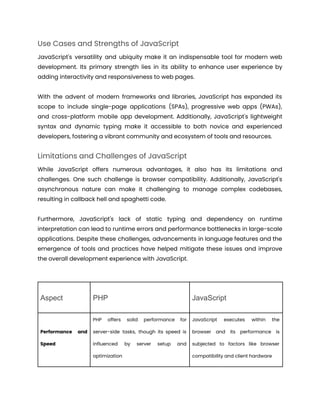
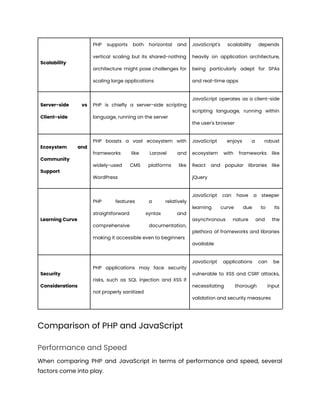
The document compares PHP and JavaScript for web development, highlighting their unique characteristics, strengths, limitations, and use cases. PHP, a server-side scripting language, is known for its versatility in building dynamic content, while JavaScript, a client-side language, enhances interactivity in web applications. Key factors for choosing between the two include project requirements, team expertise, scalability, budget, and deadline considerations.