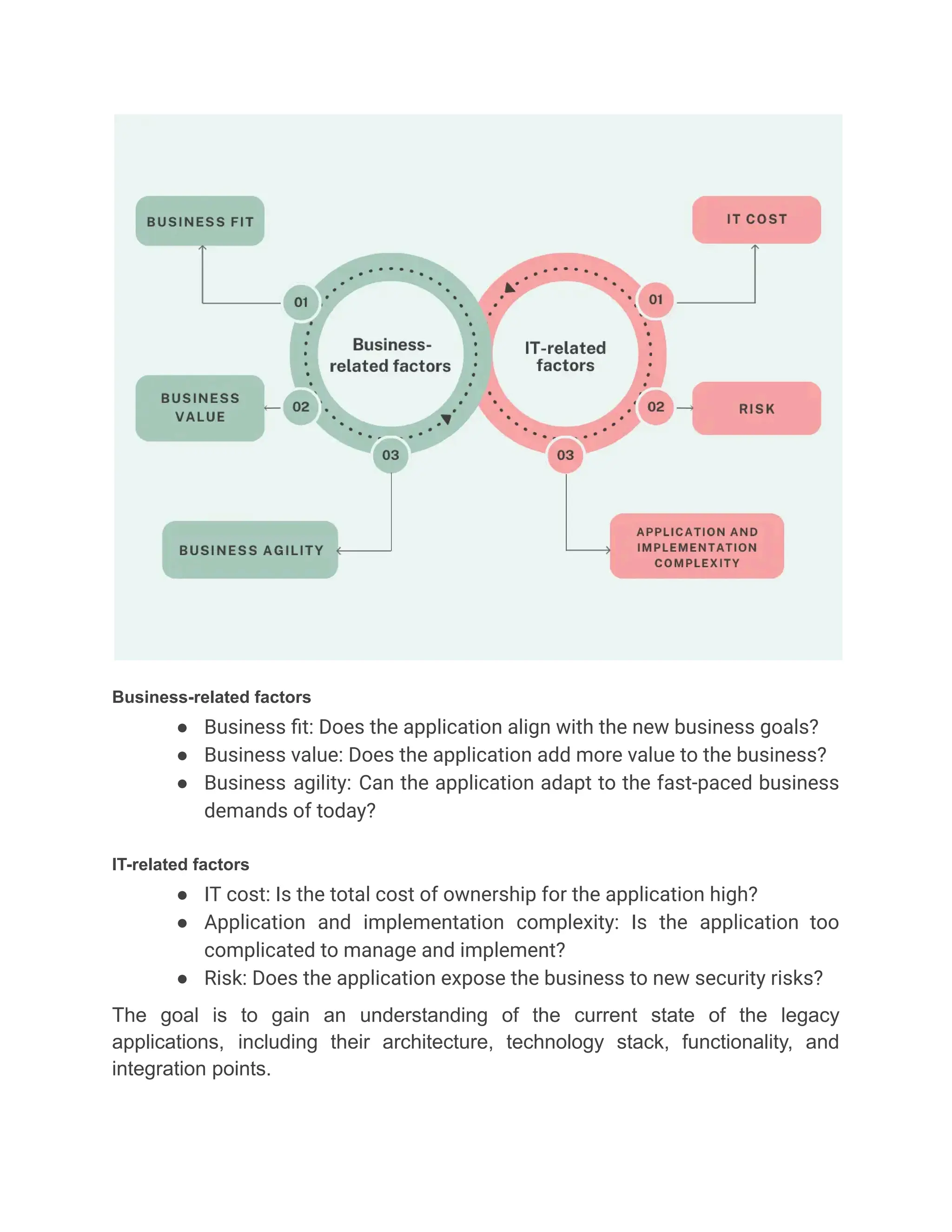
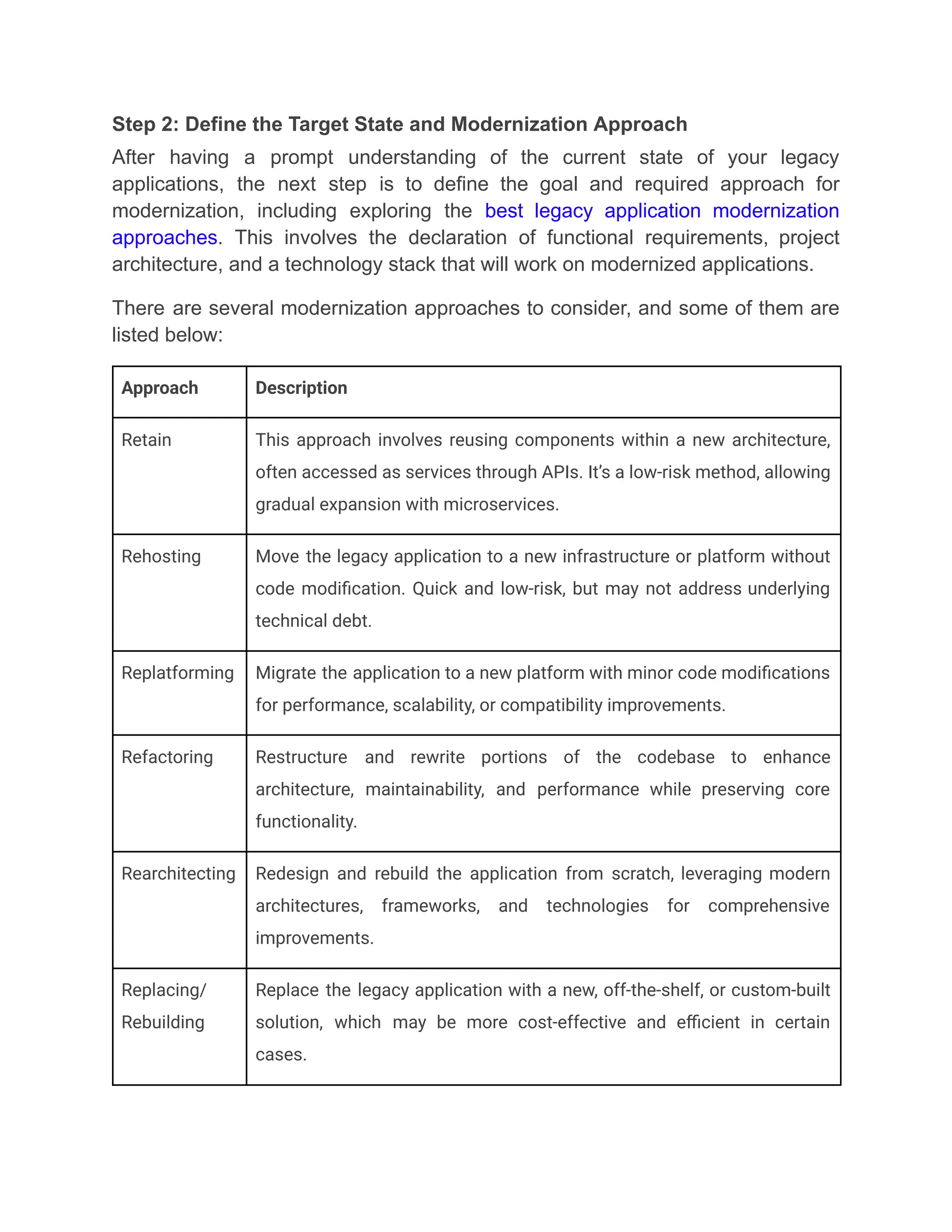
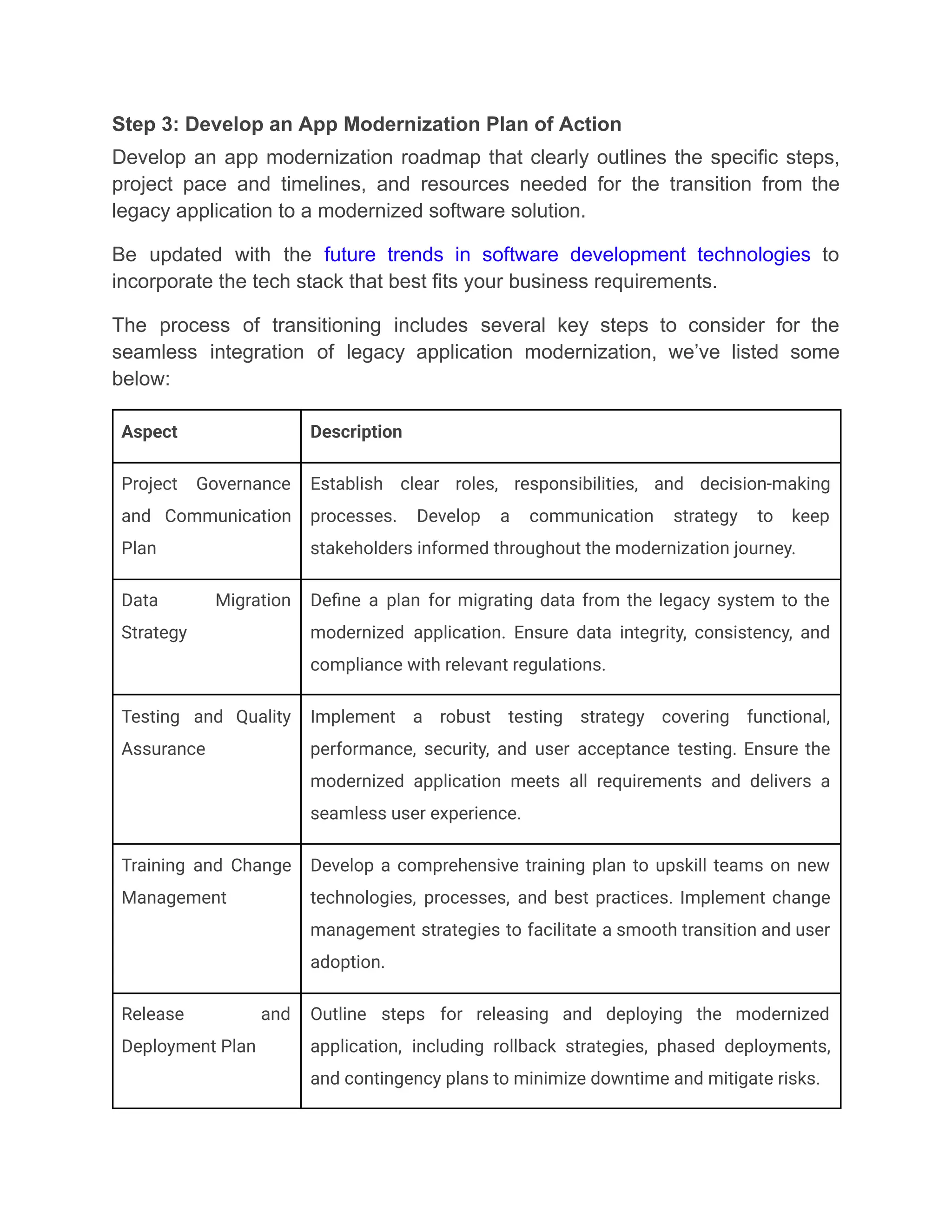
Jellyfish Technologies empowers businesses to future-proof their systems by offering legacy application modernization services that transform outdated software into scalable, secure, and high-performing solutions—leveraging cloud, microservices, and modern frameworks to ensure long-term growth, reduced costs, and operational agility in today’s fast-paced digital ecosystem.