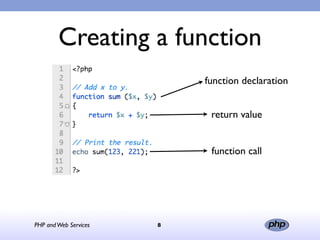
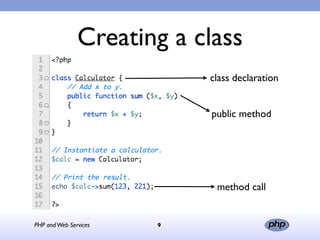
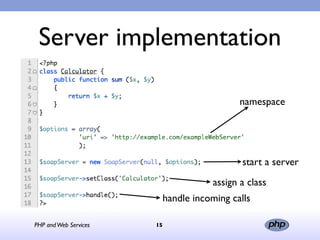
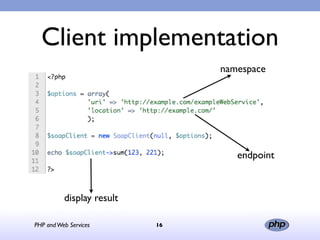
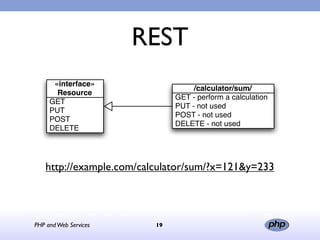
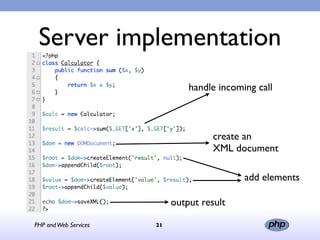
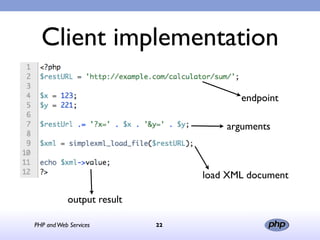
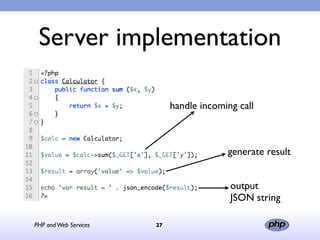
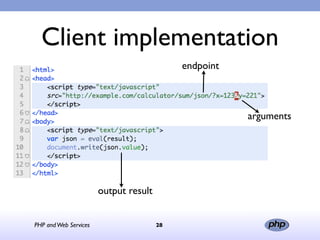
This document discusses PHP and web services. It begins by introducing PHP as an open source web scripting language created in 1994. It then discusses different types of web services standards - SOAP, REST, and JSON. SOAP uses XML, REST uses HTTP requests and responses while JSON returns responses in JavaScript format. The document provides examples of implementing web service clients and servers in PHP for each standard and concludes that PHP supports various standards but REST requires more coding than SOAP, and JSON is best for client-side applications.