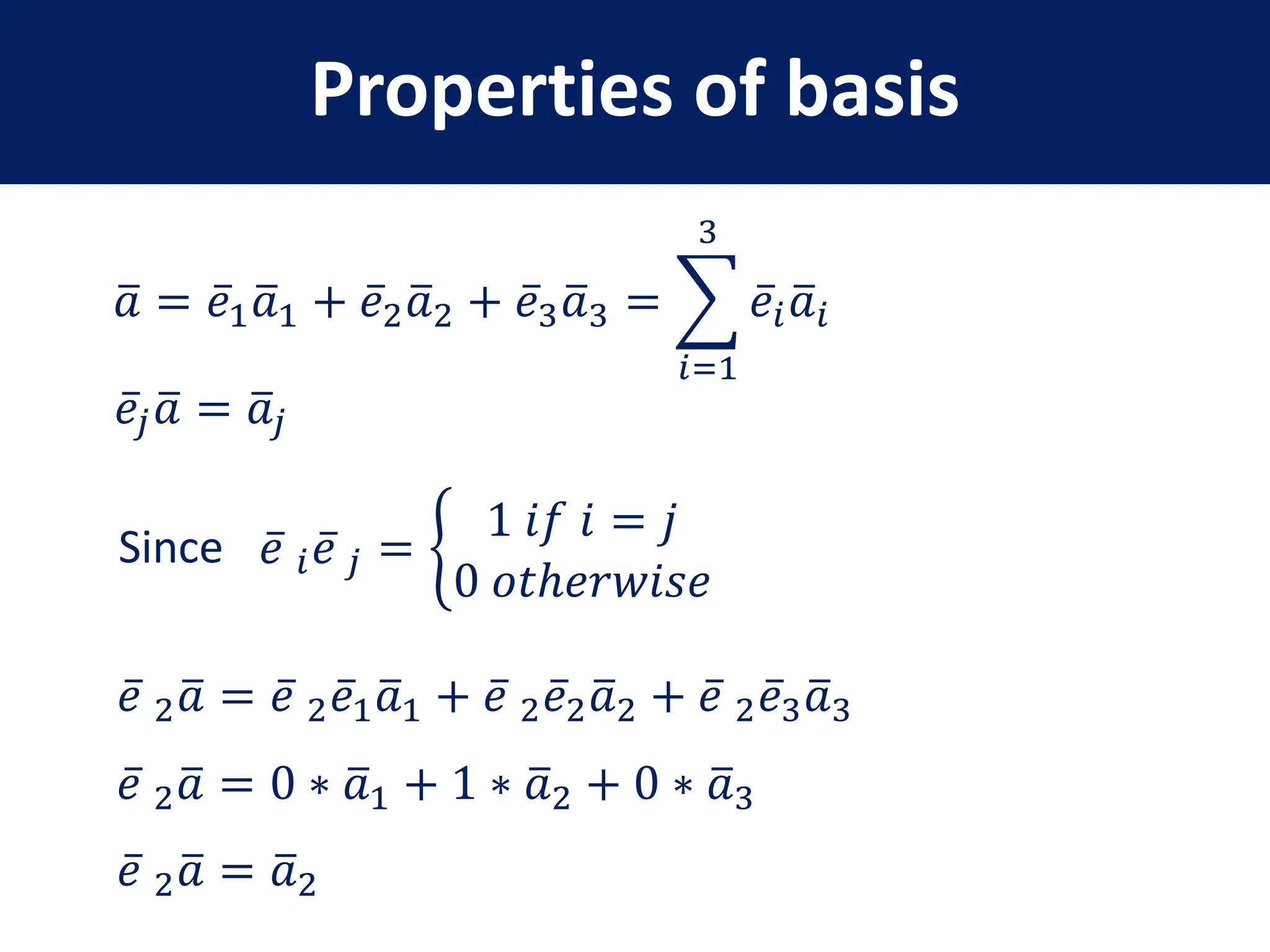
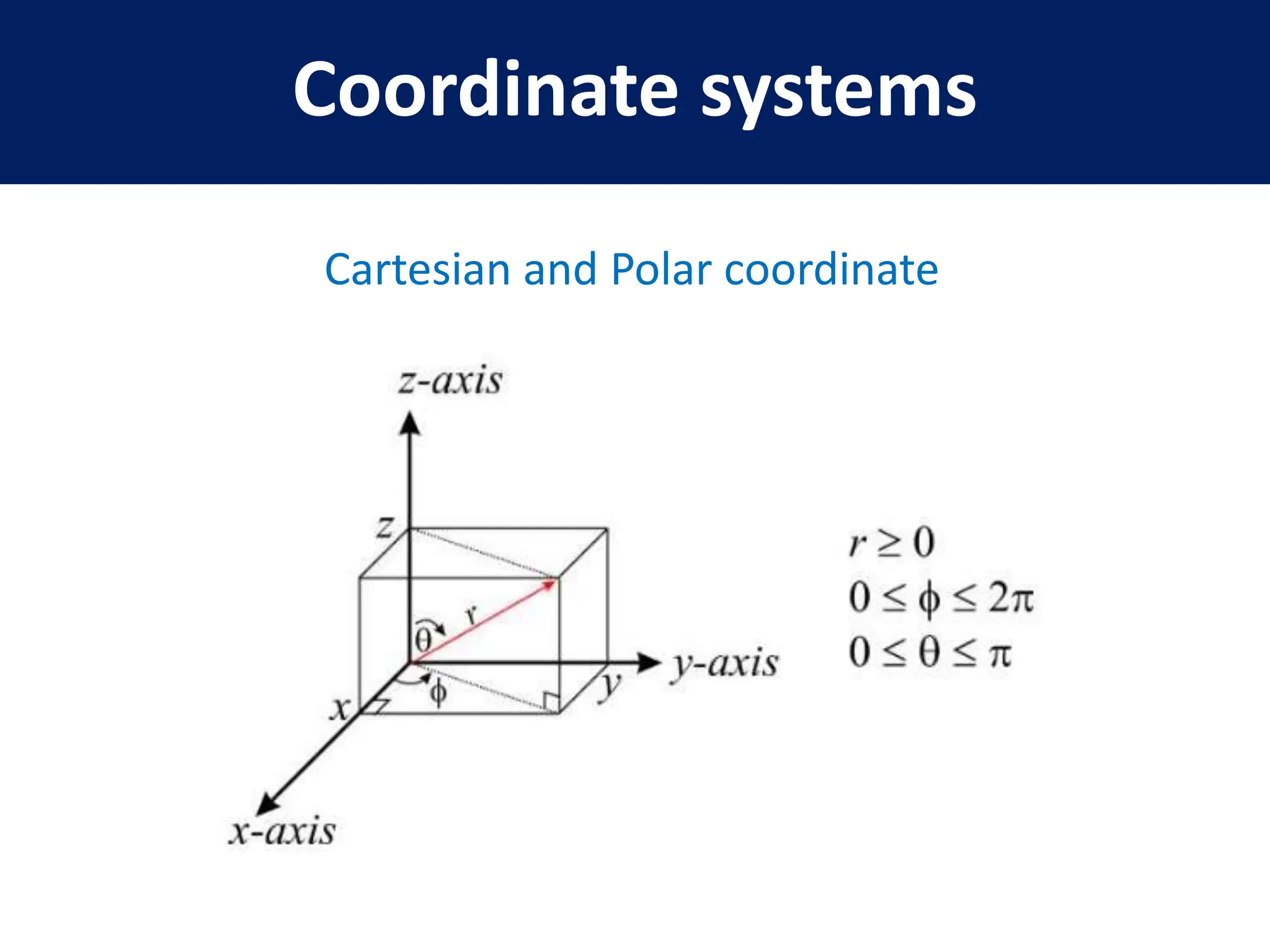
- Representation of 3D vectors in terms of basis vectors and components
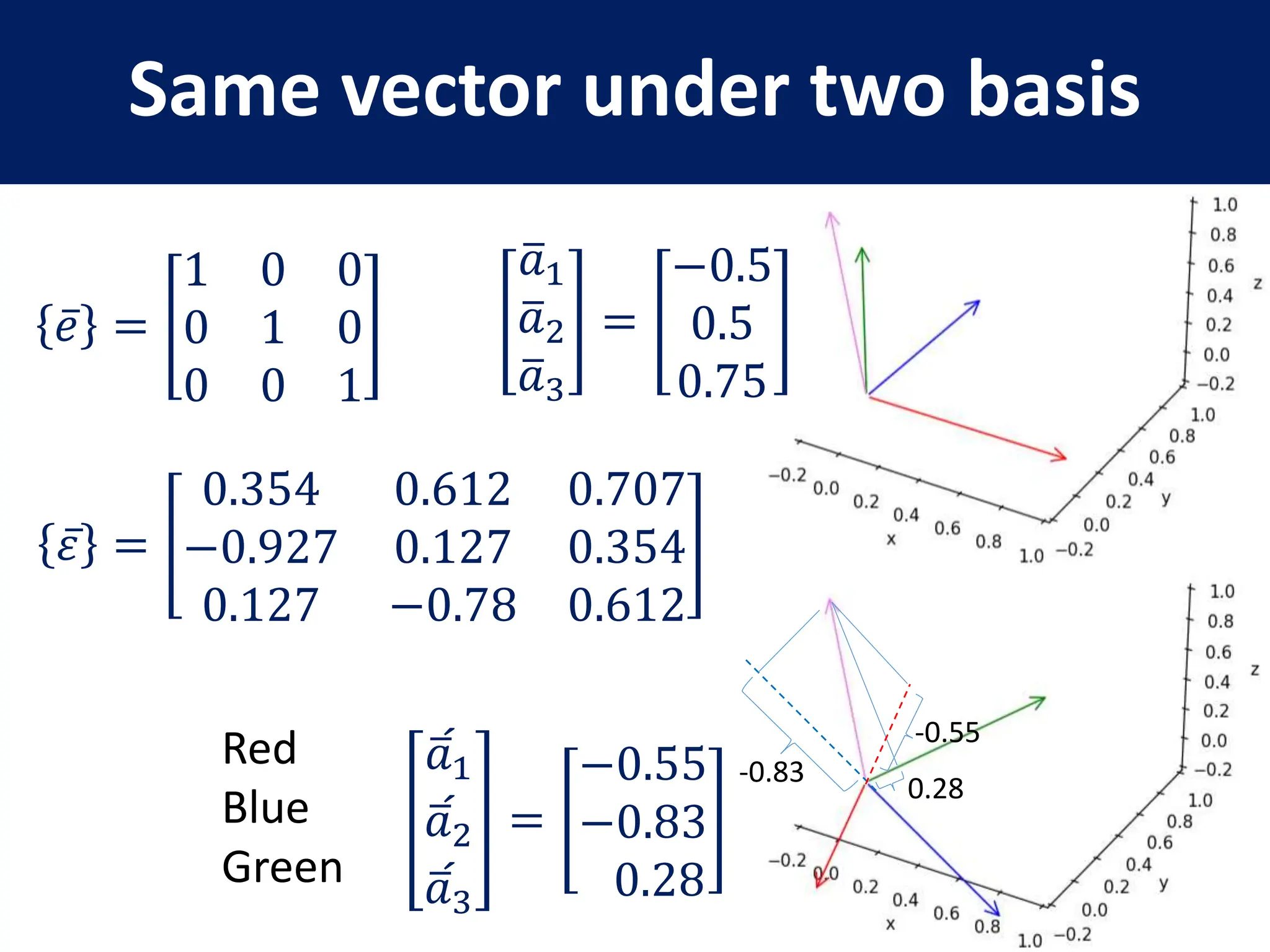
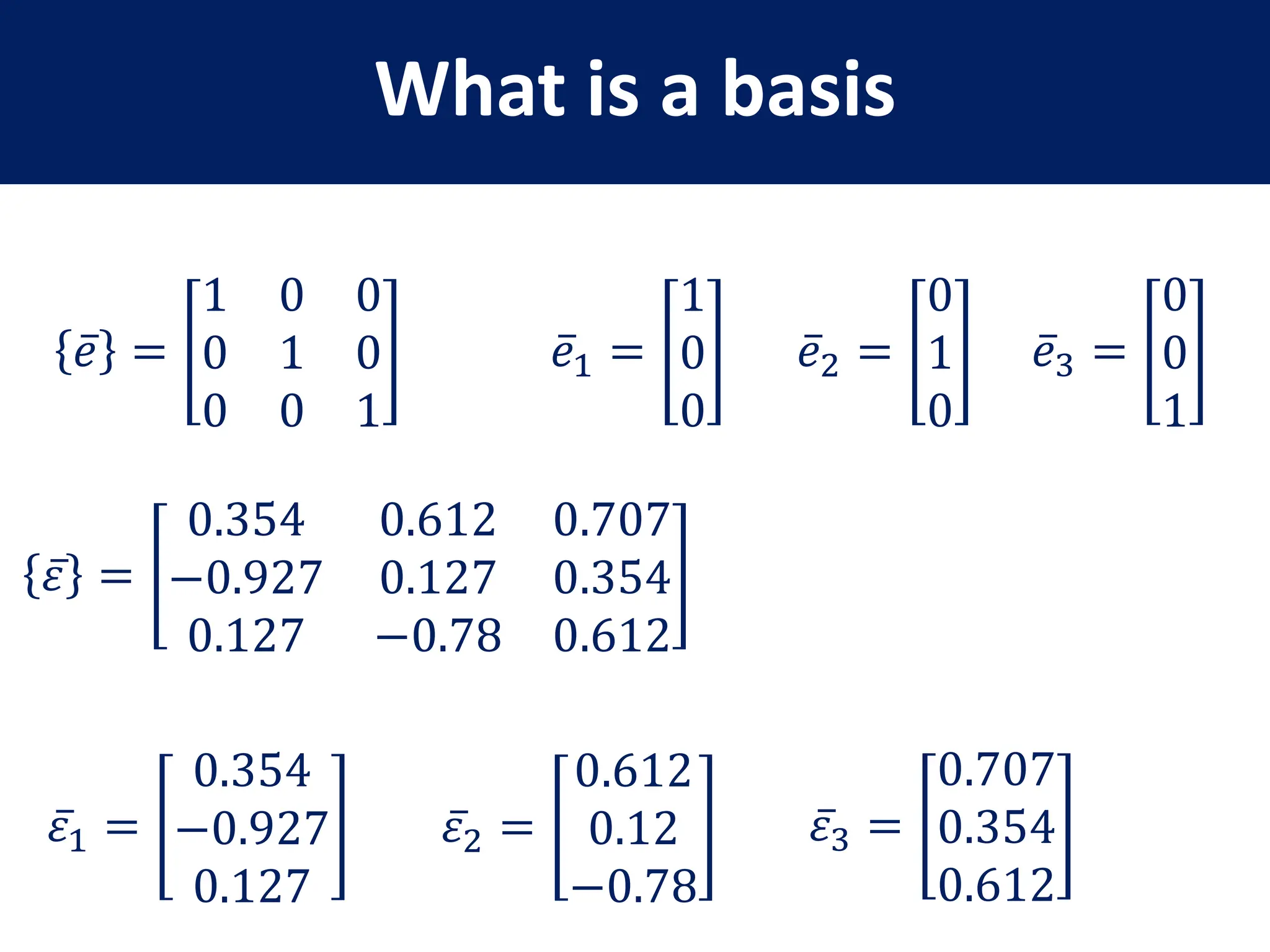
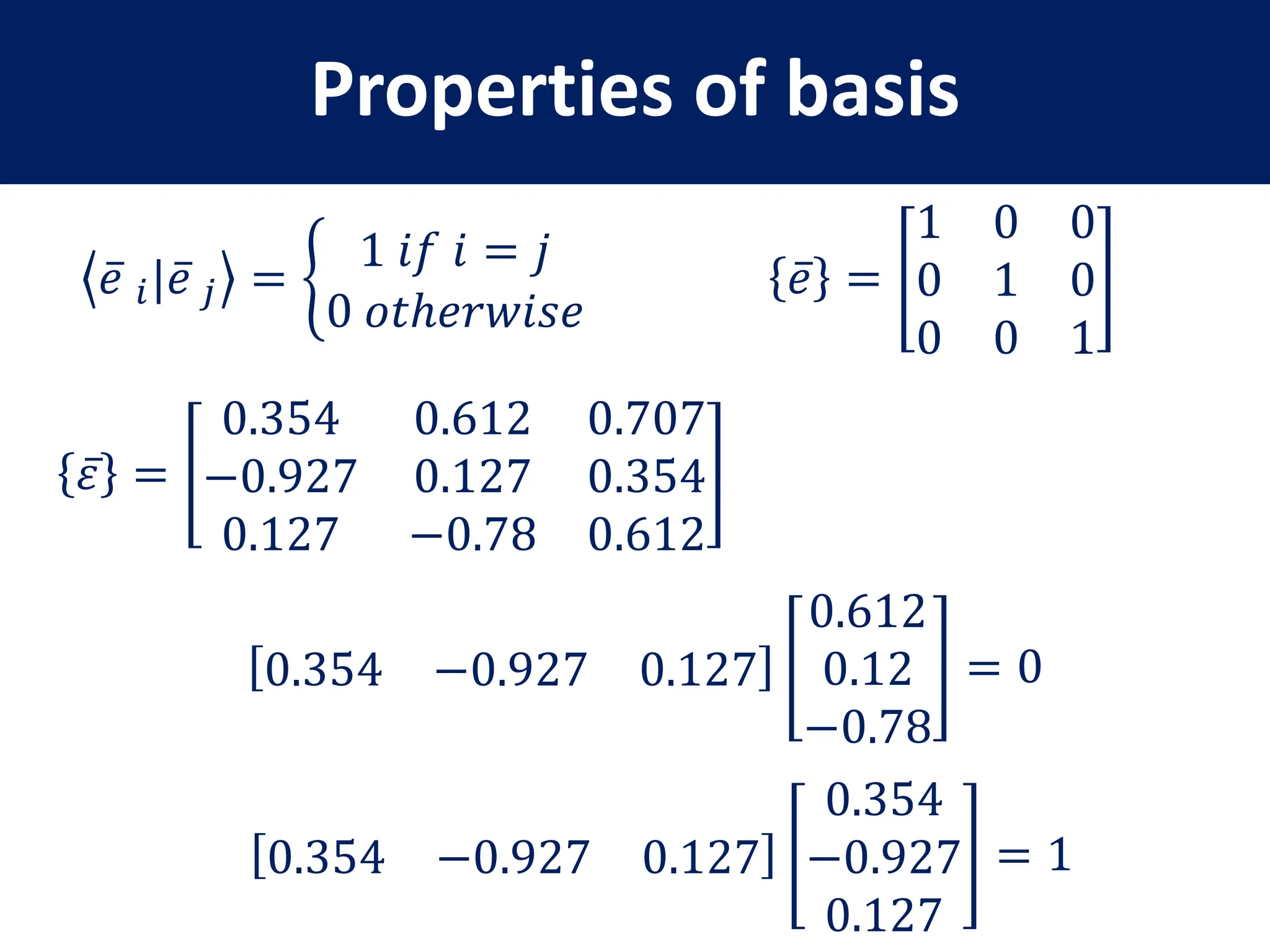
- Definition of a basis and examples of standard and non-standard bases
- Representation of vectors and operators in terms of matrices
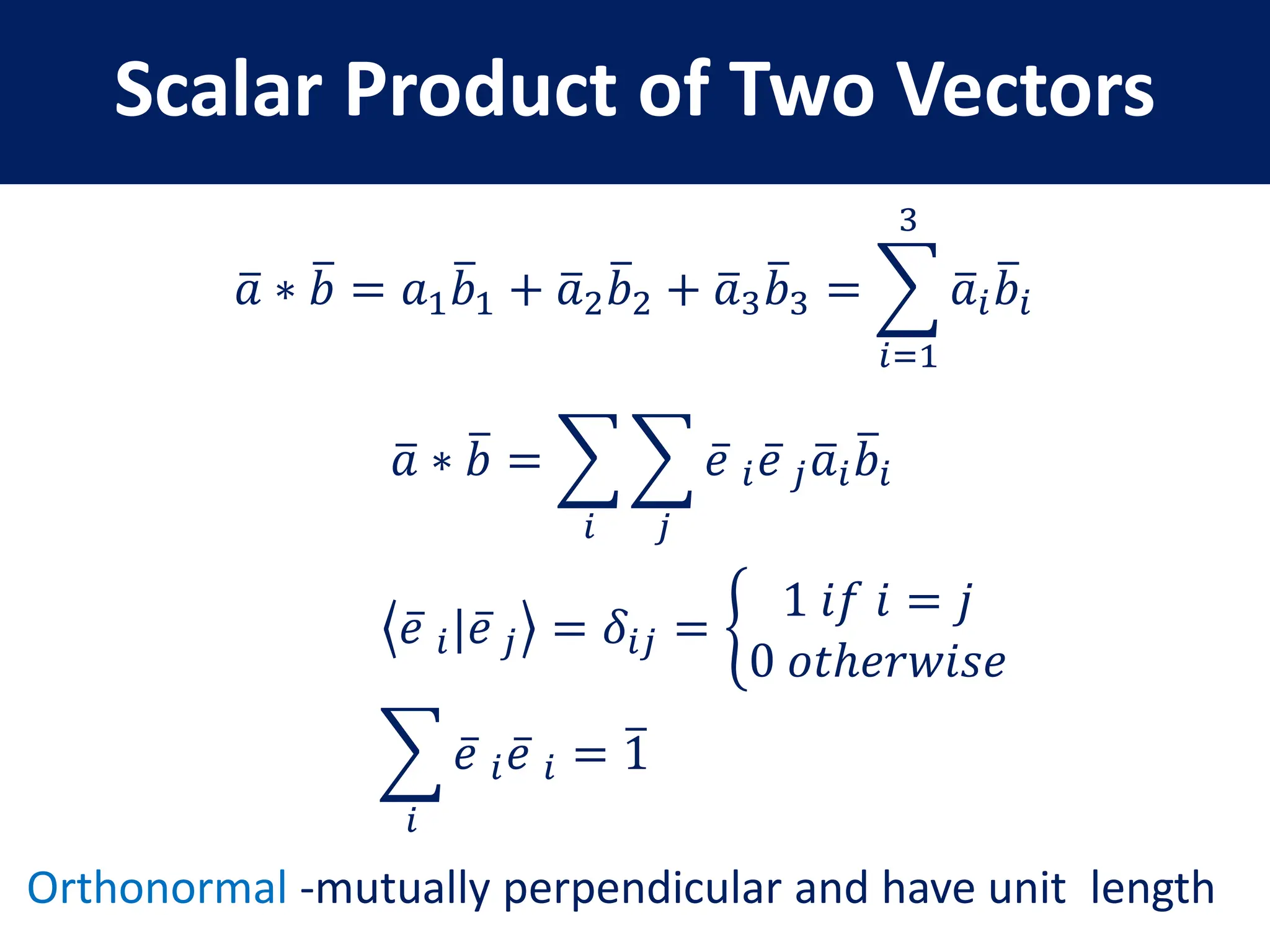
- Properties of bases, operators, and matrices like orthogonality, linearity, and order of operations
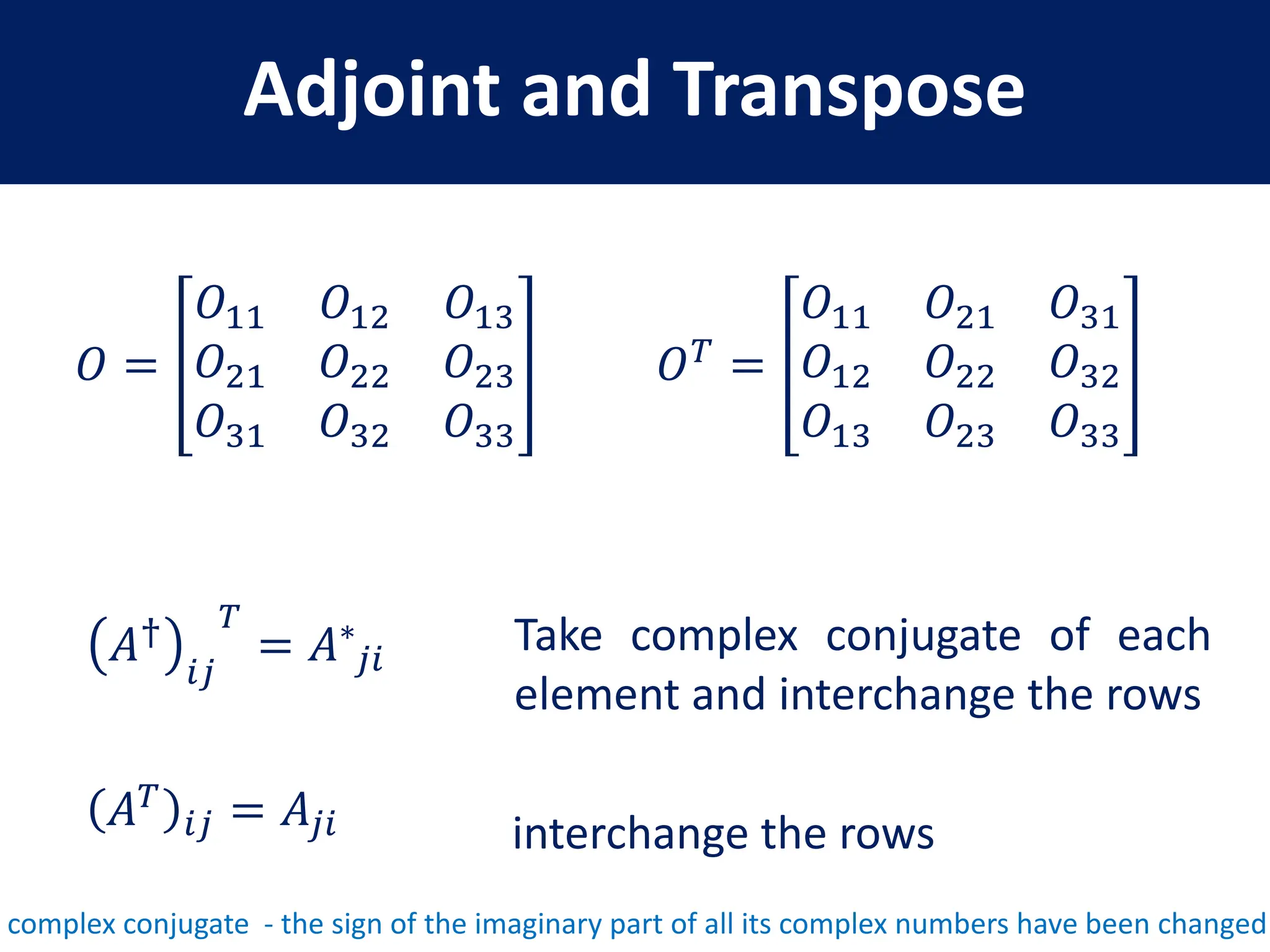
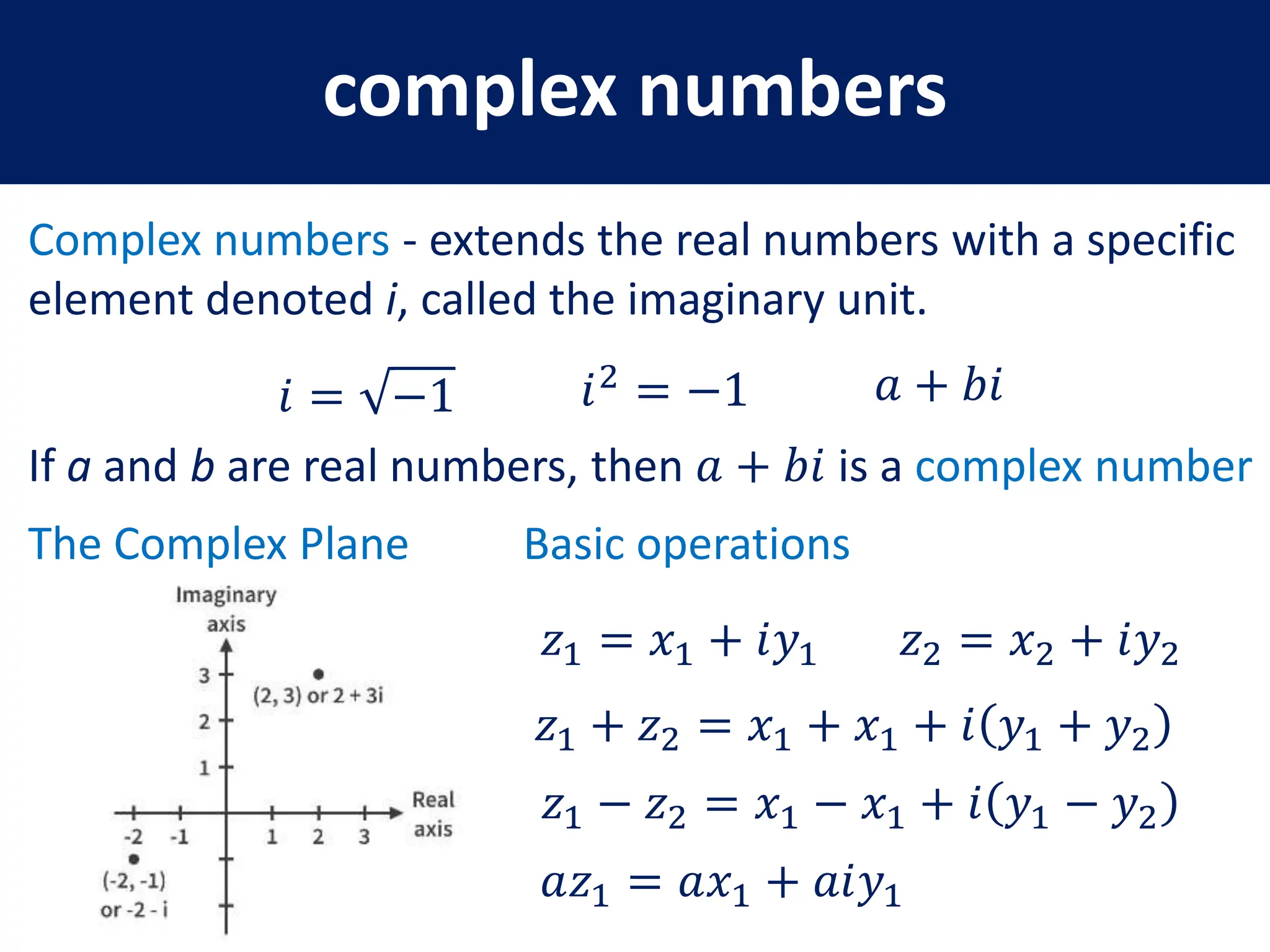
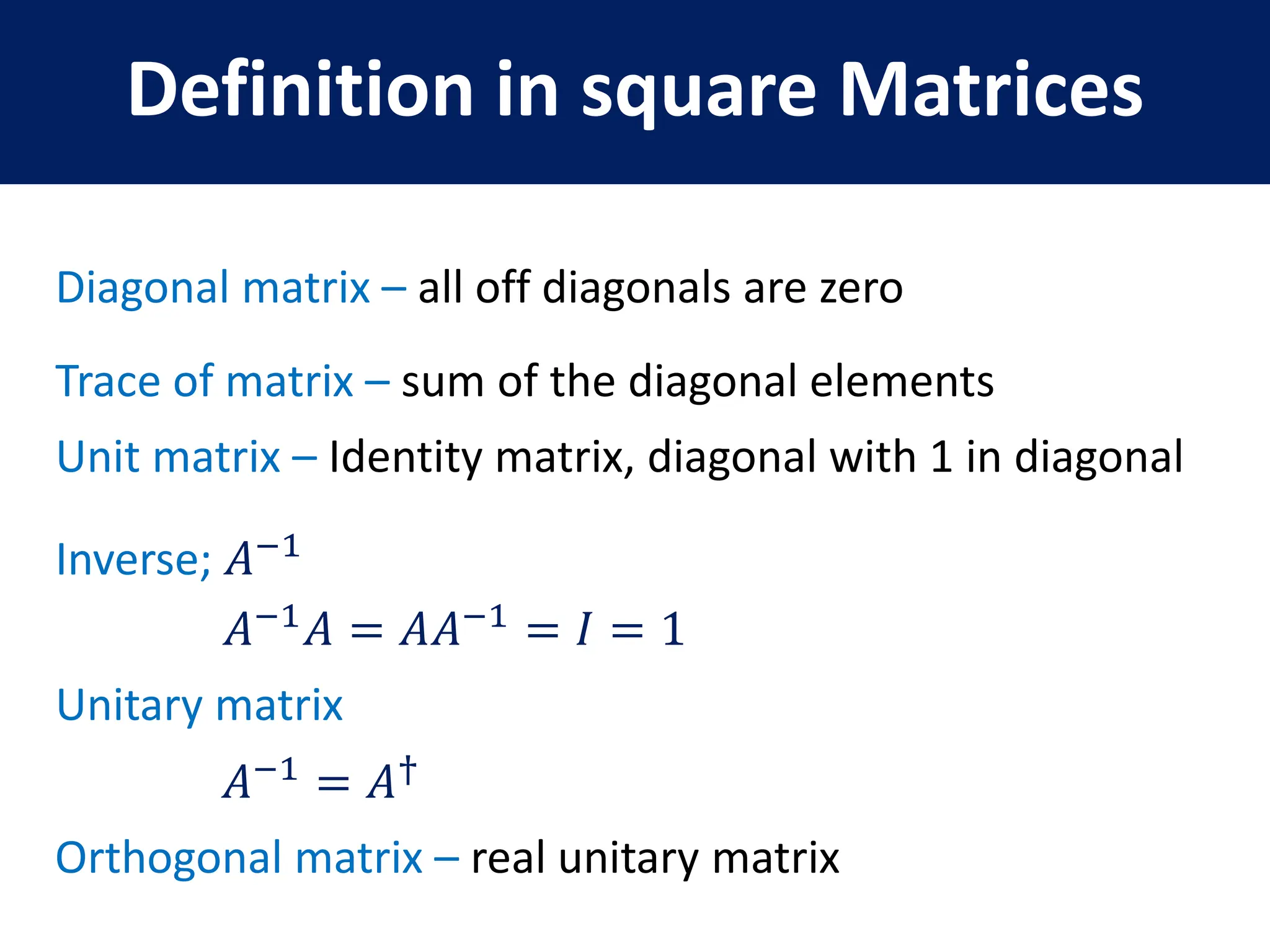
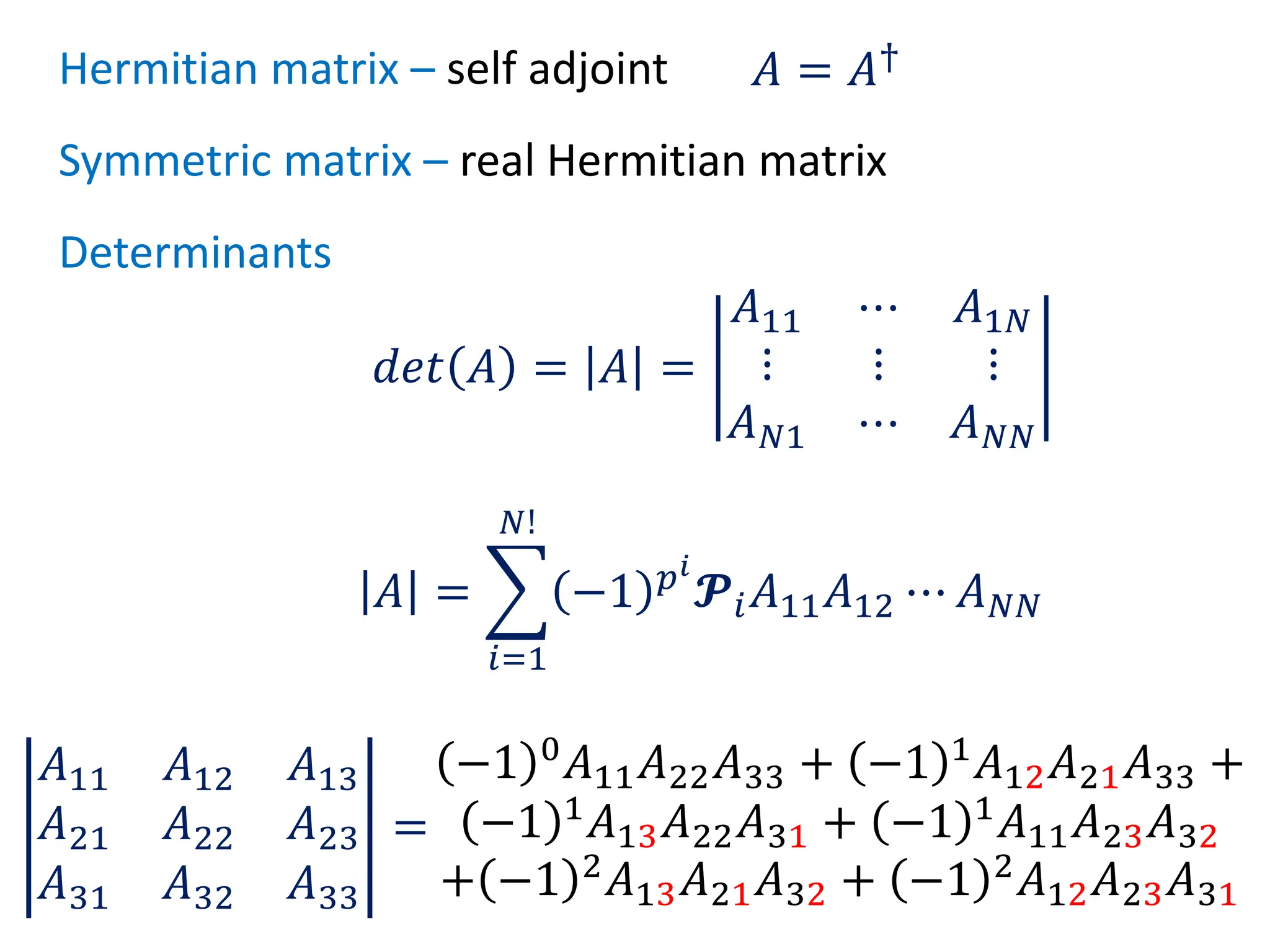
- Key matrix operations like transpose, adjoint, determinant, and representation of vectors and operators